Introduction
Apache Camel is a powerful open source integration framework based on known Enterprise Integration Patterns with powerful Bean Integration.
Camel lets you create the Enterprise Integration Patterns to implement routing and mediation rules in either a Java based Domain Specific Language (or Fluent API), via Spring based Xml Configuration files or via the Scala DSL. This means you get smart completion of routing rules in your IDE whether in your Java, Scala or XML editor.
Apache Camel uses URIs so that it can easily work directly with any kind of Transport or messaging model such as HTTP, ActiveMQ, JMS, JBI, SCA, MINA or CXF Bus API together with working with pluggable Data Format options. Apache Camel is a small library which has minimal dependencies for easy embedding in any Java application. Apache Camel lets you work with the same API regardless which kind of Transport used, so learn the API once and you will be able to interact with all the Components that is provided out-of-the-box.
Apache Camel has powerful Bean Binding and integrated seamless with popular frameworks such as Spring and Guice.
Apache Camel has extensive Testing support allowing you to easily unit test your routes.
Apache Camel can be used as a routing and mediation engine for the following projects:
- Apache ServiceMix which is the most popular and powerful distributed open source ESB and JBI container
- Apache ActiveMQ which is the most popular and powerful open source message broker
- Apache CXF which is a smart web services suite (JAX-WS)
- Apache MINA a networking framework
So don't get the hump, try Camel today! ![]()
Quickstart
To start using Apache Camel quickly, you can read through some simple examples in this chapter. For readers who would like a more thorough introduction, please skip ahead to Chapter 3.
Walk through an Example Code
This mini-guide takes you through the source code of a simple example.
Camel can be configured either by using Spring or directly in Java - which this example does.
We start with creating a CamelContext - which is a container for Components, Routes etc:
CamelContext context = new DefaultCamelContext();
There is more than one way of adding a Component to the CamelContext. You can add components implicitly - when we set up the routing - as we do here for the FileComponent:
context.addRoutes(new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("test-jms:queue:test.queue").to("file://test"); // set up a listener on the file component from("file://test").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange e) { System.out.println("Received exchange: " + e.getIn()); } }); } });
or explicitly - as we do here when we add the JMS Component:
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false"); // Note we can explicity name the component context.addComponent("test-jms", JmsComponent.jmsComponentAutoAcknowledge(connectionFactory));
The above works with any JMS provider. If we know we are using ActiveMQ we can use an even simpler form using the activeMQComponent() method while specifying the brokerURL used to connect to ActiveMQ
camelContext.addComponent("activemq", activeMQComponent("vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false"));
In normal use, an external system would be firing messages or events directly into Camel through one if its Components but we are going to use the ProducerTemplate which is a really easy way for testing your configuration:
ProducerTemplate template = context.createProducerTemplate();
Next you must start the camel context. If you are using Spring to configure the camel context this is automatically done for you; though if you are using a pure Java approach then you just need to call the start() method
camelContext.start();
This will start all of the configured routing rules.
So after starting the CamelContext, we can fire some objects into camel:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { template.sendBody("test-jms:queue:test.queue", "Test Message: " + i); }
What happens?
From the ProducerTemplate - we send objects (in this case text) into the CamelContext to the Component test-jms:queue:test.queue. These text objects will be converted automatically into JMS Messages and posted to a JMS Queue named test.queue. When we set up the Route, we configured the FileComponent to listen of the test.queue.
The File FileComponent will take messages off the Queue, and save them to a directory named test. Every message will be saved in a file that corresponds to its destination and message id.
Finally, we configured our own listener in the Route - to take notifications from the FileComponent and print them out as text.
That's it!
If you have the time then use 5 more minutes to Walk through another example that demonstrates the Spring DSL (XML based) routing.
| Camel 1.4.0 change In Camel 1.4.0, CamelTemplate has been marked as @deprecated. ProducerTemplate should be used instead and its created from the CamelContext itself. ProducerTemplate template = context.createProducerTemplate(); |
Walk through another example
Introduction
We continue the walk from Walk through an Example. This time we take a closer look at the routing and explains a few pointers so you wont walk into a bear trap, but can enjoy a walk after hours to the local pub for a large beer ![]()
First we take a moment to look at the Enterprise Integration Patterns that is the base pattern catalog for integrations. In particular we focus on the Pipes and Filters EIP pattern, that is a central pattern. This is used for: route through a sequence of processing steps, each performing a specific function - much like the Java Servlet Filters.
Pipes and filters
In this sample we want to process a message in a sequence of steps where each steps can perform their specific function. In our example we have a JMS queue for receiving new orders. When an order is received we need to process it in several steps:
- validate
- register
- send confirm email
This can be created in a route like this:
<route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <pipeline> <bean ref="validateOrder"/> <bean ref="registerOrder"/> <bean ref="sendConfirmEmail"/> </pipeline> </route>
| Pipeline is default In the route above we specify pipeline but it can be omitted as its default, so you can write the route as: <route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <bean ref="validateOrder"/> <bean ref="registerOrder"/> <bean ref="sendConfirmEmail"/> </route> This is commonly used not to state the pipeline. An example where the pipeline needs to be used, is when using a multicast and "one" of the endpoints to send to (as a logical group) is a pipeline of other endpoints. For example. <route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <multicast> <to uri="log:org.company.log.Category"/> <pipeline> <bean ref="validateOrder"/> <bean ref="registerOrder"/> <bean ref="sendConfirmEmail"/> </pipeline> </multicast> </route> The above sends the order (from jms:queue:order) to two locations at the same time, our log component, and to the "pipeline" of beans which goes one to the other. If you consider the opposite, sans the <pipeline> <route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <multicast> <to uri="log:org.company.log.Category"/> <bean ref="validateOrder"/> <bean ref="registerOrder"/> <bean ref="sendConfirmEmail"/> </multicast> </route> you would see that multicast would not "flow" the message from one bean to the next, but rather send the order to all 4 endpoints (1x log, 3x bean) in parallel, which is not (for this example) what we want. We need the message to flow to the validateOrder, then to the registerOrder, then the sendConfirmEmail so adding the pipeline, provides this facility. |
Where as the bean ref is a reference for a spring bean id, so we define our beans using regular Spring XML as:
<bean id="validateOrder" class="com.mycompany.MyOrderValidator"/>
Our validator bean is a plain POJO that has no dependencies to Camel what so ever. So you can implement this POJO as you like. Camel uses rather intelligent Bean Binding to invoke your POJO with the payload of the received message. In this example we will not dig into this how this happens. You should return to this topic later when you got some hands on experience with Camel how it can easily bind routing using your existing POJO beans.
So what happens in the route above. Well when an order is received from the JMS queue the message is routed like Pipes and Filters:
1. payload from the JMS is sent as input to the validateOrder bean
2. the output from validateOrder bean is sent as input to the registerOrder bean
3. the output from registerOrder bean is sent as input to the sendConfirmEmail bean
Using Camel Components
In the route lets imagine that the registration of the order has to be done by sending data to a TCP socket that could be a big mainframe. As Camel has many Components we will use the camel-mina component that supports TCP connectivity. So we change the route to:
<route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <bean ref="validateOrder"/> <to uri="mina:tcp://mainframeip:4444?textline=true"/> <bean ref="sendConfirmEmail"/> </route>
What we now have in the route is a to type that can be used as a direct replacement for the bean type. The steps is now:
1. payload from the JMS is sent as input to the validateOrder bean
2. the output from validateOrder bean is sent as text to the mainframe using TCP
3. the output from mainframe is sent back as input to the sendConfirmEmai bean
What to notice here is that the to is not the end of the route (the world ![]() ) in this example it's used in the middle of the Pipes and Filters. In fact we can change the bean types to to as well:
) in this example it's used in the middle of the Pipes and Filters. In fact we can change the bean types to to as well:
<route> <from uri="jms:queue:order"/> <to uri="bean:validateOrder"/> <to uri="mina:tcp://mainframeip:4444?textline=true"/> <to uri="bean:sendConfirmEmail"/> </route>
As the to is a generic type we must state in the uri scheme which component it is. So we must write bean: for the Bean component that we are using.
Conclusion
This example was provided to demonstrate the Spring DSL (XML based) as opposed to the pure Java DSL from the first example. And as well to point about that the to doesn't have to be the last node in a route graph.
This example is also based on the in-only message exchange pattern. What you must understand as well is the in-out message exchange pattern, where the caller expects a response. We will look into this in another example.
See also
The Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIP) book
The purpose of a "patterns" book is not to advocate new techniques that the authors have invented, but rather to document existing best practices within a particular field. By doing this, the authors of a patterns book hope to spread knowledge of best practices and promote a vocabulary for discussing architectural designs.
One of the most famous patterns books is Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-oriented Software by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides. Some people refer to this as the "gang of four" book, partly to distinguish this book from other books that use "Design Patterns" in their titles and, perhaps, partly because they cannot remember the names of all four authors.
Since the publication of Design Patterns, many other patterns books, of varying quality, have been written. One famous patterns book is called Enterprise Integration Patterns: Designing, Building, and Deploying Messaging Solutions by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolfe. It is common for people to refer to this book as EIP, which is an acronym of its title. As the subtitle of EIP suggests, the book focusses on design patterns for asynchronous messaging systems. The book discusses 65 patterns. Each pattern is given a textual name and most are also given a graphical symbol. The graphical symbols are intended to be used in architectural diagrams.
The Camel project
Camel (http://activemq.apache.org/camel/) is an open-source, Java-based project that is a part of the Apache ActiveMQ project. Camel provides a class library that, according to its documentation, can be used to implement 31 design patterns in the EIP book. I am not sure why the Camel documentation discusses only 31 of the 65 EIP design patterns. Perhaps this is due to incomplete documentation. Or perhaps it means that the Camel project, which is less than 1 year old at the time of writing, is not yet as feature rich as the EIP book.
Because Camel implements many of the design patterns in the EIP book, it would be a good idea for people who work with Camel to read the EIP book.
Online documentation for Camel
The Camel project was started in early 2007. At the time of writing, the Camel project is too young for there to be published books available on how to use Camel. Instead, the only source of documentation seems to the documentation page on the Apache Camel website.
Problems with Camel's online documentation
Currently, the online documentation for the Apache Camel project suffers from two problems. First, the documentation is incomplete. Second, there is no clearly specified reading order to the documentation. For example, there is no table of contents. Instead, documentation is fragmented over a collection of 60+ web pages, and hypertext links haphazardly tie these web pages to each other. This documentation might suffice as reference material for people already familiar with Camel but it does not qualify as a tutorial for beginners.
The problems with the documentation are unlikely to be due to, say, its author(s) lacking writing ability. Rather, it is more likely that the problems are due to the author(s) lack of time. I expect Camel's documentation will improve over time. I am writing this overview of Camel to partially counter some of the problems that currently afflict the Camel documentation. In particular, this document aims to serve as a (so far, incomplete) "beginner's guide to Camel". As such, this document tries to complement, rather than compete with, the online Camel documentation.
A useful tip for navigating the online documentation
There is one useful hint I can provide for reading the online Camel documentation. Each documentation page has a logo at the top, and immediately underneath this is a think reddish bar that contains some hypertext links. The Hypertext links on left side of this reddish bar indicate your position in documentation. For example, If you are on the "Languages" documentation page then the left-hand side of the reddish bar contains the following links.
Apache Camel > Documentation > Architecture > Languages
As you might expect, clicking on "Apache Camel" takes you back to the home page of the Apache Camel project, and clicking on "Documentation" takes you to the main documentation page. You can interpret the "Architeture" and "Languages" buttons as indicating you are in the "Languages" section of the "Architecture" chapter. Doing this gives you at least some sense of where you are within the documentation. If you are patient then you can spend a few hours clicking on all the hypertext links you can find in the documentation pages, bookmark each page with a hierarchical name (for example, you might bookmark the above page with the name "Camel – Arch – Languages") and then you can use your bookmarks to serve as a primitive table of contents for the online Camel documentation.
Online Javadoc documentation
The Apache Camel website provides Javadoc documentation. It is important to note that the Javadoc documentation is spread over several independent Javadoc hierarchies rather than being all contained in a single Javadoc hierarchy. In particular, there is one Javadoc hierarchy for the core APIs of Camel, and a separate Javadoc hierarchy for each communications technology supported by Camel. For example, if you will be using Camel with ActiveMQ and FTP then you need to look at the Javadoc hierarchies for the core API, ActiveMQ API and FTP API.
Concepts and terminology fundamental to Camel
I said in Section 3.1 ("Problems with Camel's online documentation") that the online Camel documentation does not provide a tutorial for beginners. Because of this, in this section I try to explain some of the concepts and terminology that are fundamental to Camel. This section is not a complete Camel tutorial, but it is a first step in that direction.
Endpoint
The term endpoint is often used when talking about inter-process communication. For example, in client-server communication, the client is one endpoint and the server is the other endpoint. Depending on the context, an endpoint might refer to an address, such as a host:port pair for TCP-based communication, or it might refer to a software entity that is contactable at that address. For example, if somebody uses "www.example.com:80" as an example of an endpoint, they might be referring to the actual port at that host name (that is, an address), or they might be referring to the web server (that is, software contactable at that address). Often, the distinction between the address and software contactable at that address is not an important one.
Some middleware technologies make it possible for several software entities to be contactable at the same physical address. For example, CORBA is an object-oriented, remote-procedure-call (RPC) middleware standard. If a CORBA server process contains several objects then a client can communicate with any of these objects at the same physical address (host:port), but a client communicates with a particular object via that object's logical address (called an IOR in CORBA terminology), which consists of the physical address (host:port) plus an id that uniquely identifies the object within its server process. (An IOR contains some additional information that is not relevant to this present discussion.) When talking about CORBA, some people may use the term "endpoint" to refer to a CORBA server's physical address, while other people may use the term to refer to the logical address of a single CORBA object, and other people still might use the term to refer to any of the following:
- The physical address (host:port) of the CORBA server process
- The logical address (host:port plus id) of a CORBA object.
- The CORBA server process (a relatively heavyweight software entity)
- A CORBA object (a lightweight software entity)
Because of this, you can see that the term endpoint is ambiguous in at least two ways. First, it is ambiguous because it might refer to an address or to a software entity contactable at that address. Second, it is ambiguous in the granularity of what it refers to: a heavyweight versus lightweight software entity, or physical address versus logical address. It is useful to understand that different people use the term endpoint in slightly different (and hence ambiguous) ways because Camel's usage of this term might be different to whatever meaning you had previously associated with the term.
Camel provides out-of-the-box support for endpoints implemented with many different communication technologies. Here are some examples of the Camel-supported endpoint technologies. - A JMS queue.
- A web service.
- A file. A file may sound like an unlikely type of endpoint, until you realize that in some systems one application might write information to a file and, later, another application might read that file.
- An FTP server.
- An email address. A client can send a message to an email address, and a server can read an incoming message from a mail server.
- A POJO (plain old Java object).
In a Camel-based application, you create (Camel wrappers around) some endpoints and connect these endpoints with routes, which I will discuss later in Section 4.8 ("Routes, RouteBuilders and Java DSL"). Camel defines a Java interface called Endpoint. Each Camel-supported endpoint has a class that implements this Endpoint interface. As I discussed in Section 3.3 ("Online Javadoc documentation"), Camel provides a separate Javadoc hierarchy for each communications technology supported by Camel. Because of this, you will find documentation on, say, the JmsEndpoint class in the JMS Javadoc hierarchy, while documentation for, say, the FtpEndpoint class is in the FTP Javadoc hierarchy.
CamelContext
A CamelContext object represents the Camel runtime system. You typically have one CamelContext object in an application. A typical application executes the following steps.
- Create a CamelContext object.
- Add endpoints – and possibly Components, which are discussed in Section 4.5 ("Components") – to the CamelContext object.
- Add routes to the CamelContext object to connect the endpoints.
- Invoke the start() operation on the CamelContext object. This starts Camel-internal threads that are used to process the sending, receiving and processing of messages in the endpoints.
- Eventually invoke the stop() operation on the CamelContext object. Doing this gracefully stops all the endpoints and Camel-internal threads.
Note that the CamelContext.start() operation does not block indefinitely. Rather, it starts threads internal to each Component and Endpoint and then start() returns. Conversely, CamelContext.stop() waits for all the threads internal to each Endpoint and Component to terminate and then stop() returns.
If you neglect to call CamelContext.start() in your application then messages will not be processed because internal threads will not have been created.
If you neglect to call CamelContext.stop() before terminating your application then the application may terminate in an inconsistent state. If you neglect to call CamelContext.stop() in a JUnit test then the test may fail due to messages not having had a chance to be fully processed.
CamelTemplate
Camel used to have a class called CamelClient, but this was renamed to be CamelTemplate to be similar to a naming convention used in some other open-source projects, such as the TransactionTemplate and JmsTemplate classes in Spring.
The CamelTemplate class is a thin wrapper around the CamelContext class. It has methods that send a Message or Exchange – both discussed in Section 4.6 ("Message and Exchange")) – to an Endpoint – discussed in Section 4.1 ("Endpoint"). This provides a way to enter messages into source endpoints, so that the messages will move along routes – discussed in Section 4.8 ("Routes, RouteBuilders and Java DSL") – to destination endpoints.
The Meaning of URL, URI, URN and IRI
Some Camel methods take a parameter that is a URI string. Many people know that a URI is "something like a URL" but do not properly understand the relationship between URI and URL, or indeed its relationship with other acronyms such as IRI and URN.
Most people are familiar with URLs (uniform resource locators), such as "http://...", "ftp://...", "mailto:...". Put simply, a URL specifies the location of a resource.
A URI (uniform resource identifier) is a URL or a URN. So, to fully understand what URI means, you need to first understand what is a URN.
URN is an acronym for uniform resource name. There are may "unique identifier" schemes in the world, for example, ISBNs (globally unique for books), social security numbers (unique within a country), customer numbers (unique within a company's customers database) and telephone numbers. Each "unique identifier" scheme has its own notation. A URN is a wrapper for different "unique identifier" schemes. The syntax of a URN is "urn:<scheme-name>:<unique-identifier>". A URN uniquely identifies a resource, such as a book, person or piece of equipment. By itself, a URN does not specify the location of the resource. Instead, it is assumed that a registry provides a mapping from a resource's URN to its location. The URN specification does not state what form a registry takes, but it might be a database, a server application, a wall chart or anything else that is convenient. Some hypothetical examples of URNs are "urn:employee:08765245", "urn:customer:uk:3458:hul8" and "urn:foo:0000-0000-9E59-0000-5E-2". The <scheme-name> ("employee", "customer" and "foo" in these examples) part of a URN implicitly defines how to parse and interpret the <unique-identifier> that follows it. An arbitrary URN is meaningless unless: (1) you know the semantics implied by the <scheme-name>, and (2) you have access to the registry appropriate for the <scheme-name>. A registry does not have to be public or globally accessible. For example, "urn:employee:08765245" might be meaningful only within a specific company.
To date, URNs are not (yet) as popular as URLs. For this reason, URI is widely misused as a synonym for URL.
IRI is an acronym for internationalized resource identifier. An IRI is simply an internationalized version of a URI. In particular, a URI can contain letters and digits in the US-ASCII character set, while a IRI can contain those same letters and digits, and also European accented characters, Greek letters, Chinese ideograms and so on.
Components
Component is confusing terminology; EndpointFactory would have been more appropriate because a Component is a factory for creating Endpoint instances. For example, if a Camel-based application uses several JMS queues then the application will create one instance of the JmsComponent class (which implements the Component interface), and then the application invokes the createEndpoint() operation on this JmsComponent object several times. Each invocation of JmsComponent.createEndpoint() creates an instance of the JmsEndpoint class (which implements the Endpoint interface). Actually, application-level code does not invoke Component.createEndpoint() directly. Instead, application-level code normally invokes CamelContext.getEndpoint(); internally, the CamelContext object finds the desired Component object (as I will discuss shortly) and then invokes createEndpoint() on it.
Consider the following code.
myCamelContext.getEndpoint("pop3://john.smith@mailserv.example.com?password=myPassword");
The parameter to getEndpoint() is a URI. The URI prefix (that is, the part before ":") specifies the name of a component. Internally, the CamelContext object maintains a mapping from names of components to Component objects. For the URI given in the above example, the CamelContext object would probably map the pop3 prefix to an instance of the MailComponent class. Then the CamelContext object invokes createEndpoint("pop3://john.smith@mailserv.example.com?password=myPassword") on that MailComponent object. The createEndpoint() operation splits the URI into its component parts and uses these parts to create and configure an Endpoint object.
In the previous paragraph, I mentioned that a CamelContext object maintains a mapping from component names to Component objects. This raises the question of how this map is populated with named Component objects. There are two ways of populating the map. The first way is for application-level code to invoke CamelContext.addComponent(String componentName, Component component). The example below shows a single MailComponent object being registered in the map under 3 different names.
Component mailComponent = new org.apache.camel.component.mail.MailComponent(); myCamelContext.addComponent("pop3", mailComponent); myCamelContext.addComponent("imap", mailComponent); myCamelContext.addComponent("smtp", mailComponent);
The second (and preferred) way to populate the map of named Component objects in the CamelContext object is to let the CamelContext object perform lazy initialization. This approach relies on developers following a convention when they write a class that implements the Component interface. I illustrate the convention by an example. Let's assume you write a class called com.example.myproject.FooComponent and you want Camel to automatically recognize this by the name "foo". To do this, you have to write a properties file called "META-INF/services/org/apache/camel/component/foo" (without a ".properties" file extension) that has a single entry in it called class, the value of which is the fully-scoped name of your class. This is shown below.
class=com.example.myproject.FooComponent
If you want Camel to also recognize the class by the name "bar" then you write another properties file in the same directory called "bar" that has the same contents. Once you have written the properties file(s), you create a jar file that contains the com.example.myproject.FooComponent class and the properties file(s), and you add this jar file to your CLASSPATH. Then, when application-level code invokes createEndpoint("foo:...") on a CamelContext object, Camel will find the "foo"" properties file on the CLASSPATH, get the value of the class property from that properties file, and use reflection APIs to create an instance of the specified class.
As I said in Section 4.1 ("Endpoint"), Camel provides out-of-the-box support for numerous communication technologies. The out-of-the-box support consists of classes that implement the Component interface plus properties files that enable a CamelContext object to populate its map of named Component objects.
Earlier in this section I gave the following example of calling CamelContext.getEndpoint().
myCamelContext.getEndpoint("pop3://john.smith@mailserv.example.com?password=myPassword");
When I originally gave that example, I said that the parameter to getEndpoint() was a URI. I said that because the online Camel documentation and the Camel source code both claim the parameter is a URI. In reality, the parameter is restricted to being a URL. This is because when Camel extracts the component name from the parameter, it looks for the first ":", which is a simplistic algorithm. To understand why, recall from Section 4.4 ("The Meaning of URL, URI, URN and IRI") that a URI can be a URL or a URN. Now consider the following calls to getEndpoint.
myCamelContext.getEndpoint("pop3:..."); myCamelContext.getEndpoint("jms:..."); myCamelContext.getEndpoint("urn:foo:..."); myCamelContext.getEndpoint("urn:bar:...");
Camel identifies the components in the above example as "pop3", "jms", "urn" and "urn". It would be more useful if the latter components were identified as "urn:foo" and "urn:bar" or, alternatively, as "foo" and "bar" (that is, by skipping over the "urn:" prefix). So, in practice you must identify an endpoint with a URL (a string of the form "<scheme>:...") rather than with a URN (a string of the form "urn:<scheme>:..."). This lack of proper support for URNs means the you should consider the parameter to getEndpoint() as being a URL rather than (as claimed) a URI.
Message and Exchange
The Message interface provides an abstraction for a single message, such as a request, reply or exception message.
There are concrete classes that implement the Message interface for each Camel-supported communications technology. For example, the JmsMessage class provides a JMS-specific implementation of the Message interface. The public API of the Message interface provides get- and set-style methods to access the message id, body and individual header fields of a messge.
The Exchange interface provides an abstraction for an exchange of messages, that is, a request message and its corresponding reply or exception message. In Camel terminology, the request, reply and exception messages are called in, out and fault messages.
There are concrete classes that implement the Exchange interface for each Camel-supported communications technology. For example, the JmsExchange class provides a JMS-specific implementation of the Exchange interface. The public API of the Exchange interface is quite limited. This is intentional, and it is expected that each class that implements this interface will provide its own technology-specific operations.
Application-level programmers rarely access the Exchange interface (or classes that implement it) directly. However, many classes in Camel are generic types that are instantiated on (a class that implements) Exchange. Because of this, the Exchange interface appears a lot in the generic signatures of classes and methods.
Processor
The Processor interface represents a class that processes a message. The signature of this interface is shown below.
package org.apache.camel; public interface Processor { void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception; }
Notice that the parameter to the process() method is an Exchange rather than a Message. This provides flexibility. For example, an implementation of this method initially might call exchange.getIn() to get the input message and process it. If an error occurs during processing then the method can call exchange.setException().
An application-level developer might implement the Processor interface with a class that executes some business logic. However, there are many classes in the Camel library that implement the Processor interface in a way that provides support for a design pattern in the EIP book. For example, ChoiceProcessor implements the message router pattern, that is, it uses a cascading if-then-else statement to route a message from an input queue to one of several output queues. Another example is the FilterProcessor class which discards messages that do not satisfy a stated predicate (that is, condition).
Routes, RouteBuilders and Java DSL
A route is the step-by-step movement of a Message from an input queue, through arbitrary types of decision making (such as filters and routers) to a destination queue (if any). Camel provides two ways for an application developer to specify routes. One way is to specify route information in an XML file. A discussion of that approach is outside the scope of this document. The other way is through what Camel calls a Java DSL (domain-specific language).
Introduction to Java DSL
For many people, the term "domain-specific language" implies a compiler or interpreter that can process an input file containing keywords and syntax specific to a particular domain. This is not the approach taken by Camel. Camel documentation consistently uses the term "Java DSL" instead of "DSL", but this does not entirely avoid potential confusion. The Camel "Java DSL" is a class library that can be used in a way that looks almost like a DSL, except that it has a bit of Java syntactic baggage. You can see this in the example below. Comments afterwards explain some of the constructs used in the example.
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("queue:a").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("queue:b"); from("queue:c").choice() .when(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("queue:d") .when(header("foo").isEqualTo("cheese")).to("queue:e") .otherwise().to("queue:f"); } }; CamelContext myCamelContext = new DefaultCamelContext(); myCamelContext.addRoutes(builder);
The first line in the above example creates an object which is an instance of an anonymous subclass of RouteBuilder with the specified configure() method.
The CamelContext.addRoutes(RouterBuilder builder) method invokes builder.setContext(this) – so the RouteBuilder object knows which CamelContext object it is associated with – and then invokes builder.configure(). The body of configure() invokes methods such as from(), filter(), choice(), when(), isEqualTo(), otherwise() and to().
The RouteBuilder.from(String uri) method invokes getEndpoint(uri) on the CamelContext associated with the RouteBuilder object to get the specified Endpoint and then puts a FromBuilder "wrapper" around this Endpoint. The FromBuilder.filter(Predicate predicate) method creates a FilterProcessor object for the Predicate (that is, condition) object built from the header("foo").isEqualTo("bar") expression. In this way, these operations incrementally build up a Route object (with a RouteBuilder wrapper around it) and add it to the CamelContext object associated with the RouteBuilder.
Critique of Java DSL
The online Camel documentation compares Java DSL favourably against the alternative of configuring routes and endpoints in a XML-based Spring configuration file. In particular, Java DSL is less verbose than its XML counterpart. In addition, many integrated development environments (IDEs) provide an auto-completion feature in their editors. This auto-completion feature works with Java DSL, thereby making it easier for developers to write Java DSL.
However, there is another option that the Camel documentation neglects to consider: that of writing a parser that can process DSL stored in, say, an external file. Currently, Camel does not provide such a DSL parser, and I do not know if it is on the "to do" list of the Camel maintainers. I think that a DSL parser would offer a significant benefit over the current Java DSL. In particular, the DSL would have a syntactic definition that could be expressed in a relatively short BNF form. The effort required by a Camel user to learn how to use DSL by reading this BNF would almost certainly be significantly less than the effort currently required to study the API of the RouterBuilder classes.
Architecture
Camel uses a Java based Routing Domain Specific Language (DSL) or an Xml Configuration to configure routing and mediation rules which are added to a CamelContext to implement the various Enterprise Integration Patterns.
At a high level Camel consists of a CamelContext which contains a collection of Component instances. A Component is essentially a factory of Endpoint instances. You can explicitly configure Component instances in Java code or an IoC container like Spring or Guice, or they can be auto-discovered using URIs.
An Endpoint acts rather like a URI or URL in a web application or a Destination in a JMS system; you can communicate with an endpoint; either sending messages to it or consuming messages from it. You can then create a Producer or Consumer on an Endpoint to exchange messages with it.
The DSL makes heavy use of pluggable Languages to create an Expression or Predicate to make a truly powerful DSL which is extensible to the most suitable language depending on your needs. The following languages are supported
- Bean Language for using Java for expressions
- Constant
- the unified EL from JSP and JSF
- Header
- JXPath
- Mvel
- OGNL
- Property
- Scala DSL
- Scripting Languages such as
- Simple
- SQL
- XPath
- XQuery
Most of these languages is also supported used as Annotation Based Expression Language.
For a full details of the individual languages see the Language Appendix
URIs
Camel makes extensive use of URIs to allow you to refer to endpoints which are lazily created by a Component if you refer to them within Routes
Current Supported URIs
| Component / ArtifactId / URI | Description |
|---|---|
ActiveMQ / activemq-camel
activemq:[topic:]destinationName | For JMS Messaging with Apache ActiveMQ |
ActiveMQ Journal / activemq-core
activemq.journal:directory-on-filesystem | Uses ActiveMQ's fast disk journaling implementation to store message bodies in a rolling log file |
AMQP / camel-amqp
amqp:[topic:]destinationName | For Messaging with AMQP protocol |
Atom / camel-atom
atom:uri | Working with Apache Abdera for atom integration, such as consuming an atom feed. |
Bean / camel-core
bean:beanName[?method=someMethod] | Uses the Bean Binding to bind message exchanges to beans in the Registry. Is also used for exposing and invoking POJO (Plain Old Java Objects). |
Browse / camel-core
browse:someName | Provdes a simple BrowsableEndpoint which can be useful for testing, visualisation tools or debugging. The exchanges sent to the endpoint are all available to be browsed. |
Cache / camel-cache
cache://cachename[?options] | The cache component facilitates creation of caching endpoints and processors using EHCache as the cache implementation. |
Cometd / camel-cometd
cometd://host:port/channelname | Used to deliver messages using the jetty cometd implementation of the bayeux protocol |
CXF / camel-cxf
cxf:address[?serviceClass=...] | Working with Apache CXF for web services integration |
CXFRS / camel-cxf
cxfrs:address[?resourcesClasses=...] | Working with Apache CXF for REST services integration |
DataSet / camel-core
dataset:name | For load & soak testing the DataSet provides a way to create huge numbers of messages for sending to Components or asserting that they are consumed correctly |
Direct / camel-core
direct:name | Synchronous call to another endpoint |
Esper / camel-esper in camel-extra
esper:name | Working with the Esper Library for Event Stream Processing |
Event / camel-spring
event://default spring-event://default | Working with Spring ApplicationEvents |
File / camel-core
file://nameOfFileOrDirectory | Sending messages to a file or polling a file or directory. Camel 1.x use this link File. |
Flatpack / camel-flatpack
flatpack:[fixed|delim]:configFile | Processing fixed width or delimited files or messages using the FlatPack library |
Freemarker / camel-freemarker
freemarker:someTemplateResource | Generates a response using a Freemarker template |
FTP / camel-ftp
ftp://host[:port]/fileName | Sending and receiving files over FTP. Camel 1.x use this link FTP. |
GHttp / camel-gae
ghttp://hostname[:port][/path][?options] ghttp:///path[?options] | Provides connectivity to the URL fetch service of Google App Engine but can also be used to receive messages from servlets. See also Camel Components for Google App Engine. |
GTask / camel-gae
gtask://queue-name | supports asynchronous message processing on Google App Engine by using the task queueing service as message queue. See also Camel Components for Google App Engine. |
GMail / camel-gae
gmail://user@gmail.com[?options] gmail://user@googlemail.com[?options] | Supports sending of emails via the mail service of Google App Engine. See also Camel Components for Google App Engine. |
Hibernate / camel-hibernate in camel-extra
hibernate://entityName | For using a database as a queue via the Hibernate library |
HL7 / camel-hl7
mina:tcp://hostname[:port] | For working with the HL7 MLLP protocol and the HL7 model using the HAPI library |
HTTP / camel-http
http://hostname[:port] | For calling out to external HTTP servers |
iBATIS / camel-ibatis
ibatis://sqlOperationName | Performs a query, poll, insert, update or delete in a relational database using Apache iBATIS |
IMap / camel-mail
imap://hostname[:port] | Receiving email using IMap |
IRC / camel-irc
irc:host[:port]/#room | For IRC communication |
JavaSpace / camel-javaspace
javaspace:jini://host?spaceName=mySpace?... | Sending and receiving messages through JavaSpace |
JBI / servicemix-camel
jbi:serviceName | For JBI integration such as working with Apache ServiceMix |
JCR / camel-jcr
jcr://user:password@repository/path/to/node | Storing a message in a JCR (JSR-170) compliant repository like Apache Jackrabbit |
JDBC / camel-jdbc
jdbc:dataSourceName?options | For performing JDBC queries and operations |
Jetty / camel-jetty
jetty:url | For exposing services over HTTP |
JMS / camel-jms
jms:[topic:]destinationName | Working with JMS providers |
JPA / camel-jpa
jpa://entityName | For using a database as a queue via the JPA specification for working with OpenJPA, Hibernate or TopLink |
JT/400 / camel-jt400
jt400://user:pwd@system/<path_to_dtaq>
| For integrating with data queues on an AS/400 (aka System i, IBM i, i5, ...) system |
LDAP / camel-ldap
ldap:host[:port]?base=...[&scope=<scope>]
| Performing searches on LDAP servers (<scope> must be one of object|onelevel|subtree) |
Log / camel-core
log:loggingCategory[?level=ERROR] | Uses Jakarta Commons Logging to log the message exchange to some underlying logging system like log4j |
Mail / camel-mail
mail://user-info@host:port | Sending and receiving email |
MINA / camel-mina
[tcp|udp|multicast]:host[:port] | Working with Apache MINA |
Mock / camel-core
mock:name | For testing routes and mediation rules using mocks |
MSV / camel-msv
msv:someLocalOrRemoteResource | Validates the payload of a message using the MSV Library |
Multicast / camel-mina
multicast://host:port | Working with TCP protocols using Apache MINA |
POP / camel-mail
pop3://user-info@host:port | Receiving email using POP3 and JavaMail |
Printer / camel-printer
lpr://host:port/path/to/printer[?options] | The printer component facilitates creation of printer endpoints to local, remote and wireless printers. The endpoints provide the ability to print camel directed payloads when utilized on camel routes. |
Quartz / camel-quartz
quartz://groupName/timerName | Provides a scheduled delivery of messages using the Quartz scheduler |
Ref / camel-core
ref:name | Component for lookup of existing endpoints bound in the Registry. |
Restlet / camel-restlet
restlet:restletUrl[?options] | Component for consuming and producing Restful resources using Restlet |
RMI / camel-rmi
rmi://host[:port] | Working with RMI |
RNC / camel-jing
rnc:/relativeOrAbsoluteUri | Validates the payload of a message using RelaxNG Compact Syntax |
RNG / camel-jing
rng:/relativeOrAbsoluteUri | Validates the payload of a message using RelaxNG |
RSS / camel-rss
rss:uri | Working with ROME for RSS integration, such as consuming an RSS feed. |
SEDA / camel-core
seda:name | Asynchronous call to another endpoint in the same Camel Context |
SERVLET / camel-servlet
servlet:uri | For exposing services over HTTP through the servlet which is deployed into the Web container. |
SFTP / camel-ftp
sftp://host[:port]/fileName | Sending and receiving files over SFTP |
Smooks / camel-smooks in camel-extra
unmarshal(edi) | For working with EDI parsing using the Smooks library |
SMTP / camel-mail
smtp://user-info@host[:port] | Sending email using SMTP and JavaMail |
SNMP / camel-snmp
snmp://host[:port]?options | Polling OID values and receiving traps using SNMP via SNMP4J library |
SpringIntegration / camel-spring-integration
spring-integration:defaultChannelName | The bridge component of Camel and Spring Integration |
SQL / camel-sql
sql:select * from table where id=# | Performing SQL queries using JDBC |
Stream / camel-stream
stream:[in|out|err|file] | Read or write to an input/output/error/file stream rather like unix pipes |
StringTemplate / camel-stringtemplate
string-template:someTemplateResource | Generates a response using a String Template |
TCP / camel-mina
tcp://host:port | Working with TCP protocols using Apache MINA |
Test / camel-spring
test:expectedMessagesEndpointUri | Creates a Mock endpoint which expects to receive all the message bodies that could be polled from the given underlying endpoint |
Timer / camel-core
timer://name | A timer endpoint |
UDP / camel-mina
udp://host:port | Working with UDP protocols using Apache MINA |
Validation / camel-spring
validation:someLocalOrRemoteResource | Validates the payload of a message using XML Schema and JAXP Validation |
Velocity / camel-velocity
velocity:someTemplateResource | Generates a response using an Apache Velocity template |
VM / camel-core
vm:name | Asynchronous call to another endpoint in the same JVM |
XMPP / camel-xmpp
xmpp://host:port/room | Working with XMPP and Jabber |
XQuery / camel-saxon
xquery:someXQueryResource | Generates a response using an XQuery template |
XSLT / camel-spring
xslt:someTemplateResource | Generates a response using an XSLT template |
For a full details of the individual components see the Component Appendix
Enterprise Integration Patterns
Camel supports most of the Enterprise Integration Patterns from the excellent book of the same name by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf. Its a highly recommended book, particularly for users of Camel.
Pattern Index
There now follows a list of the Enterprise Integration Patterns from the book along with examples of the various patterns using Apache Camel
Messaging Systems
| | Message Channel | How does one application communicate with another using messaging? |
| | Message | How can two applications connected by a message channel exchange a piece of information? |
| | Pipes and Filters | How can we perform complex processing on a message while maintaining independence and flexibility? |
| | Message Router | How can you decouple individual processing steps so that messages can be passed to different filters depending on a set of conditions? |
| | Message Translator | How can systems using different data formats communicate with each other using messaging? |
| | Message Endpoint | How does an application connect to a messaging channel to send and receive messages? |
Messaging Channels
| | Point to Point Channel | How can the caller be sure that exactly one receiver will receive the document or perform the call? |
| | Publish Subscribe Channel | How can the sender broadcast an event to all interested receivers? |
| | Dead Letter Channel | What will the messaging system do with a message it cannot deliver? |
| | Guaranteed Delivery | How can the sender make sure that a message will be delivered, even if the messaging system fails? |
| | Message Bus | What is an architecture that enables separate applications to work together, but in a de-coupled fashion such that applications can be easily added or removed without affecting the others? |
Message Construction
| | Event Message | How can messaging be used to transmit events from one application to another? |
| | Request Reply | When an application sends a message, how can it get a response from the receiver? |
| | Correlation Identifier | How does a requestor that has received a reply know which request this is the reply for? |
| | Return Address | How does a replier know where to send the reply? |
Message Routing
| | Content Based Router | How do we handle a situation where the implementation of a single logical function (e.g., inventory check) is spread across multiple physical systems? |
| | Message Filter | How can a component avoid receiving uninteresting messages? |
| | Dynamic Router | How can you avoid the dependency of the router on all possible destinations while maintaining its efficiency? |
| | Recipient List | How do we route a message to a list of (static or dynamically) specified recipients? |
| | Splitter | How can we process a message if it contains multiple elements, each of which may have to be processed in a different way? |
| | Aggregator | How do we combine the results of individual, but related messages so that they can be processed as a whole? |
| | Resequencer | How can we get a stream of related but out-of-sequence messages back into the correct order? |
| | Composed Message Processor | How can you maintain the overall message flow when processing a message consisting of multiple elements, each of which may require different processing? |
 | Scatter-Gather | How do you maintain the overall message flow when a message needs to be sent to multiple recipients, each of which may send a reply? |
| | Routing Slip | How do we route a message consecutively through a series of processing steps when the sequence of steps is not known at design-time and may vary for each message? |
 | Throttler | How can I throttle messages to ensure that a specific endpoint does not get overloaded, or we don't exceed an agreed SLA with some external service? |
 | Delayer | How can I delay the sending of a message? |
 | Load Balancer | How can I balance load across a number of endpoints? |
 | Multicast | How can I route a message to a number of endpoints at the same time? |
 | Loop | How can I repeat processing a message in a loop? |
Message Transformation
| | Content Enricher | How do we communicate with another system if the message originator does not have all the required data items available? |
| | Content Filter | How do you simplify dealing with a large message, when you are interested only in a few data items? |
| | Claim Check | How can we reduce the data volume of message sent across the system without sacrificing information content? |
| | Normalizer | How do you process messages that are semantically equivalent, but arrive in a different format? |
 | Sort | How can I sort the body of a message? |
Messaging Endpoints
 | Messaging Mapper | How do you move data between domain objects and the messaging infrastructure while keeping the two independent of each other? |
| | Event Driven Consumer | How can an application automatically consume messages as they become available? |
| | Polling Consumer | How can an application consume a message when the application is ready? |
| | Competing Consumers | How can a messaging client process multiple messages concurrently? |
| | Message Dispatcher | How can multiple consumers on a single channel coordinate their message processing? |
| | Selective Consumer | How can a message consumer select which messages it wishes to receive? |
| | Durable Subscriber | How can a subscriber avoid missing messages while it's not listening for them? |
 | Idempotent Consumer | How can a message receiver deal with duplicate messages? |
| | Transactional Client | How can a client control its transactions with the messaging system? |
| | Messaging Gateway | How do you encapsulate access to the messaging system from the rest of the application? |
| | Service Activator | How can an application design a service to be invoked both via various messaging technologies and via non-messaging techniques? |
System Management
| | Detour | How can you route a message through intermediate steps to perform validation, testing or debugging functions? |
| | Wire Tap | How do you inspect messages that travel on a point-to-point channel? |
For a full breakdown of each pattern see the Book Pattern Appendix
CookBook
This document describes various recipes for working with Camel
- Bean Integration describes how to work with beans and Camel in a loosely coupled way so that your beans do not have to depend on any Camel APIs
- Annotation Based Expression Language binds expressions to method parameters
- Bean Binding defines which methods are invoked and how the Message is converted into the parameters of the method when it is invoked
- Bean Injection for injecting Camel related resources into your POJOs
- Parameter Binding Annotations for extracting various headers, properties or payloads from a Message
- POJO Consuming for consuming and possibly routing messages from Camel
- POJO Producing for producing camel messages from your POJOs
- RecipientList Annotation for creating a Recipient List from a POJO method
- Using Exchange Pattern Annotations describes how pattern annotations can be used to change the behaviour of method invocations
- Hiding Middleware describes how to avoid your business logic being coupled to any particular middleware APIs allowing you to easily switch from in JVM SEDA to JMS, ActiveMQ, Hibernate, JPA, JDBC, iBATIS or JavaSpace etc.
- Visualisation describes how to visualise your Enterprise Integration Patterns to help you understand your routing rules
- Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) for monitoring business processes across systems
- Extract Transform Load (ETL) to load data into systems or databases
- Testing for testing distributed and asynchronous systems using a messaging approach
- Camel Test for creating test cases using a single Java class for all your configuration and routing
- Spring Testing uses Spring Test together with either XML or Java Config to dependency inject your test classes
- Guice uses Guice to dependency inject your test classes
- Templating is a great way to create service stubs to be able to test your system without some back end system.
- Database for working with databases
- Parallel Processing and Ordering on how using parallel processing and SEDA or JMS based load balancing can be achieved.
- Asynchronous Processing in Camel Routes.
- Implementing Virtual Topics on other JMS providers shows how to get the effect of Virtual Topics and avoid issues with JMS durable topics
- Camel Transport for CXF describes how to put the Camel context into the CXF transport layer.
Bean Integration
Camel supports the integration of beans and POJOs in a number of ways
Bean Binding
Whenever Camel invokes a bean method, either via the Bean component, Spring Remoting or POJO Consuming then the Bean Binding mechanism is used to figure out what method to use (if it is not explicit) and how to bind the Message to the parameters possibly using the Parameter Binding Annotations
Annotations
If a bean is defined in Spring XML or scanned using the Spring 2.5 component scanning mechanism and a <camelContext> is used or a CamelBeanPostProcessor then we process a number of Camel annotations to do various things such as injecting resources or producing, consuming or routing messages.
- POJO Consuming to consume and possibly route messages from Camel
- POJO Producing to make it easy to produce camel messages from your POJOs
- RecipientList Annotation for creating a Recipient List from a POJO method
- Bean Injection to inject Camel related resources into your POJOs
- Using Exchange Pattern Annotations describes how the pattern annotations can be used to change the behaviour of method invocations with Spring Remoting or POJO Producing
Spring Remoting
We support a Spring Remoting provider which uses Camel as the underlying transport mechanism. The nice thing about this approach is we can use any of the Camel transport Components to communicate between beans. It also means we can use Content Based Router and the other Enterprise Integration Patterns in between the beans; in particular we can use Message Translator to be able to convert what the on-the-wire messages look like in addition to adding various headers and so forth.
Bean Component
The Bean component supports the creation of a proxy via ProxyHelper to a Java interface; which the implementation just sends a message containing a BeanInvocation to some Camel endpoint.
Then there is a server side implementation which consumes a message and uses the Bean Binding to bind the message to invoke a method passing in its parameters.
Annotation Based Expression Language
You can also use any of the Languages supported in Camel to bind expressions to method parameters when using Bean Integration. For example you can use any of these annotations:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Bean | Inject a Bean expression |
| @BeanShell | Inject a BeanShell expression |
| @Constant | Inject a Constant expression |
| @EL | Inject an EL expression |
| @Groovy | Inject a Groovy expression |
| @Header | Inject a Header expression |
| @JavaScript | Inject a JavaScript expression |
| @MVEL | Inject a Mvel expression |
| @OGNL | Inject an OGNL expression |
| @PHP | Inject a PHP expression |
| @Python | Inject a Python expression |
| @Ruby | Inject a Ruby expression |
| @Simple | Inject an Simple expression |
| @XPath | Inject an XPath expression |
| @XQuery | Inject an XQuery expression |
Example:
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@XPath("/foo/bar/text()") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
Advanced example using @Bean
And an example of using the the @Bean binding annotation, where you can use a Pojo where you can do whatever java code you like:
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@Bean("myCorrelationIdGenerator") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
And then we can have a spring bean with the id myCorrelationIdGenerator where we can compute the id.
public class MyIdGenerator { private UserManager userManager; public String generate(@Header(name = "user") String user, @Body String payload) throws Exception { User user = userManager.lookupUser(user); String userId = user.getPrimaryId(); String id = userId + generateHashCodeForPayload(payload); return id; } }
The Pojo MyIdGenerator has one public method that accepts two parameters. However we have also annotated this one with the @Header and @Body annotation to help Camel know what to bind here from the Message from the Exchange being processed.
Of course this could be simplified a lot if you for instance just have a simple id generator. But we wanted to demonstrate that you can use the Bean Binding annotations anywhere.
public class MySimpleIdGenerator { public static int generate() { // generate a unique id return 123; } }
And finally we just need to remember to have our bean registered in the Spring Registry:
<bean id="myCorrelationIdGenerator" class="com.mycompany.MyIdGenerator"/>
Example using Groovy
In this example we have an Exchange that has a User object stored in the in header. This User object has methods to get some user information. We want to use Groovy to inject an expression that extracts and concats the fullname of the user into the fullName parameter.
public void doSomething(@Groovy("$request.header['user'].firstName $request.header['user'].familyName) String fullName, @Body String body) {
// process the inbound message here
}
Groovy supports GStrings that is like a template where we can insert $ placeholders that will be evaluated by Groovy.
Bean Binding
The Bean Binding in Camel defines both which methods are invoked and also how the Message is converted into the parameters of the method when it is invoked.
Choosing the method to invoke
The binding of a Camel Message to a bean method call can occur in different ways, order if importance:
- if the message contains the header CamelBeanMethodName (org.apache.camel.MethodName in Camel 1.x) then that method is invoked, converting the body to whatever the argument is to the method
- the method name can be specified explicitly in the DSL or when using POJO Consuming
- Camel 2.0: if the bean has a method that is marked with @Handler annotation then that method is selected
- if the bean can be converted to a Processor using the Type Converter mechanism then this is used to process the message. This mechanism is used by the ActiveMQ component to allow any JMS MessageListener to be invoked directly by Camel without having to write any integration glue code. You can use the same mechanism to integrate Camel into any other messaging/remoting frameworks.
- if the body of the message can be converted to a BeanInvocation (the default payload used by the ProxyHelper) - then that its used to invoke the method and pass the arguments
- otherwise the type of the method body is used to try find a method which matches; an error is thrown if a single method cannot be chosen unambiguously.
- you can also use Exchange as the parameter itself, but then the return type must be void.
In case where Camel will not be able to choose a method to invoke an AmbiguousMethodCallException is thrown.
By default the return value is set on the outbound message body.
Parameter binding
When a method have been chosen to be invoked Camel will bind to the parameters of the method.
The following Camel specific types is automatic binded:
- org.apache.camel.Exchange
- org.apache.camel.Message
- Camel 2.0: org.apache.camel.CamelContext
- org.apache.camel.TypeConverter
- Camel 2.0: org.apache.camel.spi.Registry
- java.lang.Exception
So if you declare any of the given type above they will be provided by Camel. A note on the Exception is that it will bind to the caught exception of the Exchange. So its often usable if you use a Pojo to handle a given using using eg an onException route.
What is most interresting is that Camel will also try to bind the body of the Exchange to the first parameter of the method signature (albeit not of any of the types above). So if we for instance declare e parameter as: String body then Camel will bind the IN body to this type. Camel will also automatic type convert to the given type declared.
Okay lets show some examples.
Below is just a simple method with a body binding. Camel will bind the IN body to the body parameter and convert it to a String type.
public String doSomething(String body)
And in this sample we got one of the automatic binded type as well, for instance the Registry that we can use to lookup beans.
public String doSomething(String body, Registry registry)
And we can also use Exchange as well:
public String doSomething(String body, Exchange exchange)
You can have multiple types as well
public String doSomething(String body, Exchange exchange, TypeConverter converter)
And imagine you use a Pojo to handle a given custom exception InvalidOrderException then we can bind that as well:
Notice we can bind to it even if we use a sub type of java.lang.Exception as Camel still knows its an exception and thus can bind the caused exception (if any exists).
public String badOrder(String body, InvalidOrderException invalid)
So what about headers and other stuff? Well now it gets a bit tricky so we can use annotations to help us. See next section for details.
Binding Annotations
You can use the Parameter Binding Annotations to customize how parameter values are created from the Message
Examples
For example a Bean such as:
public class Bar { public String doSomething(String body) { // process the in body and return whatever you want return "Bye World"; }
Or the Exchange example. Notice that the return type must be void when there is only a single parameter:
public class Bar { public void doSomething(Exchange exchange) { // process the exchange exchange.getIn().setBody("Bye World"); }
@Handler
Available as of Camel 2.0
You can mark a method in your bean with the @Handler annotation to indicate that this method should be used for Bean Binding.
This has the advantage as you do not have to specify the method name in the Camel route. And thus you do not run into problems when you rename the method name using an IDE that don't find all references.
public class Bar { @Handler public String doSomething(String body) { // process the in body and return whatever you want return "Bye World"; }
POJO consuming
For example you could use POJO Consuming to write a bean like this
| @Consume requires camel-spring Using the @Consume annotations requires camel-spring that uses the org.apache.camel.spring.CamelBeanPostProcessor to perform the setup for this consumer and the needed bean bindings. |
| @MessageDriven is @deprecated The @MessageDriven has been replaced with @Consume in Camel 1.5.0 or newer. Its now marked as @deprecated and will be removed in Camel 2.0. |
public class Foo { @Consume(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
Here Camel with subscribe to an ActiveMQ queue, then convert the message payload to a String (so dealing with TextMessage, ObjectMessage and BytesMessage in JMS), then process this method.
Bean Injection
We support the injection of various resources using @EndpointInject. This can be used to inject
- Endpoint instances which can be used for testing when used with Mock endpoints; see the Spring Testing for an example.
- ProducerTemplate instances for POJO Producing
- client side proxies for POJO Producing which is a simple approach to Spring Remoting
Parameter Binding Annotations
| camel-core The annotations below are all part of camel-core and thus does not require camel-spring or Spring. These annotations can be used with the Bean component or when invoking beans in the DSL |
Annotations can be used to define an Expression or to extract various headers, properties or payloads from a Message when invoking a bean method (see Bean Integration for more detail of how to invoke bean methods) together with being useful to help disambiguate which method to invoke.
If no annotations are used then Camel assumes that a single parameter is the body of the message. Camel will then use the Type Converter mechanism to convert from the expression value to the actual type of the parameter.
The core annotations are as follows
| Annotation | Meaning | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| @Body | To bind to an inbound message body | |
| @ExchangeException | To bind to an Exception set on the exchange (Camel 2.0) | |
| @Header | To bind to an inbound message header | String name of the header |
| @Headers | To bind to the Map of the inbound message headers | |
| @OutHeaders | To bind to the Map of the outbound message headers | |
| @Property | To bind to a named property on the exchange | String name of the property |
| @Properties | To bind to the property map on the exchange | |
| @Handler | Camel 2.0: Not part as a type parameter but stated in this table anyway to spread the good word that we have this annotation in Camel now. See more at Bean Binding. |
The follow annotations @Headers, @OutHeaders and @Properties binds to the backing java.util.Map so you can alter the content of these maps directly, for instance using the put method to add a new entry. See the OrderService class at Exception Clause for such an example.
Example
In this example below we have a @MessageDriven consumer that consumes JMS messages from the activemq queue. We use the @Header and @Body parameter binding annotations to bind from the JMSMessage to the method parameters.
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@Header(name = "JMSCorrelationID") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
In the above Camel will extract the value of Message.getJMSCorrelationID(), then using the Type Converter to adapt the value to the type of the parameter if required - it will inject the parameter value for the correlationID parameter. Then the payload of the message will be converted to a String and injected into the body parameter.
You don't need to use the @MessageDriven annotation; as you could use the Camel DSL to route to the beans method
Using the DSL to invoke the bean method
Here is another example which does not use POJO Consuming annotations but instead uses the DSL to route messages to the bean method
public class Foo { public void doSomething(@Header(name = "JMSCorrelationID") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
The routing DSL then looks like this
from("activemq:someQueue"). to("bean:myBean");
Here myBean would be looked up in the Registry (such as JNDI or the Spring ApplicationContext), then the body of the message would be used to try figure out what method to call.
If you want to be explicit you can use
from("activemq:someQueue"). to("bean:myBean?methodName=doSomething");
And here we have a nifty example for you to show some great power in Camel. You can mix and match the annotations with the normal parameters, so we can have this example with annotations and the Exchange also:
public void doSomething(@Header(name = "user") String user, @Body String body, Exchange exchange) {
exchange.getIn().setBody(body + "MyBean");
}
Annotation Based Expression Language
You can also use any of the Languages supported in Camel to bind expressions to method parameters when using Bean Integration. For example you can use any of these annotations:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Bean | Inject a Bean expression |
| @BeanShell | Inject a BeanShell expression |
| @Constant | Inject a Constant expression |
| @EL | Inject an EL expression |
| @Groovy | Inject a Groovy expression |
| @Header | Inject a Header expression |
| @JavaScript | Inject a JavaScript expression |
| @MVEL | Inject a Mvel expression |
| @OGNL | Inject an OGNL expression |
| @PHP | Inject a PHP expression |
| @Python | Inject a Python expression |
| @Ruby | Inject a Ruby expression |
| @Simple | Inject an Simple expression |
| @XPath | Inject an XPath expression |
| @XQuery | Inject an XQuery expression |
Example:
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@XPath("/foo/bar/text()") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
Advanced example using @Bean
And an example of using the the @Bean binding annotation, where you can use a Pojo where you can do whatever java code you like:
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@Bean("myCorrelationIdGenerator") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
And then we can have a spring bean with the id myCorrelationIdGenerator where we can compute the id.
public class MyIdGenerator { private UserManager userManager; public String generate(@Header(name = "user") String user, @Body String payload) throws Exception { User user = userManager.lookupUser(user); String userId = user.getPrimaryId(); String id = userId + generateHashCodeForPayload(payload); return id; } }
The Pojo MyIdGenerator has one public method that accepts two parameters. However we have also annotated this one with the @Header and @Body annotation to help Camel know what to bind here from the Message from the Exchange being processed.
Of course this could be simplified a lot if you for instance just have a simple id generator. But we wanted to demonstrate that you can use the Bean Binding annotations anywhere.
public class MySimpleIdGenerator { public static int generate() { // generate a unique id return 123; } }
And finally we just need to remember to have our bean registered in the Spring Registry:
<bean id="myCorrelationIdGenerator" class="com.mycompany.MyIdGenerator"/>
Example using Groovy
In this example we have an Exchange that has a User object stored in the in header. This User object has methods to get some user information. We want to use Groovy to inject an expression that extracts and concats the fullname of the user into the fullName parameter.
public void doSomething(@Groovy("$request.header['user'].firstName $request.header['user'].familyName) String fullName, @Body String body) {
// process the inbound message here
}
Groovy supports GStrings that is like a template where we can insert $ placeholders that will be evaluated by Groovy.
@MessageDriven or @Consume
| @MessageDriven is @deprecated @MessageDriven is deprecated in Camel 1.x. You should use @Consume instead. Its removed in Camel 2.0. |
To consume a message you use either the @MessageDriven annotation or from 1.5.0 the @Consume annotation to mark a particular method of a bean as being a consumer method. The uri of the annotation defines the Camel Endpoint to consume from.
e.g. lets invoke the onCheese() method with the String body of the inbound JMS message from ActiveMQ on the cheese queue; this will use the Type Converter to convert the JMS ObjectMessage or BytesMessage to a String - or just use a TextMessage from JMS
public class Foo { @Consume(uri="activemq:cheese") public void onCheese(String name) { ... } }
The Bean Binding is then used to convert the inbound Message to the parameter list used to invoke the method .
What this does is basically create a route that looks kinda like this
from(uri).bean(theBean, "methodName");
| When using more than one CamelContext When you use more than 1 CamelContext you might end up with each of them creating a POJO Consuming. |
Using context option to apply only a certain CamelContext
Available as of Camel 2.0
See the warning above.
You can use the context option to specify which CamelContext the consumer should only apply for. For example:
@Consume(uri="activemq:cheese", context="camel-1") public void onCheese(String name) {
The consumer above will only be created for the CamelContext that have the context id = camel-1. You set this id in the XML tag:
<camelContext id="camel-1" ...>
Using an explicit route
If you want to invoke a bean method from many different endpoints or within different complex routes in different circumstances you can just use the normal routing DSL or the Spring XML configuration file.
For example
from(uri).beanRef("myBean", "methodName");
which will then look up in the Registry and find the bean and invoke the given bean name. (You can omit the method name and have Camel figure out the right method based on the method annotations and body type).
Use the Bean endpoint
You can always use the bean endpoint
from(uri).to("bean:myBean/methodName");
Which approach to use?
Using the @MessageDriven/@Consume annotations are simpler when you are creating a simple route with a single well defined input URI.
However if you require more complex routes or the same bean method needs to be invoked from many places then please use the routing DSL as shown above.
There are two different ways to send messages to any Camel Endpoint from a POJO
@EndpointInject
To allow sending of messages from POJOs you can use @EndpointInject() annotation. This will inject either a ProducerTemplate or CamelTemplate so that the bean can send message exchanges.
e.g. lets send a message to the foo.bar queue in ActiveMQ at some point
public class Foo { @EndpointInject(uri="activemq:foo.bar") ProducerTemplate producer; public void doSomething() { if (whatever) { producer.sendBody("<hello>world!</hello>"); } } }
The downside of this is that your code is now dependent on a Camel API, the ProducerTemplate. The next section describes how to remove this
Hiding the Camel APIs from your code using @Produce
We recommend Hiding Middleware APIs from your application code so the next option might be more suitable.
You can add the @Produce annotation to an injection point (a field or property setter) using a ProducerTemplate or using some interface you use in your business logic. e.g.
public interface MyListener { String sayHello(String name); } public class MyBean { @Produce(uri = "activemq:foo") protected MyListener producer; public void doSomething() { // lets send a message String response = producer.sayHello("James"); } }
Here Camel will automatically inject a smart client side proxy at the @Produce annotation - an instance of the MyListener instance. When we invoke methods on this interface the method call is turned into an object and using the Camel Spring Remoting mechanism it is sent to the endpoint - in this case the ActiveMQ endpoint to queue foo; then the caller blocks for a response.
If you want to make asynchronous message sends then use an @InOnly annotation on the injection point.
@RecipientList Annotation
As of 1.5.0 we now support the use of @RecipientList on a bean method to easily create a dynamic Recipient List using a Java method.
Simple Example using @Consume
package com.acme.foo; public class RouterBean { @Consume(uri = "activemq:foo") @RecipientList public String[] route(String body) { return new String[]{"activemq:bar", "activemq:whatnot"}; } }
For example if the above bean is configured in Spring when using a <camelContext> element as follows
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd "> <camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"/> <bean id="myRecipientList" class="com.acme.foo.RouterBean"/> </beans>
then a route will be created consuming from the foo queue on the ActiveMQ component which when a message is received the message will be forwarded to the endpoints defined by the result of this method call - namely the bar and whatnot queues.
How it works
The return value of the @RecipientList method is converted to either a java.util.Collection / java.util.Iterator or array of objects where each element is converted to an Endpoint or a String, or if you are only going to route to a single endpoint then just return either an Endpoint object or an object that can be converted to a String. So the following methods are all valid
@RecipientList public String[] route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public List<String> route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public Endpoint route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public Endpoint[] route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public Collection<Endpoint> route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public URI route(String body) { ... } @RecipientList public URI[] route(String body) { ... }
Then for each endpoint or URI the message is forwarded a separate copy to that endpoint.
You can then use whatever Java code you wish to figure out what endpoints to route to; for example you can use the Bean Binding annotations to inject parts of the message body or headers or use Expression values on the message.
More Complex Example Using DSL
In this example we will use more complex Bean Binding, plus we will use a separate route to invoke the Recipient List
public class RouterBean2 { @RecipientList public String route(@Header("customerID") String custID String body) { if (custID == null) return null; return "activemq:Customers.Orders." + custID; } } public class MyRouteBuilder extends RouteBuilder { protected void configure() { from("activemq:Orders.Incoming").recipientList(bean("myRouterBean", "route")); } }
Notice how we are injecting some headers or expressions and using them to determine the recipients using Recipient List EIP.
See the Bean Integration for more details.
Using Exchange Pattern Annotations
When working with POJO Producing or Spring Remoting you invoke methods which typically by default are InOut for Request Reply. That is there is an In message and an Out for the result. Typically invoking this operation will be synchronous, the caller will block until the server returns a result.
Camel has flexible Exchange Pattern support - so you can also support the Event Message pattern to use InOnly for asynchronous or one way operations. These are often called 'fire and forget' like sending a JMS message but not waiting for any response.
From 1.5 onwards Camel supports annotations for specifying the message exchange pattern on regular Java methods, classes or interfaces.
Specifying InOnly methods
Typically the default InOut is what most folks want but you can customize to use InOnly using an annotation.
public interface Foo { Object someInOutMethod(String input); String anotherInOutMethod(Cheese input); @InOnly void someInOnlyMethod(Document input); }
The above code shows three methods on an interface; the first two use the default InOut mechanism but the someInOnlyMethod uses the InOnly annotation to specify it as being a oneway method call.
Class level annotations
You can also use class level annotations to default all methods in an interface to some pattern such as
@InOnly public interface Foo { void someInOnlyMethod(Document input); void anotherInOnlyMethod(String input); }
Annotations will also be detected on base classes or interfaces. So for example if you created a client side proxy for
public class MyFoo implements Foo { ... }
Then the methods inherited from Foo would be InOnly.
Overloading a class level annotation
You can overload a class level annotation on specific methods. A common use case for this is if you have a class or interface with many InOnly methods but you want to just annote one or two methods as InOut
@InOnly public interface Foo { void someInOnlyMethod(Document input); void anotherInOnlyMethod(String input); @InOut String someInOutMethod(String input); }
In the above Foo interface the someInOutMethod will be InOut
Using your own annotations
You might want to create your own annotations to represent a group of different bits of metadata; such as combining synchrony, concurrency and transaction behaviour.
So you could annotate your annotation with the @Pattern annotation to default the exchange pattern you wish to use.
For example lets say we want to create our own annotation called @MyAsyncService
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
// lets add the message exchange pattern to it
@Pattern(ExchangePattern.InOnly)
// lets add some other annotations - maybe transaction behaviour?
public @interface MyAsyncService {
}
Now we can use this annotation and Camel will figure out the correct exchange pattern...
public interface Foo { void someInOnlyMethod(Document input); void anotherInOnlyMethod(String input); @MyAsyncService String someInOutMethod(String input); }
When writing software these days, its important to try and decouple as much middleware code from your business logic as possible.
This provides a number of benefits...
- you can choose the right middleware solution for your deployment and switch at any time
- you don't have to spend a large amount of time learning the specifics of any particular technology, whether its JMS or JavaSpace or Hibernate or JPA or iBATIS whatever
For example if you want to implement some kind of message passing, remoting, reliable load balancing or asynchronous processing in your application we recommend you use Camel annotations to bind your services and business logic to Camel Components which means you can then easily switch between things like
- in JVM messaging with SEDA
- using JMS via ActiveMQ or other JMS providers for reliable load balancing, grid or publish and subscribe
- for low volume, but easier administration since you're probably already using a database you could use
- use JavaSpace
How to decouple from middleware APIs
The best approach when using remoting is to use Spring Remoting which can then use any messaging or remoting technology under the covers. When using Camel's implementation you can then use any of the Camel Components along with any of the Enterprise Integration Patterns.
Another approach is to bind Java beans to Camel endpoints via the Bean Integration. For example using POJO Consuming and POJO Producing you can avoid using any Camel APIs to decouple your code both from middleware APIs and Camel APIs! ![]()
Visualisation
Camel supports the visualisation of your Enterprise Integration Patterns using the GraphViz DOT files which can either be rendered directly via a suitable GraphViz tool or turned into HTML, PNG or SVG files via the Camel Maven Plugin.
Here is a typical example of the kind of thing we can generate

If you click on the actual generated htmlyou will see that you can navigate from an EIP node to its pattern page, along with getting hover-over tool tips ec.
How to generate
See Camel Dot Maven Goal or the other maven goals Camel Maven Plugin
For OS X users
If you are using OS X then you can open the DOT file using graphviz which will then automatically re-render if it changes, so you end up with a real time graphical representation of the topic and queue hierarchies!
Also if you want to edit the layout a little before adding it to a wiki to distribute to your team, open the DOT file with OmniGraffle then just edit away ![]()
Business Activity Monitoring
The Camel BAM module provides a Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) framework for testing business processes across multiple message exchanges on different Endpoint instances.
For example if you have a simple system which you submit Purchase Orders into system A and then receive Invoices from system B, you might want to test that for a specific Purchase Order you receive a matching Invoice from system B within a specific time period.
How Camel BAM Works
What Camel BAM does is use a Correlation Identifier on an input message to determine which Process Instance a message belongs to. The process instance is an entity bean which can maintain state for each Activity (where an activity typically maps to a single endpoint, such as the receipt of Purchase orders, or the receipt of Invoices).
You can then add rules which are fired when a message is received on any activity such as to set time expectations, or to perform real time reconciliation of values across activities etc.
Simple Example
The following example shows how to perform some time based rules on a simple business process of 2 activities A and B (which maps to the Purchase Order and Invoice example above). If you want to experiment with this scenario you could edit the Test Case which defines the activities and rules, then tests that they work.
return new ProcessBuilder(jpaTemplate, transactionTemplate) { public void configure() throws Exception { // lets define some activities, correlating on an XPath on the message bodies ActivityBuilder a = activity("seda:a").name("a") .correlate(xpath("/hello/@id")); ActivityBuilder b = activity("seda:b").name("b") .correlate(xpath("/hello/@id")); // now lets add some rules b.starts().after(a.completes()) .expectWithin(seconds(1)) .errorIfOver(seconds(errorTimeout)).to("mock:overdue"); } };
As you can see in the above example, we define two activities first, then we define rules on when we expect the activities on an individual process instance to complete by along with the time at which we should assume there is an error. The ProcessBuilder is-a RouteBuilder and can be added to any CamelContext
Complete Example
For a complete example please see the BAM Example which is part of the standard Camel Examples
Use Cases
In the world of finance a common requirement is tracking financial trades. Often a trader will submit a Front Office Trade which then flows through the Middle Office and Back Office through various systems to settle the trade so that money is exchanged. You may wish to add tests that front and back office trades match up within a time period; if they don't match or a back office trade does not arrive within a required amount of time, you might want to fire off an alarm.
Extract Transform Load (ETL)
The ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a mechanism for loading data into systems or databases using some kind of Data Format from a variety of sources; often files then using Pipes and Filters, Message Translator and possible other Enterprise Integration Patterns.
So you could query data from various Camel Components such as File, HTTP or JPA, perform multiple patterns such as Splitter or Message Translator then send the messages to some other Component.
To show how this all fits together, try the ETL Example
Mock Component
Testing of distributed and asynchronous processing is notoriously difficult. The Mock, Test and DataSet endpoints work great with the Camel Testing Framework to simplify your unit and integration testing using Enterprise Integration Patterns and Camel's large range of Components together with the powerful Bean Integration.
The Mock component provides a powerful declarative testing mechanism, which is similar to jMock in that it allows declarative expectations to be created on any Mock endpoint before a test begins. Then the test is run, which typically fires messages to one or more endpoints, and finally the expectations can be asserted in a test case to ensure the system worked as expected.
This allows you to test various things like:
- The correct number of messages are received on each endpoint,
- The correct payloads are received, in the right order,
- Messages arrive on an endpoint in order, using some Expression to create an order testing function,
- Messages arrive match some kind of Predicate such as that specific headers have certain values, or that parts of the messages match some predicate, such as by evaluating an XPath or XQuery Expression.
Note that there is also the Test endpoint which is a Mock endpoint, but which uses a second endpoint to provide the list of expected message bodies and automatically sets up the Mock endpoint assertions. In other words, it's a Mock endpoint that automatically sets up its assertions from some sample messages in a File or database, for example.
URI format
mock:someName[?options]
Where someName can be any string that uniquely identifies the endpoint.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reportGroup | null | A size to use a throughput logger for reporting |
Simple Example
Here's a simple example of Mock endpoint in use. First, the endpoint is resolved on the context. Then we set an expectation, and then, after the test has run, we assert that our expectations have been met.
MockEndpoint resultEndpoint = context.resolveEndpoint("mock:foo", MockEndpoint.class); resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(2); // send some messages ... // now lets assert that the mock:foo endpoint received 2 messages resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
You typically always call the assertIsSatisfied() method to test that the expectations were met after running a test.
Camel will by default wait 20 seconds when the assertIsSatisfied() is invoked. This can be configured by setting the setResultWaitTime(millis) method.
Setting expectations
You can see from the javadoc of MockEndpoint the various helper methods you can use to set expectations. The main methods are as follows:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| expectedMessageCount(int) | To define the expected message count on the endpoint. |
| expectedMinimumMessageCount(int) | To define the minimum number of expected messages on the endpoint. |
| expectedBodiesReceived(...) | To define the expected bodies that should be received (in order). |
| expectedHeaderReceived(...) | To define the expected header that should be received |
| expectsAscending(Expression) | To add an expectation that messages are received in order, using the given Expression to compare messages. |
| expectsDescending(Expression) | To add an expectation that messages are received in order, using the given Expression to compare messages. |
| expectsNoDuplicates(Expression) | To add an expectation that no duplicate messages are received; using an Expression to calculate a unique identifier for each message. This could be something like the JMSMessageID if using JMS, or some unique reference number within the message. |
Here's another example:
resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived("firstMessageBody", "secondMessageBody", "thirdMessageBody");
Adding expectations to specific messages
In addition, you can use the message(int messageIndex) method to add assertions about a specific message that is received.
For example, to add expectations of the headers or body of the first message (using zero-based indexing like java.util.List), you can use the following code:
resultEndpoint.message(0).header("foo").isEqualTo("bar");
There are some examples of the Mock endpoint in use in the camel-core processor tests.
A Spring Example
First, here's the spring.xml file
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="file:src/test/data?noop=true"/> <filter> <xpath>/person/city = 'London'</xpath> <to uri="mock:matched"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> <bean id="myBean" class="org.apache.camel.spring.mock.MyAssertions" scope="singleton"/>
As you can see, it defines a simple routing rule which consumes messages from the local src/test/data directory. The noop flag just means not to delete or move the file after its been processed.
Also note we instantiate a bean called myBean, here is the source of the MyAssertions bean.
public class MyAssertions implements InitializingBean { @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:matched") private MockEndpoint matched; @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:notMatched") private MockEndpoint notMatched; public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // lets add some expectations matched.expectedMessageCount(1); notMatched.expectedMessageCount(0); } public void assertEndpointsValid() throws Exception { // now lets perform some assertions that the test worked as we expect Assert.assertNotNull("Should have a matched endpoint", matched); Assert.assertNotNull("Should have a notMatched endpoint", notMatched); MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(matched, notMatched); } }
The bean is injected with a bunch of Mock endpoints using the @EndpointInject annotation, it then sets a bunch of expectations on startup (using Spring's InitializingBean interface and afterPropertiesSet() method) before the CamelContext starts up.
Then in our test case (which could be JUnit or TesNG) we lookup myBean in Spring (or have it injected into our test) and then invoke the assertEndpointsValid() method on it to verify that the mock endpoints have their assertions met. You could then inspect the message exchanges that were delivered to any of the endpoints using the getReceivedExchanges() method on the Mock endpoint and perform further assertions or debug logging.
Here is the actual JUnit test case we use.
See Also
Testing
Testing is a crucial activity in any piece of software development or integration. Typically Camel Riders use various different technologies wired together in a variety of patterns with different expression languages together with different forms of Bean Integration and Dependency Injection so its very easy for things to go wrong! ![]() . Testing is the crucial weapon to ensure that things work as you would expect.
. Testing is the crucial weapon to ensure that things work as you would expect.
Camel is a Java library so you can easily wire up tests in whatever unit testing framework you use (JUnit 3.x, 4.x or TestNG). However the Camel project has tried to make the testing of Camel as easy and powerful as possible so we have introduced the following features.
Testing mechanisms
The following mechanisms are supported
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Camel Test | is a library letting you easily create Camel test cases using a single Java class for all your configuration and routing without using Spring or Guice for Dependency Injection which does not require an in depth knowledge of Spring+SpringTest or Guice |
| Spring Testing | uses Spring Test together with either XML or Java Config to dependency inject your test classes |
| Guice | uses Guice to dependency inject your test classes |
In all approaches the test classes look pretty much the same in that they all reuse the Camel binding and injection annotations.
Camel Test Example
Here is the Camel Test example.
public class FilterTest extends CamelTestSupport { @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:result") protected MockEndpoint resultEndpoint; @Produce(uri = "direct:start") protected ProducerTemplate template; public void testSendMatchingMessage() throws Exception { String expectedBody = "<matched/>"; resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived(expectedBody); template.sendBodyAndHeader(expectedBody, "foo", "bar"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } public void testSendNotMatchingMessage() throws Exception { resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(0); template.sendBodyAndHeader("<notMatched/>", "foo", "notMatchedHeaderValue"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } @Override protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("mock:result"); } }; } }
Notice how it derives from the Camel helper class CamelTestSupport but has no Spring or Guice dependency injection configuration but instead overrides the createRouteBuilder() method.
Spring Test with XML Config Example
Here is the Spring Testing example using XML Config.
@ContextConfiguration public class FilterTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:result") protected MockEndpoint resultEndpoint; @Produce(uri = "direct:start") protected ProducerTemplate template; @DirtiesContext public void testSendMatchingMessage() throws Exception { String expectedBody = "<matched/>"; resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived(expectedBody); template.sendBodyAndHeader(expectedBody, "foo", "bar"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } @DirtiesContext public void testSendNotMatchingMessage() throws Exception { resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(0); template.sendBodyAndHeader("<notMatched/>", "foo", "notMatchedHeaderValue"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } }
Notice that we use @DirtiesContext on the test methods to force Spring Testing to automatically reload the CamelContext after each test method - this ensures that the tests don't clash with each other (e.g. one test method sending to an endpoint that is then reused in another test method).
Also notice the use of @ContextConfiguration to indicate that by default we should look for the FilterTest-context.xml on the classpath to configure the test case which looks like this
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd "> <camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <filter> <xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath> <to uri="mock:result"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
Spring Test with Java Config Example
Here is the Spring Testing example using Java Config. For more information see Spring Java Config.
@ContextConfiguration(
locations = "org.apache.camel.spring.javaconfig.patterns.FilterTest$ContextConfig",
loader = JavaConfigContextLoader.class)
public class FilterTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests {
@EndpointInject(uri = "mock:result")
protected MockEndpoint resultEndpoint;
@Produce(uri = "direct:start")
protected ProducerTemplate template;
@DirtiesContext
@Test
public void testSendMatchingMessage() throws Exception {
String expectedBody = "<matched/>";
resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived(expectedBody);
template.sendBodyAndHeader(expectedBody, "foo", "bar");
resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
}
@DirtiesContext
@Test
public void testSendNotMatchingMessage() throws Exception {
resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(0);
template.sendBodyAndHeader("<notMatched/>", "foo", "notMatchedHeaderValue");
resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
}
@Configuration
public static class ContextConfig extends SingleRouteCamelConfiguration {
@Bean
public RouteBuilder route() {
return new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("direct:start").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("mock:result");
}
};
}
}
}
This is similar to the XML Config example above except that there is no XML file and instead the nested ContextConfig class does all of the configuration; so your entire test case is contained in a single Java class. We currently have to reference by class name this class in the @ContextConfiguration which is a bit ugly. Please vote for SJC-238 to address this and make Spring Test work more cleanly with Spring JavaConfig.
Its totally optional but for the ContextConfig implementation we derive from SingleRouteCamelConfiguration which is a helper Spring Java Config class which will configure the CamelContext for us and then register the RouteBuilder we create.
Testing endpoints
Camel provides a number of endpoints which can make testing easier.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DataSet | For load & soak testing this endpoint provides a way to create huge numbers of messages for sending to Components and asserting that they are consumed correctly |
| Mock | For testing routes and mediation rules using mocks and allowing assertions to be added to an endpoint |
| Test | Creates a Mock endpoint which expects to receive all the message bodies that could be polled from the given underlying endpoint |
The main endpoint is the Mock endpoint which allows expectations to be added to different endpoints; you can then run your tests and assert that your expectations are met at the end.
Stubbing out physical transport technologies
If you wish to test out a route but want to avoid actually using a real physical transport (for example to unit test a transformation route rather than performing a full integration test) then the following endpoints can be useful.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct | Direct invocation of the consumer from the producer so that single threaded (non-SEDA) in VM invocation is performed which can be useful to mock out physical transports |
| SEDA | Delivers messages asynchonously to consumers via a java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue which is good for testing asynchronous transports |
Camel Test
As a simple alternative to using Spring Testing or Guice the camel-test module was introduced into the Camel 2.0 trunk so you can perform powerful Testing of your Enterprise Integration Patterns easily.
Adding to your pom.xml
To get started using Camel Test you will need to add an entry to your pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-test</artifactId> <version>${camel-version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
You might also want to add commons-logging and log4j to ensure nice logging messages (and maybe adding a log4j.properties file into your src/test/resources directory).
<dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
Writing your test
You firstly need to derive from the class CamelTestSupport and typically you will need to override the createRouteBuilder() method to create routes to be tested.
Here is an example.
public class FilterTest extends CamelTestSupport { @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:result") protected MockEndpoint resultEndpoint; @Produce(uri = "direct:start") protected ProducerTemplate template; public void testSendMatchingMessage() throws Exception { String expectedBody = "<matched/>"; resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived(expectedBody); template.sendBodyAndHeader(expectedBody, "foo", "bar"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } public void testSendNotMatchingMessage() throws Exception { resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(0); template.sendBodyAndHeader("<notMatched/>", "foo", "notMatchedHeaderValue"); resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(); } @Override protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("mock:result"); } }; } }
Notice how you can use the various Camel binding and injection annotations to inject individual Endpoint objects - particularly the Mock endpoints which are very useful for Testing. Also you can inject producer objects such as ProducerTemplate or some application code interface for sending messages or invoking services.
JNDI
Camel uses a Registry to allow you to configure Component or Endpoint instances or Beans used in your routes. If you are not using Spring or [OSGi] then JNDI is used as the default registry implementation.
So you will also need to create a jndi.properties file in your src/test/resources directory so that there is a default registry available to initialise the CamelContext.
Here is an example jndi.properties file
java.naming.factory.initial = org.apache.camel.util.jndi.CamelInitialContextFactory
See Also
Spring Testing
Testing is a crucial part of any development or integration work. The Spring Framework offers a number of features that makes it easy to test while using Spring for Inversion of Control which works with JUnit 3.x, JUnit 4.x or TestNG.
We can reuse Spring for IoC and the Camel Mock and Test endpoints to create sophisticated integration tests that are easy to run and debug inside your IDE.
For example here is a simple unit test
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext; import org.apache.camel.component.mock.MockEndpoint; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit38.AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests; @ContextConfiguration public class MyCamelTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @Autowired protected CamelContext camelContext; public void testMocksAreValid() throws Exception { MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext); } }
This test will load a Spring XML configuration file called MyCamelTest-context.xml from the classpath in the same package structure as the MyCamelTest class and initialize it along with any Camel routes we define inside it, then inject the CamelContext instance into our test case.
For instance, like this maven folder layout:
src/main/java/com/mycompany/MyCamelTest.class src/main/resources/com/mycompany/MyCamelTest-context.xml
You can overload the method createApplicationContext to provide the Spring ApplicationContext that isn't following the above default. For instance:
protected AbstractXmlApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { return new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/config/MySpringConfig.xml"); }
Then the test method will then run which invokes the MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext) method which asserts that all of the Mock and Test endpoints have their expectations met.
xml}
Spring Test with Java Config Example
You can completely avoid using an XML configuration file by using Spring Java Config.
Here is an example using Java Config.
@ContextConfiguration(
locations = "org.apache.camel.spring.javaconfig.patterns.FilterTest$ContextConfig",
loader = JavaConfigContextLoader.class)
public class FilterTest extends AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests {
@EndpointInject(uri = "mock:result")
protected MockEndpoint resultEndpoint;
@Produce(uri = "direct:start")
protected ProducerTemplate template;
@DirtiesContext
@Test
public void testSendMatchingMessage() throws Exception {
String expectedBody = "<matched/>";
resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived(expectedBody);
template.sendBodyAndHeader(expectedBody, "foo", "bar");
resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
}
@DirtiesContext
@Test
public void testSendNotMatchingMessage() throws Exception {
resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(0);
template.sendBodyAndHeader("<notMatched/>", "foo", "notMatchedHeaderValue");
resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
}
@Configuration
public static class ContextConfig extends SingleRouteCamelConfiguration {
@Bean
public RouteBuilder route() {
return new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("direct:start").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("mock:result");
}
};
}
}
}
This is similar to the XML Config example above except that there is no XML file and instead the nested ContextConfig class does all of the configuration; so your entire test case is contained in a single Java class. We currently have to reference by class name this class in the @ContextConfiguration which is a bit ugly. Please vote for SJC-238 to address this and make Spring Test work more cleanly with Spring JavaConfig.
Adding more Mock expectations
If you wish to programmatically add any new assertions to your test you can easily do so with the following. Notice how we use @EndpointInject to inject a Camel endpoint into our code then the Mock API to add an expectation on a specific message.
@ContextConfiguration public class MyCamelTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @Autowired protected CamelContext camelContext; @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:foo") protected MockEndpoint foo; public void testMocksAreValid() throws Exception { // lets add more expectations foo.message(0).header("bar").isEqualTo("ABC"); MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext); } }
Further processing the received messages
Sometimes once a Mock endpoint has received some messages you want to then process them further to add further assertions that your test case worked as you expect.
So you can then process the received message exchanges if you like...
@ContextConfiguration public class MyCamelTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @Autowired protected CamelContext camelContext; @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:foo") protected MockEndpoint foo; public void testMocksAreValid() throws Exception { // lets add more expectations... MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext); // now lets do some further assertions List<Exchange> list = foo.getReceivedExchanges(); for (Exchange exchange : list) { Message in = exchange.getIn(); ... } } }
Sending and receiving messages
It might be that the Enterprise Integration Patterns you have defined in either Spring XML or using the Java DSL do all of the sending and receiving and you might just work with the Mock endpoints as described above. However sometimes in a test case its useful to explicitly send or receive messages directly.
To send or receive messages you should use the Bean Integration mechanism. For example to send messages inject a ProducerTemplate using the @EndpointInject annotation then call the various send methods on this object to send a message to an endpoint. To consume messages use the @MessageDriven annotation on a method to have the method invoked when a message is received.
public class Foo { @EndpointInject(uri="activemq:foo.bar") ProducerTemplate producer; public void doSomething() { // lets send a message! producer.sendBody("<hello>world!</hello>"); } // lets consume messages from the 'cheese' queue @MessageDriven(uri="activemq:cheese") public void onCheese(String name) { ... } }
See Also
- a real example test case using Mock and Spring along with its Spring XML
- Bean Integration
- Mock endpoint
- Test endpoint
Camel Guice
As of 1.5 we now have support for Google Guice as a dependency injection framework. To use it just be dependent on camel-guice.jar which also depends on the following jars.
Dependency Injecting Camel with Guice
The GuiceCamelContext is designed to work nicely inside Guice. You then need to bind it using some Guice Module.
The camel-guice library comes with a number of reusable Guice Modules you can use if you wish - or you can bind the GuiceCamelContext yourself in your own module.
- CamelModule is the base module which binds the GuiceCamelContext but leaves it up you to bind the RouteBuilder instances
- CamelModuleWithRouteTypes extends CamelModule so that in the constructor of the module you specify the RouteBuilder classes or instances to use
- CamelModuleWithMatchingRoutes extends CamelModule so that all bound RouteBuilder instances will be injected into the CamelContext or you can supply an optional Matcher to find RouteBuilder instances matching some kind of predicate.
So you can specify the exact RouteBuilder instances you want
Injector injector = Guice.createInjector(new CamelModuleWithRouteTypes(MyRouteBuilder.class, AnotherRouteBuilder.class)); // if required you can lookup the CamelContext CamelContext camelContext = injector.getInstance(CamelContext.class);
Or inject them all
Injector injector = Guice.createInjector(new CamelModuleWithRouteTypes()); // if required you can lookup the CamelContext CamelContext camelContext = injector.getInstance(CamelContext.class);
You can then use Guice in the usual way to inject the route instances or any other dependent objects.
Bootstrapping with JNDI
A common pattern used in J2EE is to bootstrap your application or root objects by looking them up in JNDI. This has long been the approach when working with JMS for example - looking up the JMS ConnectionFactory in JNDI for example.
You can follow a similar pattern with Guice using the GuiceyFruit JNDI Provider which lets you bootstrap Guice from a jndi.properties file which can include the Guice Modules to create along with environment specific properties you can inject into your modules and objects.
Configuring Component, Endpoint or RouteBuilder instances
You can use Guice to dependency inject whatever objects you need to create, be it an Endpoint, Component, RouteBuilder or arbitrary bean used within a route.
The easiest way to do this is to create your own Guice Module class which extends one of the above module classes and add a provider method for each object you wish to create. A provider method is annotated with @Provides as follows
public class MyModule extends CamelModuleWithMatchingRoutes { @Provides @JndiBind("jms") JmsComponent jms(@Named("activemq.brokerURL") String brokerUrl) { return JmsComponent.jmsComponent(new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(brokerUrl)); } }
You can optionally annotate the method with @JndiBind to bind the object to JNDI at some name if the object is a component, endpoint or bean you wish to refer to by name in your routes.
You can inject any environment specific properties (such as URLs, machine names, usernames/passwords and so forth) from the jndi.properties file easily using the @Named annotation as shown above. This allows most of your configuration to be in Java code which is typesafe and easily refactorable - then leaving some properties to be environment specific (the jndi.properties file) which you can then change based on development, testing, production etc.
Creating multiple RouteBuilder instances per type
It is sometimes useful to create multiple instances of a particular RouteBuilder with different configurations.
To do this just create multiple provider methods for each configuration; or create a single provider method that returns a collection of RouteBuilder instances.
For example
import org.apache.camel.guice.CamelModuleWithMatchingRoutes; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; public class MyModule extends CamelModuleWithMatchingRoutes { @Provides @JndiBind("foo") Collection<RouteBuilder> foo(@Named("fooUrl") String fooUrl) { return Lists.newArrayList(new MyRouteBuilder(fooUrl), new MyRouteBuilder("activemq:CheeseQueue")); } }
See Also
- there are a number of Examples you can look at to see Guice and Camel being used such as Guice JMS Example
- Guice Maven Plugin for running your Guice based routes via Maven
Templating
When you are testing distributed systems its a very common requirement to have to stub out certain external systems with some stub so that you can test other parts of the system until a specific system is available or written etc.
A great way to do this is using some kind of Template system to generate responses to requests generating a dynamic message using a mostly-static body.
There are a number of templating components you could use
Example
Here's a simple example showing how we can respond to InOut requests on the My.Queue queue on ActiveMQ with a template generated response. The reply would be sent back to the JMSReplyTo Destination.
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm");
If you want to use InOnly and consume the message and send it to another destination you could use
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
See Also
- Mock for details of mock endpoint testing (as opposed to template based stubs).
Database
Camel can work with databases in a number of different ways. This document tries to outline the most common approaches.
Database endpoints
Camel provides a number of different endpoints for working with databases
- JPA for working with hibernate, openjpa or toplink. When consuming from the endpoints entity beans are read (and deleted/updated to mark as processed) then when producing to the endpoints they are written to the database (via insert/update).
- iBATIS similar to the above but using Apache iBATIS
- JDBC similar though using explicit SQL
Database pattern implementations
Various patterns can work with databases as follows
- Idempotent Consumer
- Aggregator
- BAM for business activity monitoring
Parallel Processing and Ordering
It is a common requirement to want to use parallel processing of messages for throughput and load balancing, while at the same time process certain kinds of messages in order.
How to achieve parallel processing
You can send messages to a number of Camel Components to achieve parallel processing and load balancing such as
- SEDA for in-JVM load balancing across a thread pool
- ActiveMQ or JMS for distributed load balancing and parallel processing
- JPA for using the database as a poor mans message broker
When processing messages concurrently, you should consider ordering and concurrency issues. These are described below
Concurrency issues
Note that there is no concurrency or locking issue when using ActiveMQ, JMS or SEDA by design; they are designed for highly concurrent use. However there are possible concurrency issues in the Processor of the messages i.e. what the processor does with the message?
For example if a processor of a message transfers money from one account to another account; you probably want to use a database with pessimistic locking to ensure that operation takes place atomically.
Ordering issues
As soon as you send multiple messages to different threads or processes you will end up with an unknown ordering across the entire message stream as each thread is going to process messages concurrently.
For many use cases the order of messages is not too important. However for some applications this can be crucial. e.g. if a customer submits a purchase order version 1, then amends it and sends version 2; you don't want to process the first version last (so that you loose the update). Your Processor might be clever enough to ignore old messages. If not you need to preserve order.
Recommendations
This topic is large and diverse with lots of different requirements; but from a high level here are our recommendations on parallel processing, ordering and concurrency
- for distributed locking, use a database by default, they are very good at it

- to preserve ordering across a JMS queue consider using Exclusive Consumers in the ActiveMQ component
- even better are Message Groups which allows you to preserve ordering across messages while still offering parallelisation via the JMSXGrouopID header to determine what can be parallelized
- if you receive messages out of order you could use the Resequencer to put them back together again
A good rule of thumb to help reduce ordering problems is to make sure each single can be processed as an atomic unit in parallel (either without concurrency issues or using say, database locking); or if it can't, use a Message Group to relate the messages together which need to be processed in order by a single thread.
Using Message Groups with Camel
To use a Message Group with Camel you just need to add a header to the output JMS message based on some kind of Correlation Identifier to correlate messages which should be processed in order by a single thread - so that things which don't correlate together can be processed concurrently.
For example the following code shows how to create a message group using an XPath expression taking an invoice's product code as the Correlation Identifier
from("activemq:a").setHeader("JMSXGroupID", xpath("/invoice/productCode")).to("activemq:b");
You can of course use the Xml Configuration if you prefer
Asynchronous Processing
Overview
| A new API in Camel 2.0 The API used on this wiki pages is the old async API in Camel 1.x. We replaced this with a new API in Camel 2.0 and its documented here Async. |
Camel supports a more complex asynchronous processing model. The asynchronous processors implement the AsyncProcessor interface which is derived from the more synchronous Processor interface. There are advantages and disadvantages when using asynchronous processing when compared to using the standard synchronous processing model.
Advantages:
- Processing routes that are composed fully of asynchronous processors do not use up threads waiting for processors to complete on blocking calls. This can increase the scalability of your system by reducing the number of threads needed to process the same workload.
- Processing routes can be broken up into SEDA processing stages where different thread pools can process the different stages. This means that your routes can be processed concurrently.
Disadvantages:
- Implementing asynchronous processors is more complex than implementing the synchronous versions.
When to Use
We recommend that processors and components be implemented the more simple synchronous APIs unless you identify a performance of scalability requirement that dictates otherwise. A Processor whose process() method blocks for a long time would be good candidates for being converted into an asynchronous processor.
Interface Details
public interface AsyncProcessor extends Processor { boolean process(Exchange exchange, AsyncCallback callback); }
The AsyncProcessor defines a single process() method which is very similar to it's synchronous Processor.process() brethren. Here are the differences:
- A non-null AsyncCallback MUST be supplied which will be notified when the exchange processing is completed.
- It MUST not throw any exceptions that occurred while processing the exchange. Any such exceptions must be stored on the exchange's Exception property.
- It MUST know if it will complete the processing synchronously or asynchronously. The method will return true if it does complete synchronously, otherwise it returns false.
- When the processor has completed processing the exchange, it must call the callback.done(boolean sync) method. The sync parameter MUST match the value returned by the process() method.
Implementing Processors that Use the AsyncProcessor API
All processors, even synchronous processors that do not implement the AsyncProcessor interface, can be coerced to implement the AsyncProcessor interface. This is usually done when you are implementing a Camel component consumer that supports asynchronous completion of the exchanges that it is pushing through the Camel routes. Consumers are provided a Processor object when created. All Processor object can be coerced to a AsyncProcessor using the following API:
Processor processor = ... AsyncProcessor asyncProcessor = AsyncProcessorTypeConverter.convert(processor);
For a route to be fully asynchronous and reap the benefits to lower Thread usage, it must start with the consumer implementation making use of the asynchronous processing API. If it called the synchronous process() method instead, the consumer's thread would be forced to be blocked and in use for the duration that it takes to process the exchange.
It is important to take note that just because you call the asynchronous API, it does not mean that the processing will take place asynchronously. It only allows the possibility that it can be done without tying up the caller's thread. If the processing happens asynchronously is dependent on the configuration of the Camel route.
Normally, the the process call is passed in an inline inner AsyncCallback class instance which can reference the exchange object that was declared final. This allows it to finish up any post processing that is needed when the called processor is done processing the exchange. See below for an example.
final Exchange exchange = ... AsyncProcessor asyncProcessor = ... asyncProcessor.process(exchange, new AsyncCallback() { public void done(boolean sync) { if (exchange.isFailed()) { ... // do failure processing.. perhaps rollback etc. } else { ... // processing completed successfully, finish up // perhaps commit etc. } } });
Asynchronous Route Sequence Scenarios
Now that we have understood the interface contract of the AsyncProcessor, and have seen how to make use of it when calling processors, lets looks a what the thread model/sequence scenarios will look like for some sample routes.
The Jetty component's consumers support async processing by using continuations. Suffice to say it can take a http request and pass it to a camel route for async processing. If the processing is indeed async, it uses Jetty continuation so that the http request is 'parked' and the thread is released. Once the camel route finishes processing the request, the jetty component uses the AsyncCallback to tell Jetty to 'un-park' the request. Jetty un-parks the request, the http response returned using the result of the exchange processing.
Notice that the jetty continuations feature is only used "If the processing is indeed async". This is why AsyncProcessor.process() implementations MUST accurately report if request is completed synchronously or not.
The jhc component's producer allows you to make HTTP requests and implement the AsyncProcessor interface. A route that uses both the jetty asynchronous consumer and the jhc asynchronous producer will be a fully asynchronous route and has some nice attributes that can be seen if we take a look at a sequence diagram of the processing route. For the route:
from("jetty:http://localhost:8080/service").to("jhc:http://localhost/service-impl");
The sequence diagram would look something like this:

The diagram simplifies things by making it looks like processors implement the AsyncCallback interface when in reality the AsyncCallback interfaces are inline inner classes, but it illustrates the processing flow and shows how 2 separate threads are used to complete the processing of the original http request. The first thread is synchronous up until processing hits the jhc producer which issues the http request. It then reports that the exchange processing will complete async since it will use a NIO to complete getting the response back. Once the jhc component has received a full response it uses AsyncCallback.done() method to notify the caller. These callback notifications continue up until it reaches the original jetty consumer which then un-parks the http request and completes it by providing the response.
Mixing Synchronous and Asynchronous Processors
It is totally possible and reasonable to mix the use of synchronous and asynchronous processors/components. The pipeline processor is the backbone of a Camel processing route. It glues all the processing steps together. It is implemented as an AsyncProcessor and supports interleaving synchronous and asynchronous processors as the processing steps in the pipeline.
Lets say we have 2 custom processors, MyValidator and MyTransformation, both of which are synchronous processors. Lets say we want to load file from the data/in directory validate them with the MyValidator() processor, Transform them into JPA java objects using MyTransformation and then insert them into the database using the JPA component. Lets say that the transformation process takes quite a bit of time and we want to allocate 20 threads to do parallel transformations of the input files. The solution is to make use of the thread processor. The thread is AsyncProcessor that forces subsequent processing in asynchronous thread from a thread pool.
The route might look like:
from("file:data/in").process(new MyValidator()).thread(20).process(new MyTransformation()).to("jpa:PurchaseOrder");
The sequence diagram would look something like this:

You would actually have multiple threads executing the 2nd part of the thread sequence.
Staying synchronous in an AsyncProcessor
Generally speaking you get better throughput processing when you process things synchronously. This is due to the fact that starting up an asynchronous thread and doing a context switch to it adds a little bit of of overhead. So it is generally encouraged that AsyncProcessors do as much work as they can synchronously. When they get to a step that would block for a long time, at that point they should return from the process call and let the caller know that it will be completing the call asynchronously.
Implementing Virtual Topics on other JMS providers
ActiveMQ supports Virtual Topics since durable topic subscriptions kinda suck (see this page for more detail) mostly since they don't support Competing Consumers.
Most folks want Queue semantics when consuming messages; so that you can support Competing Consumers for load balancing along with things like Message Groups and Exclusive Consumers to preserve ordering or partition the queue across consumers.
However if you are using another JMS provider you can implement Virtual Topics by switching to ActiveMQ ![]() or you can use the following Camel pattern.
or you can use the following Camel pattern.
First here's the ActiveMQ approach.
- send to activemq:topic:VirtualTopic.Orders
- for consumer A consume from activemq:Consumer.A.VirtualTopic.Orders
When using another message broker use the following pattern
- send to jms:Orders
- add this route with a to() for each logical durable topic subscriber
from("jms:Orders").to("jms:Consumer.A", "jms:Consumer.B", ...);
- for consumer A consume from jms:Consumer.A
What's the Camel Transport for CXF
In CXF you offer or consume a webservice by defining it´s address. The first part of the address specifies the protocol to use. For example address="http://localhost:90000" in an endpoint configuration means your service will be offered using the http protocol on port 9000 of localhost. When you integrate Camel Tranport into CXF you get a new transport "camel". So you can specify address="camel://direct:MyEndpointName" to bind the CXF service address to a camel direct endpoint.
Technically speaking Camel transport for CXF is a component which implements the CXF transport API with the Camel core library. This allows you to use camel´s routing engine and integration patterns support smoothly together with your CXF services.
Integrate Camel into CXF transport layer
To include the Camel Tranport into your CXF bus you use the CamelTransportFactory. You can do this in Java as well as in Spring.
Setting up the Camel Transport in Spring
You can use the following snippet in your applicationcontext if you want to configure anything special. If you only want to activate the camel transport you do not have to do anything in your application context. As soon as you include the camel-cxf jar in your app cxf will scan the jar and load a CamelTransportFactory for you.
<bean class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.transport.CamelTransportFactory"> <property name="bus" ref="cxf" /> <property name="camelContext" ref="camelContext" /> <!-- checkException new added in Camel 2.1 and Camel 1.6.2 --> <!-- If checkException is true , CamelDestination will check the outMessage's exception and set it into camel exchange. You can also override this value in CamelDestination's configuration. The default value is false. This option should be set true when you want to leverage the camel's error handler to deal with fault message --> <property name="checkException" value="true" /> <property name="transportIds"> <list> <value>http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel</value> </list> </property> </bean>
Integrating the Camel Transport in a programmatic way
Camel transport provides a setContext method that you could use to set the Camel context into the transport factory. If you want this factory take effect, you need to register the factory into the CXF bus. Here is a full example for you.
import org.apache.cxf.Bus; import org.apache.cxf.BusFactory; import org.apache.cxf.transport.ConduitInitiatorManager; import org.apache.cxf.transport.DestinationFactoryManager; ... BusFactory bf = BusFactory.newInstance(); Bus bus = bf.createBus(); CamelTransportFactory camelTransportFactory = new CamelTransportFactory(); camelTransportFactory.setCamelContext(context) // register the conduit initiator ConduitInitiatorManager cim = bus.getExtension(ConduitInitiatorManager.class); cim.registerConduitInitiator(CamelTransportFactory.TRANSPORT_ID, camelTransportFactory); // register the destination factory DestinationFactoryManager dfm = bus.getExtension(DestinationFactoryManager.class); dfm.registerDestinationFactory(CamelTransportFactory.TRANSPORT_ID, camelTransportFactory); // set or bus as the default bus for cxf BusFactory.setDefaultBus(bus);
Configure the destination and conduit
Namespace
The elements used to configure an Camel transport endpoint are defined in the namespace http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel. It is commonly referred to using the prefix camel. In order to use the Camel transport configuration elements you will need to add the lines shown below to the beans element of your endpoint's configuration file. In addition, you will need to add the configuration elements' namespace to the xsi:schemaLocation attribute.
<beans ...
xmlns:camel="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel
...
xsi:schemaLocation="...
http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel
http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel.xsd
...>
The destination element
You configure an Camel transport server endpoint using the camel:destination element and its children. The camel:destination element takes a single attribute, name, the specifies the WSDL port element that corresponds to the endpoint. The value for the name attribute takes the form portQName.camel-destination. The example below shows the camel:destination element that would be used to add configuration for an endpoint that was specified by the WSDL fragment <port binding="widgetSOAPBinding" name="widgetSOAPPort> if the endpoint's target namespace was http://widgets.widgetvendor.net.
...
<camel:destination name="{http://widgets/widgetvendor.net}widgetSOAPPort.http-destination>
<camelContext id="context" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="direct:EndpointC" />
<to uri="direct:EndpointD" />
</route>
</camelContext>
</camel:destination>
...
The camel:destination element has a number of child elements that specify configuration information. They are described below.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| camel-spring:camelContext | You can specify the camel context in the camel destination |
| camel:camelContextRef | The camel context id which you want inject into the camel destination |
The conduit element
You configure an Camel transport client using the camel:conduit element and its children. The camel:conduit element takes a single attribute, name, that specifies the WSDL port element that corresponds to the endpoint. The value for the name attribute takes the form portQName.camel-conduit. For example, the code below shows the camel:conduit element that would be used to add configuration for an endpoint that was specified by the WSDL fragment <port binding="widgetSOAPBinding" name="widgetSOAPPort> if the endpoint's target namespace was http://widgets.widgetvendor.net.
... <camelContext id="conduit_context" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:EndpointA" /> <to uri="direct:EndpointB" /> </route> </camelContext> <camel:conduit name="{http://widgets/widgetvendor.net}widgetSOAPPort.camel-conduit"> <camel:camelContextRef>conduit_context</camel:camelContextRef> </camel:conduit> <camel:conduit name="*.camel-conduit"> <!-- you can also using the wild card to specify the camel-conduit that you want to configure --> ... </camel:conduit> ...
The camel:conduit element has a number of child elements that specify configuration information. They are described below.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| camel-spring:camelContext | You can specify the camel context in the camel conduit |
| camel:camelContextRef | The camel context id which you want inject into the camel conduit |
Example Using Camel as a load balancer for CXF
This example show how to use the camel load balance feature in CXF, and you need load the configuration file in CXF and publish the endpoints on the address "camel://direct:EndpointA" and "camel://direct:EndpointB"
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:camel="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf/cxfEndpoint.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd "> <bean id = "roundRobinRef" class="org.apache.camel.processor.loadbalancer.RoundRobinLoadBalancer" /> <camelContext id="dest_context" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="jetty:http://localhost:9091/GreeterContext/GreeterPort"/> <loadBalance ref="roundRobinRef"> <to uri="direct:EndpointA"/> <to uri="direct:EndpointB"/> </loadBalance> </route> </camelContext> <!-- Inject the camel context to the Camel transport's destination --> <camel:destination name="{http://apache.org/hello_world_soap_http}CamelPort.camel-destination"> <camel:camelContextRef>dest_context</camel:camelContextRef> </camel:destination> </beans>
Complete Howto and Example for attaching Camel to CXF
Better JMS Transport for CXF Webservice using Apache Camel
Tutorials
There now follows the documentation on camel tutorials
- Tutorial for Camel on Google App Engine
This tutorial demonstrates the usage of the Camel Components for Google App Engine.
- Tutorial on Spring Remoting with JMS
This tutorial is focused on different techniques with Camel for Client-Server communication.
- Report Incident - This tutorial introduces Camel steadily and is based on a real life integration problem
This is a very long tutorial beginning from the start; its for entry level to Camel. Its based on a real life integration, showing how Camel can be introduced in an existing solution. We do this in baby steps. The tutorial is currently work in progress, so check it out from time to time. The tutorial explains some of the inner building blocks Camel uses under the covers. This is good knowledge to have when you start using Camel on a higher abstract level where it can do wonders in a few lines of routing DSL.
- Using Camel with ServiceMix a tutorial on using Camel inside Apache ServiceMix.
- Better JMS Transport for CXF Webservice using Apache Camel Describes how to use the Camel Transport for CXF to attach a CXF Webservice to a JMS Queue
- Tutorial how to use good old Axis 1.4 with Camel
This tutorial shows that Camel does work with the good old frameworks such as AXIS that is/was widely used for WebService.
- Tutorial on using Camel in a Web Application
This tutorial gives an overview of how to use Camel inside Tomcat, Jetty or any other servlet engine
- Tutorial on Camel 1.4 for Integration
Another real-life scenario. The company sells widgets, with a somewhat unique business process (their customers periodically report what they've purchased in order to get billed). However every customer uses a different data format and protocol. This tutorial goes through the process of integrating (and testing!) several customers and their electronic reporting of the widgets they've bought, along with the company's response.
- Tutorial how to build a Service Oriented Architecture using Camel with OSGI - Updated 20/11/2009
The tutorial has been designed in two parts. The first part introduces basic concept to create a simple SOA solution using Camel and OSGI and deploy it in a OSGI Server like Apache Felix Karaf and Spring DM Server while the second extends the ReportIncident tutorial part 4 to show How we can separate the different layers (domain, service, ...) of an application and deploy them in separate bundles. The Web Application has also be modified in order to communicate to the OSGI bundles.
- Examples
While not actual tutorials you might find working through the source of the various Examples useful
Tutorial on Spring Remoting with JMS
| Thanks This tutorial was kindly donated to Apache Camel by Martin Gilday. |
Preface
This tutorial aims to guide the reader through the stages of creating a project which uses Camel to facilitate the routing of messages from a JMS queue to a Spring service. The route works in a synchronous fashion returning a response to the client.
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses Maven to setup the Camel project and for dependencies for artifacts.
Distribution
This sample is distributed with the Camel distribution as examples/camel-example-spring-jms.
About
This tutorial is a simple example that demonstrates more the fact how well Camel is seamless integrated with Spring to leverage the best of both worlds. This sample is client server solution using JMS messaging as the transport. The sample has two flavors of servers and also for clients demonstrating different techniques for easy communication.
The Server is a JMS message broker that routes incoming messages to a business service that does computations on the received message and returns a response.
The EIP patterns used in this sample are:
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Channel | We need a channel so the Clients can communicate with the server. |
| Message | The information is exchanged using the Camel Message interface. |
| Message Translator | This is where Camel shines as the message exchange between the Server and the Clients are text based strings with numbers. However our business service uses int for numbers. So Camel can do the message translation automatically. |
| Message Endpoint | It should be easy to send messages to the Server from the the clients. This is archived with Camels powerful Endpoint pattern that even can be more powerful combined with Spring remoting. The tutorial have clients using each kind of technique for this. |
| Point to Point Channel | We using JMS queues so there are only one receive of the message exchange |
| Event Driven Consumer | Yes the JMS broker is of course event driven and only reacts when the client sends a message to the server. |
We use the following Camel components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| ActiveMQ | We use Apache ActiveMQ as the JMS broker on the Server side |
| Bean | We use the bean binding to easily route the messages to our business service. This is a very powerful component in Camel. |
| File | In the AOP enabled Server we store audit trails as files. |
| JMS | Used for the JMS messaging |
Create the Camel Project
For the purposes of the tutorial a single Maven project will be used for both the client and server. Ideally you would break your application down into the appropriate components. |
mvn archetype:create -DgroupId=org.example -DartifactId=CamelWithJmsAndSpring
Update the POM with Dependencies
First we need to have dependencies for the core Camel jars, its spring, jms components and finally ActiveMQ as the message broker.
<!-- required by both client and server --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-core</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-jms</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-spring</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId> <artifactId>activemq-camel</artifactId> </dependency>
As we use spring xml configuration for the ActiveMQ JMS broker we need this dependency:
<!-- xbean is required for ActiveMQ broker configuration in the spring xml file --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.xbean</groupId> <artifactId>xbean-spring</artifactId> </dependency>
And dependencies for the AOP enable server example. These dependencies are of course only needed if you need full blown AOP stuff using AspejctJ with bytecode instrumentation.
<!-- required jars for aspectj AOP support --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${spring-version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId> <version>1.6.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.6.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib-nodep</artifactId> <version>2.1_3</version> </dependency>
Writing the Server
Create the Spring Service
For this example the Spring service (= our business service) on the server will be a simple multiplier which trebles in the received value.
public interface Multiplier { /** * Multiplies the given number by a pre-defined constant. * * @param originalNumber The number to be multiplied * @return The result of the multiplication */ int multiply(int originalNumber); }
And the implementation of this service is:
@Service(value = "multiplier") public class Treble implements Multiplier { public int multiply(final int originalNumber) { return originalNumber * 3; } }
Notice that this class has been annotated with the @Service spring annotation. This ensures that this class is registered as a bean in the registry with the given name multiplier.
Define the Camel Routes
public class ServerRoutes extends RouteBuilder { @Override public void configure() throws Exception { // route from the numbers queue to our business that is a spring bean registered with the id=multiplier // Camel will introspect the multiplier bean and find the best candidate of the method to invoke. // You can add annotations etc to help Camel find the method to invoke. // As our multiplier bean only have one method its easy for Camel to find the method to use. from("jms:queue:numbers").to("multiplier"); // Camel has several ways to configure the same routing, we have defined some of them here below // as above but with the bean: prefix //from("jms:queue:numbers").to("bean:multiplier"); // beanRef is using explicity bean bindings to lookup the multiplier bean and invoke the multiply method //from("jms:queue:numbers").beanRef("multiplier", "multiply"); // the same as above but expressed as a URI configuration //from("activemq:queue:numbers").to("bean:multiplier?methodName=multiply"); } }
This defines a Camel route from the JMS queue named numbers to the Spring bean named multiplier. Camel will create a consumer to the JMS queue which forwards all received messages onto the the Spring bean, using the method named multiply.
Configure Spring
The Spring config file is placed under META-INF/spring as this is the default location used by the Camel Maven Plugin, which we will later use to run our server.
First we need to do the standard scheme declarations in the top. In the camel-server.xml we are using spring beans as the default bean: namespace and springs context:. For configuring ActiveMQ we use broker: and for Camel we of course have camel:. Notice that we don't use version numbers for the camel-spring schema. At runtime the schema is resolved in the Camel bundle. If we use a specific version number such as 1.4 then its IDE friendly as it would be able to import it and provide smart completion etc. See Xml Reference for further details.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:camel="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring" xmlns:broker="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core-5.3.0.xsd">
We use Spring annotations for doing IoC dependencies and its component-scan features comes to the rescue as it scans for spring annotations in the given package name:
<!-- let Spring do its IoC stuff in this package --> <context:component-scan base-package="org.apache.camel.example.server"/>
Camel will of course not be less than Spring in this regard so it supports a similar feature for scanning of Routes. This is configured as shown below.
Notice that we also have enabled the JMXAgent so we will be able to introspect the Camel Server with a JMX Console.
<!-- declare a camel context that scans for classes that is RouteBuilder
in the package org.apache.camel.example.server -->
<camel:camelContext id="camel">
<camel:package>org.apache.camel.example.server</camel:package>
<!-- enable JMX connector so we can connect to the server and browse mbeans -->
<!-- Camel will log at INFO level the service URI to use for connecting with jconsole -->
<camel:jmxAgent id="agent" createConnector="true"/>
</camel:camelContext>
The ActiveMQ JMS broker is also configured in this xml file. We set it up to listen on TCP port 61616.
<!-- lets configure the ActiveMQ JMS broker server to listen on TCP 61616 --> <broker:broker useJmx="false" persistent="false" brokerName="localhost"> <broker:transportConnectors> <broker:transportConnector name="tcp" uri="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </broker:transportConnectors> </broker:broker>
As this examples uses JMS then Camel needs a JMS component that is connected with the ActiveMQ broker. This is configured as shown below:
<!-- lets configure the Camel ActiveMQ to use the ActiveMQ broker declared above --> <bean id="jms" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </bean>
Notice: The JMS component is configured in standard Spring beans, but the gem is that the bean id can be referenced from Camel routes - meaning we can do routing using the JMS Component by just using jms: prefix in the route URI. What happens is that Camel will find in the Spring Registry for a bean with the id="jms". Since the bean id can have arbitrary name you could have named it id="jmsbroker" and then referenced to it in the routing as from="jmsbroker:queue:numbers).to("multiplier");
We use the vm protocol to connect to the ActiveMQ server as its embedded in this application.
| component-scan | Defines the package to be scanned for Spring stereotype annotations, in this case, to load the "multiplier" bean |
| camel-context | Defines the package to be scanned for Camel routes. Will find the ServerRoutes class and create the routes contained within it |
| jms bean | Creates the Camel JMS component |
AOP Enabled Server
The example has an enhanced Server example that uses fullblown AspejctJ AOP for doing a audit tracking of invocations of the business service.
We leverage Spring AOP support in the {{camel-server-aop.xml} configuration file. First we must declare the correct XML schema's to use:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:camel="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:broker="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core-5.3.0.xsd">
Then we include all the existing configuration from the normal server example:
<!-- let Spring do its IoC stuff in this package --> <context:component-scan base-package="org.apache.camel.example.server"/> <!-- lets configure the ActiveMQ JMS broker server to listen on TCP 61616 --> <broker:broker useJmx="false" persistent="false" brokerName="localhost"> <broker:transportConnectors> <broker:transportConnector name="tcp" uri="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </broker:transportConnectors> </broker:broker> <!-- lets configure the Camel JMS consumer to use the ActiveMQ broker declared above --> <bean id="jms" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsComponent"> <property name="connectionFactory"> <bean class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <!-- use the vm protocol as the JMS broker is running in the same jvm as Camel --> <property name="brokerURL" value="vm://localhost"/> </bean> </property> </bean>
Then we enable the AspejctJ AOP auto proxy feature of Spring that will scan for classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation:
<!-- turn on AspejctJ AOP to weave all @Aspects beans declared in this spring xml file --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
Then we define our Audit tracker bean that does the actual audit logging. It's also the class that is annotated with the @Aspect so Spring will pick this up, as the aspect.
<!-- Aspect that tracks all the invocations of the business service --> <bean id="AuditTracker" class="org.apache.camel.example.server.AuditTracker"> <!-- define what store to use for audit backup --> <property name="store" ref="AuditStore"/> </bean>
And the gem is that we inject the AuditTracker aspect bean with a Camel endpoint that defines where the audit should be stored. Noticed how easy it is to setup as we have just defined an endpoint URI that is file based, meaning that we stored the audit tracks as files. We can change this tore to any Camel components as we wish. To store it on a JMS queue simply change the URI to jms:queue:audit.
<!-- declare a camel context that scans for classes that is RouteBuilder
in the package org.apache.camel.example.server -->
<camel:camelContext id="camel">
<camel:package>org.apache.camel.example.server</camel:package>
<!-- enable JMX connector so we can connect to the server and browse mbeans -->
<!-- Camel will log at INFO level the service URI to use for connecting with jconsole -->
<camel:jmxAgent id="agent" createConnector="true"/>
<!-- the audit store endpoint is configued as file based.
In Camel 2.0 the endpoint should be defined in camel context -->
<camel:endpoint id="AuditStore" uri="file://target/store"/>
</camel:camelContext>
And the full blown Aspejct for the audit tracker java code:
/** * For audit tracking of all incoming invocations of our business (Multiplier) */ @Aspect public class AuditTracker { // endpoint we use for backup store of audit tracks private Endpoint store; @Required public void setStore(Endpoint store) { this.store = store; } @Before("execution(int org.apache.camel.example.server.Multiplier.multiply(int)) && args(originalNumber)") public void audit(int originalNumber) throws Exception { String msg = "Someone called us with this number " + originalNumber; System.out.println(msg); // now send the message to the backup store using the Camel Message Endpoint pattern Exchange exchange = store.createExchange(); exchange.getIn().setBody(msg); store.createProducer().process(exchange); } }
Run the Server
The Server is started using the org.apache.camel.spring.Main class that can start camel-spring application out-of-the-box. The Server can be started in several flavors:
- as a standard java main application - just start the org.apache.camel.spring.Main class
- using maven jave:exec
- using camel:run
In this sample as there are two servers (with and without AOP) we have prepared some profiles in maven to start the Server of your choice.
The server is started with:
mvn compile exec:java -PCamelServer
Or for the AOP enabled Server example:
mvn compile exec:java -PCamelServerAOP
Writing The Clients
This sample has three clients demonstrating different Camel techniques for communication
- CamelClient using the ProducerTemplate for Spring template style coding
- CamelRemoting using Spring Remoting
- CamelEndpoint using the Message Endpoint EIP pattern using a neutral Camel API
Client Using The ProducerTemplate
We will initially create a client by directly using ProducerTemplate. We will later create a client which uses Spring remoting to hide the fact that messaging is being used.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:camel="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd">
<camel:camelContext id="camel"> <camel:template id="camelTemplate"/> </camel:camelContext>
<!-- Camel JMSProducer to be able to send messages to a remote Active MQ server --> <bean id="jms" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </bean>
The client will not use the Camel Maven Plugin so the Spring XML has been placed in src/main/resources to not conflict with the server configs.
| camelContext | The Camel context is defined but does not contain any routes |
| template | The ProducerTemplate is used to place messages onto the JMS queue |
| jms bean | This initialises the Camel JMS component, allowing us to place messages onto the queue |
And the CamelClient source code:
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Notice this client requires that the CamelServer is already running!"); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("camel-client.xml"); // get the camel template for Spring template style sending of messages (= producer) ProducerTemplate camelTemplate = (ProducerTemplate) context.getBean("camelTemplate"); System.out.println("Invoking the multiply with 22"); // as opposed to the CamelClientRemoting example we need to define the service URI in this java code int response = (Integer)camelTemplate.sendBody("jms:queue:numbers", ExchangePattern.InOut, 22); System.out.println("... the result is: " + response); System.exit(0); }
The ProducerTemplate is retrieved from a Spring ApplicationContext and used to manually place a message on the "numbers" JMS queue. The exchange pattern (ExchangePattern.InOut) states that the call should be synchronous, and that we will receive a response.
Before running the client be sure that both the ActiveMQ broker and the CamelServer are running.
Client Using Spring Remoting
Spring Remoting "eases the development of remote-enabled services". It does this by allowing you to invoke remote services through your regular Java interface, masking that a remote service is being called.
<!-- Camel proxy for a given service, in this case the JMS queue
In Camel 2.0 , the proxy should be defined in camelContext. -->
<camel:proxy
id="multiplierProxy"
serviceInterface="org.apache.camel.example.server.Multiplier"
serviceUrl="jms:queue:numbers"/>
The snippet above only illustrates the different and how Camel easily can setup and use Spring Remoting in one line configurations.
The proxy will create a proxy service bean for you to use to make the remote invocations. The serviceInterface property details which Java interface is to be implemented by the proxy. serviceUrl defines where messages sent to this proxy bean will be directed. Here we define the JMS endpoint with the "numbers" queue we used when working with Camel template directly. The value of the id property is the name that will be the given to the bean when it is exposed through the Spring ApplicationContext. We will use this name to retrieve the service in our client. I have named the bean multiplierProxy simply to highlight that it is not the same multiplier bean as is being used by CamelServer. They are in completely independent contexts and have no knowledge of each other. As you are trying to mask the fact that remoting is being used in a real application you would generally not include proxy in the name.
And the Java client source code:
public static void main(final String[] args) { System.out.println("Notice this client requires that the CamelServer is already running!"); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("camel-client-remoting.xml"); // just get the proxy to the service and we as the client can use the "proxy" as it was // a local object we are invoking. Camel will under the covers do the remote communication // to the remote ActiveMQ server and fetch the response. Multiplier multiplier = (Multiplier)context.getBean("multiplierProxy"); System.out.println("Invoking the multiply with 33"); int response = multiplier.multiply(33); System.out.println("... the result is: " + response); System.exit(0); }
Again, the client is similar to the original client, but with some important differences.
- The Spring context is created with the new camel-client-remoting.xml
- We retrieve the proxy bean instead of a ProducerTemplate. In a non-trivial example you would have the bean injected as in the standard Spring manner.
- The multiply method is then called directly. In the client we are now working to an interface. There is no mention of Camel or JMS inside our Java code.
Client Using Message Endpoint EIP Pattern
This client uses the Message Endpoint EIP pattern to hide the complexity to communicate to the Server. The Client uses the same simple API to get hold of the endpoint, create an exchange that holds the message, set the payload and create a producer that does the send and receive. All done using the same neutral Camel API for all the components in Camel. So if the communication was socket TCP based you just get hold of a different endpoint and all the java code stays the same. That is really powerful.
Okay enough talk, show me the code!
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Notice this client requires that the CamelServer is already running!"); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("camel-client.xml"); CamelContext camel = (CamelContext) context.getBean("camel"); // get the endpoint from the camel context Endpoint endpoint = camel.getEndpoint("jms:queue:numbers"); // create the exchange used for the communication // we use the in out pattern for a synchronized exchange where we expect a response Exchange exchange = endpoint.createExchange(ExchangePattern.InOut); // set the input on the in body // must you correct type to match the expected type of an Integer object exchange.getIn().setBody(11); // to send the exchange we need an producer to do it for us Producer producer = endpoint.createProducer(); // start the producer so it can operate producer.start(); // let the producer process the exchange where it does all the work in this oneline of code System.out.println("Invoking the multiply with 11"); producer.process(exchange); // get the response from the out body and cast it to an integer int response = exchange.getOut().getBody(Integer.class); System.out.println("... the result is: " + response); // stop and exit the client producer.stop(); System.exit(0); }
Switching to a different component is just a matter of using the correct endpoint. So if we had defined a TCP endpoint as: "mina:tcp://localhost:61616" then its just a matter of getting hold of this endpoint instead of the JMS and all the rest of the java code is exactly the same.
Run the Clients
The Clients is started using their main class respectively.
- as a standard java main application - just start their main class
- using maven jave:exec
In this sample we start the clients using maven:
mvn compile exec:java -PCamelClient
mvn compile exec:java -PCamelClientRemoting
mvn compile exec:java -PCamelClientEndpoint
Also see the Maven pom.xml file how the profiles for the clients is defined.
Using the Camel Maven Plugin
The Camel Maven Plugin allows you to run your Camel routes directly from Maven. This negates the need to create a host application, as we did with Camel server, simply to start up the container. This can be very useful during development to get Camel routes running quickly.
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
All that is required is a new plugin definition in your Maven POM. As we have already placed our Camel config in the default location (camel-server.xml has been placed in META-INF/spring/) we do not need to tell the plugin where the route definitions are located. Simply run mvn camel:run.
Using Camel JMX
Camel has extensive support for JMX and allows us to inspect the Camel Server at runtime. As we have enabled the JMXAgent in our tutorial we can fire up the jconsole and connect to the following service URI: service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://localhost:1099/jmxrmi/camel. Notice that Camel will log at INFO level the JMX Connector URI:
...
DefaultInstrumentationAgent INFO JMX connector thread started on service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://claus-acer:1099/jmxrmi/camel
...
In the screenshot below we can see the route and its performance metrics:
See Also
Tutorial - camel-example-reportincident
Introduction
Creating this tutorial was inspired by a real life use-case I discussed over the phone with a colleague. He was working at a client whom uses a heavy-weight integration platform from a very large vendor. He was in talks with developer shops to implement a new integration on this platform. His trouble was the shop tripled the price when they realized the platform of choice. So I was wondering how we could do this integration with Camel. Can it be done, without tripling the cost ![]() .
.
This tutorial is written during the development of the integration. I have decided to start off with a sample that isn't Camel's but standard Java and then plugin Camel as we goes. Just as when people needed to learn Spring you could consume it piece by piece, the same goes with Camel.
The target reader is person whom hasn't experience or just started using Camel.
Motivation for this tutorial
I wrote this tutorial motivated as Camel lacked an example application that was based on the web application deployment model. The entire world hasn't moved to pure OSGi deployments yet.
The use-case
The goal is to allow staff to report incidents into a central administration. For that they use client software where they report the incident and submit it to the central administration. As this is an integration in a transition phase the administration should get these incidents by email whereas they are manually added to the database. The client software should gather the incident and submit the information to the integration platform that in term will transform the report into an email and send it to the central administrator for manual processing.
The figure below illustrates this process. The end users reports the incidents using the client applications. The incident is sent to the central integration platform as webservice. The integration platform will process the incident and send an OK acknowledgment back to the client. Then the integration will transform the message to an email and send it to the administration mail server. The users in the administration will receive the emails and take it from there.

In EIP patterns
We distill the use case as EIP patterns:

Parts
This tutorial is divided into sections and parts:
Section A: Existing Solution, how to slowly use Camel
Part 1 - This first part explain how to setup the project and get a webservice exposed using Apache CXF. In fact we don't touch Camel yet.
Part 2 - Now we are ready to introduce Camel piece by piece (without using Spring or any XML configuration file) and create the full feature integration. This part will introduce different Camel's concepts and How we can build our solution using them like :
- CamelContext
- Endpoint, Exchange & Producer
- Components : Log, File
Part 3 - Continued from part 2 where we implement that last part of the solution with the event driven consumer and how to send the email through the Mail component.
Section B: The Camel Solution
Part 4 - We now turn into the path of Camel where it excels - the routing.
Part 5 - Is about how embed Camel with Spring and using CXF endpoints directly in Camel
| Using Axis 2 See this blog entry by Sagara demonstrating how to use Apache Axis 2 instead of Apache CXF as the web service framework. |
Links
Part 1
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses the following frameworks:
- Maven 2.0.9
- Apache Camel 1.4.0
- Apache CXF 2.1.1
- Spring 2.5.5
Note: The sample project can be downloaded, see the resources section.
Initial Project Setup
We want the integration to be a standard .war application that can be deployed in any web container such as Tomcat, Jetty or even heavy weight application servers such as WebLogic or WebSphere. There fore we start off with the standard Maven webapp project that is created with the following long archetype command:
mvn archetype:create -DgroupId=org.apache.camel -DartifactId=camel-example-reportincident -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp
Notice that the groupId etc. doens't have to be org.apache.camel it can be com.mycompany.whatever. But I have used these package names as the example is an official part of the Camel distribution.
Then we have the basic maven folder layout. We start out with the webservice part where we want to use Apache CXF for the webservice stuff. So we add this to the pom.xml
<properties>
<cxf-version>2.1.1</cxf-version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-core</artifactId>
<version>${cxf-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws</artifactId>
<version>${cxf-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http</artifactId>
<version>${cxf-version}</version>
</dependency>
Developing the WebService
As we want to develop webservice with the contract first approach we create our .wsdl file. As this is a example we have simplified the model of the incident to only include 8 fields. In real life the model would be a bit more complex, but not to much.
We put the wsdl file in the folder src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/wsdl and name the file report_incident.wsdl.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <wsdl:definitions xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:http="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/http/" xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" targetNamespace="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"> <!-- Type definitions for input- and output parameters for webservice --> <wsdl:types> <xs:schema targetNamespace="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"> <xs:element name="inputReportIncident"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="incidentId"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="incidentDate"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="givenName"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="familyName"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="summary"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="details"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="email"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="phone"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> <xs:element name="outputReportIncident"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="code"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:schema> </wsdl:types> <!-- Message definitions for input and output --> <wsdl:message name="inputReportIncident"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:inputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:message name="outputReportIncident"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:outputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:message> <!-- Port (interface) definitions --> <wsdl:portType name="ReportIncidentEndpoint"> <wsdl:operation name="ReportIncident"> <wsdl:input message="tns:inputReportIncident"/> <wsdl:output message="tns:outputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:portType> <!-- Port bindings to transports and encoding - HTTP, document literal encoding is used --> <wsdl:binding name="ReportIncidentBinding" type="tns:ReportIncidentEndpoint"> <soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/> <wsdl:operation name="ReportIncident"> <soap:operation soapAction="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org/ReportIncident" style="document"/> <wsdl:input> <soap:body parts="parameters" use="literal"/> </wsdl:input> <wsdl:output> <soap:body parts="parameters" use="literal"/> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> <!-- Service definition --> <wsdl:service name="ReportIncidentService"> <wsdl:port name="ReportIncidentPort" binding="tns:ReportIncidentBinding"> <soap:address location="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> </wsdl:port> </wsdl:service> </wsdl:definitions>
CXF wsdl2java
Then we integration the CXF wsdl2java generator in the pom.xml so we have CXF generate the needed POJO classes for our webservice contract.
However at first we must configure maven to live in the modern world of Java 1.5 so we must add this to the pom.xml
<!-- to compile with 1.5 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.5</source> <target>1.5</target> </configuration> </plugin>
And then we can add the CXF wsdl2java code generator that will hook into the compile goal so its automatic run all the time:
<!-- CXF wsdl2java generator, will plugin to the compile goal --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId> <artifactId>cxf-codegen-plugin</artifactId> <version>${cxf-version}</version> <executions> <execution> <id>generate-sources</id> <phase>generate-sources</phase> <configuration> <sourceRoot>${basedir}/target/generated/src/main/java</sourceRoot> <wsdlOptions> <wsdlOption> <wsdl>${basedir}/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/wsdl/report_incident.wsdl</wsdl> </wsdlOption> </wsdlOptions> </configuration> <goals> <goal>wsdl2java</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>
You are now setup and should be able to compile the project. So running the mvn compile should run the CXF wsdl2java and generate the source code in the folder &{basedir}/target/generated/src/main/java that we specified in the pom.xml above. Since its in the target/generated/src/main/java maven will pick it up and include it in the build process.
Configuration of the web.xml
Next up is to configure the web.xml to be ready to use CXF so we can expose the webservice.
As Spring is the center of the universe, or at least is a very important framework in today's Java land we start with the listener that kick-starts Spring. This is the usual piece of code:
<!-- the listener that kick-starts Spring --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
And then we have the CXF part where we define the CXF servlet and its URI mappings to which we have chosen that all our webservices should be in the path /webservices/
<!-- CXF servlet --> <servlet> <servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- all our webservices are mapped under this URI pattern --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/webservices/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Then the last piece of the puzzle is to configure CXF, this is done in a spring XML that we link to fron the web.xml by the standard Spring contextConfigLocation property in the web.xml
<!-- location of spring xml files --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:cxf-config.xml</param-value> </context-param>
We have named our CXF configuration file cxf-config.xml and its located in the root of the classpath. In Maven land that is we can have the cxf-config.xml file in the src/main/resources folder. We could also have the file located in the WEB-INF folder for instance <param-value>/WEB-INF/cxf-config.xml</param-value>.
Getting rid of the old jsp world
The maven archetype that created the basic folder structure also created a sample .jsp file index.jsp. This file src/main/webapp/index.jsp should be deleted.
Configuration of CXF
The cxf-config.xml is as follows:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd"> <import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml"/> <import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-extension-soap.xml"/> <import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml"/> <!-- implementation of the webservice --> <bean id="reportIncidentEndpoint" class="org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentEndpointImpl"/> <!-- export the webservice using jaxws --> <jaxws:endpoint id="reportIncident" implementor="#reportIncidentEndpoint" address="/incident" wsdlLocation="/WEB-INF/wsdl/report_incident.wsdl" endpointName="s:ReportIncidentPort" serviceName="s:ReportIncidentService" xmlns:s="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> </beans>
The configuration is standard CXF and is documented at the Apache CXF website.
The 3 import elements is needed by CXF and they must be in the file.
Noticed that we have a spring bean reportIncidentEndpoint that is the implementation of the webservice endpoint we let CXF expose.
Its linked from the jaxws element with the implementator attribute as we use the # mark to identify its a reference to a spring bean. We could have stated the classname directly as implementor="org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentEndpoint" but then we lose the ability to let the ReportIncidentEndpoint be configured by spring.
The address attribute defines the relative part of the URL of the exposed webservice. wsdlLocation is an optional parameter but for persons like me that likes contract-first we want to expose our own .wsdl contracts and not the auto generated by the frameworks, so with this attribute we can link to the real .wsdl file. The last stuff is needed by CXF as you could have several services so it needs to know which this one is. Configuring these is quite easy as all the information is in the wsdl already.
Implementing the ReportIncidentEndpoint
Phew after all these meta files its time for some java code so we should code the implementor of the webservice. So we fire up mvn compile to let CXF generate the POJO classes for our webservice and we are ready to fire up a Java editor.
You can use mvn idea:idea or mvn eclipse:eclipse to create project files for these editors so you can load the project. However IDEA has been smarter lately and can load a pom.xml directly.
As we want to quickly see our webservice we implement just a quick and dirty as it can get. At first beware that since its jaxws and Java 1.5 we get annotations for the money, but they reside on the interface so we can remove them from our implementations so its a nice plain POJO again:
package org.apache.camel.example.reportincident; /** * The webservice we have implemented. */ public class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl implements ReportIncidentEndpoint { public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) { System.out.println("Hello ReportIncidentEndpointImpl is called from " + parameters.getGivenName()); OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident(); out.setCode("OK"); return out; } }
We just output the person that invokes this webservice and returns a OK response. This class should be in the maven source root folder src/main/java under the package name org.apache.camel.example.reportincident. Beware that the maven archetype tool didn't create the src/main/java folder, so you should create it manually.
To test if we are home free we run mvn clean compile.
Running our webservice
Now that the code compiles we would like to run it in a web container, so we add jetty to our pom.xml so we can run mvn jetty:run:
<properties> ... <jetty-version>6.1.1</jetty-version> </properties> <build> <plugins> ... <!-- so we can run mvn jetty:run --> <plugin> <groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId> <artifactId>maven-jetty-plugin</artifactId> <version>${jetty-version}</version> </plugin>
Notice: We use Jetty v6.1.1 as never versions has troubles on my laptop. Feel free to try a newer version on your system, but v6.1.1 works flawless.
So to see if everything is in order we fire up jetty with mvn jetty:run and if everything is okay you should be able to access http://localhost:8080.
Jetty is smart that it will list the correct URI on the page to our web application, so just click on the link. This is smart as you don't have to remember the exact web context URI for your application - just fire up the default page and Jetty will help you.
So where is the damn webservice then? Well as we did configure the web.xml to instruct the CXF servlet to accept the pattern /webservices/* we should hit this URL to get the attention of CXF: http://localhost:8080/camel-example-reportincident/webservices.

Hitting the webservice
Now we have the webservice running in a standard .war application in a standard web container such as Jetty we would like to invoke the webservice and see if we get our code executed. Unfortunately this isn't the easiest task in the world - its not so easy as a REST URL, so we need tools for this. So we fire up our trusty webservice tool SoapUI and let it be the one to fire the webservice request and see the response.
Using SoapUI we sent a request to our webservice and we got the expected OK response and the console outputs the System.out so we are ready to code.

Remote Debugging
Okay a little sidestep but wouldn't it be cool to be able to debug your code when its fired up under Jetty? As Jetty is started from maven, we need to instruct maven to use debug mode.
Se we set the MAVEN_OPTS environment to start in debug mode and listen on port 5005.
MAVEN_OPTS=-Xmx512m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
Then you need to restart Jetty so its stopped with ctrl + c. Remember to start a new shell to pickup the new environment settings. And start jetty again.
Then we can from our IDE attach a remote debugger and debug as we want.
First we configure IDEA to attach to a remote debugger on port 5005:

Then we set a breakpoint in our code ReportIncidentEndpoint and hit the SoapUI once again and we are breaked at the breakpoint where we can inspect the parameters:

Adding a unit test
Oh so much hard work just to hit a webservice, why can't we just use an unit test to invoke our webservice? Yes of course we can do this, and that's the next step.
First we create the folder structure src/test/java and src/test/resources. We then create the unit test in the src/test/java folder.
package org.apache.camel.example.reportincident; import junit.framework.TestCase; /** * Plain JUnit test of our webservice. */ public class ReportIncidentEndpointTest extends TestCase { }
Here we have a plain old JUnit class. As we want to test webservices we need to start and expose our webservice in the unit test before we can test it. And JAXWS has pretty decent methods to help us here, the code is simple as:
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
...
private static String ADDRESS = "http://localhost:9090/unittest";
protected void startServer() throws Exception {
// We need to start a server that exposes or webservice during the unit testing
// We use jaxws to do this pretty simple
ReportIncidentEndpointImpl server = new ReportIncidentEndpointImpl();
Endpoint.publish(ADDRESS, server);
}
The Endpoint class is the javax.xml.ws.Endpoint that under the covers looks for a provider and in our case its CXF - so its CXF that does the heavy lifting of exposing out webservice on the given URL address. Since our class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl implements the interface ReportIncidentEndpoint that is decorated with all the jaxws annotations it got all the information it need to expose the webservice. Below is the CXF wsdl2java generated interface:
/* * */ package org.apache.camel.example.reportincident; import javax.jws.WebMethod; import javax.jws.WebParam; import javax.jws.WebResult; import javax.jws.WebService; import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding; import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding.ParameterStyle; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSeeAlso; /** * This class was generated by Apache CXF 2.1.1 * Wed Jul 16 12:40:31 CEST 2008 * Generated source version: 2.1.1 * */ /* * */ @WebService(targetNamespace = "http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org", name = "ReportIncidentEndpoint") @XmlSeeAlso({ObjectFactory.class}) @SOAPBinding(parameterStyle = SOAPBinding.ParameterStyle.BARE) public interface ReportIncidentEndpoint { /* * */ @SOAPBinding(parameterStyle = SOAPBinding.ParameterStyle.BARE) @WebResult(name = "outputReportIncident", targetNamespace = "http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org", partName = "parameters") @WebMethod(operationName = "ReportIncident", action = "http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org/ReportIncident") public OutputReportIncident reportIncident( @WebParam(partName = "parameters", name = "inputReportIncident", targetNamespace = "http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org") InputReportIncident parameters ); }
Next up is to create a webservice client so we can invoke our webservice. For this we actually use the CXF framework directly as its a bit more easier to create a client using this framework than using the JAXWS style. We could have done the same for the server part, and you should do this if you need more power and access more advanced features.
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
...
protected ReportIncidentEndpoint createCXFClient() {
// we use CXF to create a client for us as its easier than JAXWS and works
JaxWsProxyFactoryBean factory = new JaxWsProxyFactoryBean();
factory.setServiceClass(ReportIncidentEndpoint.class);
factory.setAddress(ADDRESS);
return (ReportIncidentEndpoint) factory.create();
}
So now we are ready for creating a unit test. We have the server and the client. So we just create a plain simple unit test method as the usual junit style:
public void testRendportIncident() throws Exception {
startServer();
ReportIncidentEndpoint client = createCXFClient();
InputReportIncident input = new InputReportIncident();
input.setIncidentId("123");
input.setIncidentDate("2008-07-16");
input.setGivenName("Claus");
input.setFamilyName("Ibsen");
input.setSummary("bla bla");
input.setDetails("more bla bla");
input.setEmail("davsclaus@apache.org");
input.setPhone("+45 2962 7576");
OutputReportIncident out = client.reportIncident(input);
assertEquals("Response code is wrong", "OK", out.getCode());
}
Now we are nearly there. But if you run the unit test with mvn test then it will fail. Why!!! Well its because that CXF needs is missing some dependencies during unit testing. In fact it needs the web container, so we need to add this to our pom.xml.
<!-- cxf web container for unit testing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http-jetty</artifactId>
<version>${cxf-version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Well what is that, CXF also uses Jetty for unit test - well its just shows how agile, embedable and popular Jetty is.
So lets run our junit test with, and it reports:
mvn test Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0 [INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Yep thats it for now. We have a basic project setup.
End of part 1
Thanks for being patient and reading all this more or less standard Maven, Spring, JAXWS and Apache CXF stuff. Its stuff that is well covered on the net, but I wanted a full fledged tutorial on a maven project setup that is web service ready with Apache CXF. We will use this as a base for the next part where we demonstrate how Camel can be digested slowly and piece by piece just as it was back in the times when was introduced and was learning the Spring framework that we take for granted today.
Resources
- Apache CXF user guide
-
Name Size Creator (Last Modifier) Creation Date Last Mod Date Comment 
 tutorial_reportincident_part-one.zip
tutorial_reportincident_part-one.zip14 kB Claus Ibsen Jul 17, 2008 Jul 17, 2008
Links
Part 2
Adding Camel
In this part we will introduce Camel so we start by adding Camel to our pom.xml:
<properties>
...
<camel-version>1.4.0</camel-version>
</properties>
<!-- camel -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-core</artifactId>
<version>${camel-version}</version>
</dependency>
That's it, only one dependency for now.
| Synchronize IDE If you continue from part 1, remember to update your editor project settings since we have introduce new .jar files. For instance IDEA has a feature to synchronize with Maven projects. |
Now we turn towards our webservice endpoint implementation where we want to let Camel have a go at the input we receive. As Camel is very non invasive its basically a .jar file then we can just grap Camel but creating a new instance of DefaultCamelContext that is the hearth of Camel its context.
CamelContext camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
In fact we create a constructor in our webservice and add this code:
private CamelContext camel;
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception {
// create the camel context that is the "heart" of Camel
camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
// add the log component
camel.addComponent("log", new LogComponent());
// start Camel
camel.start();
}
Logging the "Hello World"
Here at first we want Camel to log the givenName and familyName parameters we receive, so we add the LogComponent with the key log. And we must start Camel before its ready to act.
| Component Documentation The Log and File components is documented as well, just click on the links. Just return to this documentation later when you must use these components for real. |
Then we change the code in the method that is invoked by Apache CXF when a webservice request arrives. We get the name and let Camel have a go at it in the new method we create sendToCamel:
public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) {
String name = parameters.getGivenName() + " " + parameters.getFamilyName();
// let Camel do something with the name
sendToCamelLog(name);
OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident();
out.setCode("OK");
return out;
}
Next is the Camel code. At first it looks like there are many code lines to do a simple task of logging the name - yes it is. But later you will in fact realize this is one of Camels true power. Its concise API. Hint: The same code can be used for any component in Camel.
private void sendToCamelLog(String name) {
try {
// get the log component
Component component = camel.getComponent("log");
// create an endpoint and configure it.
// Notice the URI parameters this is a common pratice in Camel to configure
// endpoints based on URI.
// com.mycompany.part2 = the log category used. Will log at INFO level as default
Endpoint endpoint = component.createEndpoint("log:com.mycompany.part2");
// create an Exchange that we want to send to the endpoint
Exchange exchange = endpoint.createExchange();
// set the in message payload (=body) with the name parameter
exchange.getIn().setBody(name);
// now we want to send the exchange to this endpoint and we then need a producer
// for this, so we create and start the producer.
Producer producer = endpoint.createProducer();
producer.start();
// process the exchange will send the exchange to the log component, that will process
// the exchange and yes log the payload
producer.process(exchange);
// stop the producer, we want to be nice and cleanup
producer.stop();
} catch (Exception e) {
// we ignore any exceptions and just rethrow as runtime
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
Okay there are code comments in the code block above that should explain what is happening. We run the code by invoking our unit test with maven mvn test, and we should get this log line:
INFO: Exchange[BodyType:String, Body:Claus Ibsen]
Write to file - easy with the same code style
Okay that isn't to impressive, Camel can log ![]() Well I promised that the above code style can be used for any component, so let's store the payload in a file. We do this by adding the file component to the Camel context
Well I promised that the above code style can be used for any component, so let's store the payload in a file. We do this by adding the file component to the Camel context
// add the file component
camel.addComponent("file", new FileComponent());
And then we let camel write the payload to the file after we have logged, by creating a new method sendToCamelFile. We want to store the payload in filename with the incident id so we need this parameter also:
// let Camel do something with the name
sendToCamelLog(name);
sendToCamelFile(parameters.getIncidentId(), name);
And then the code that is 99% identical. We have change the URI configuration when we create the endpoint as we pass in configuration parameters to the file component.
And then we need to set the output filename and this is done by adding a special header to the exchange. That's the only difference:
private void sendToCamelFile(String incidentId, String name) {
try {
// get the file component
Component component = camel.getComponent("file");
// create an endpoint and configure it.
// Notice the URI parameters this is a common pratice in Camel to configure
// endpoints based on URI.
// file://target instructs the base folder to output the files. We put in the target folder
// then its actumatically cleaned by mvn clean
Endpoint endpoint = component.createEndpoint("file://target");
// create an Exchange that we want to send to the endpoint
Exchange exchange = endpoint.createExchange();
// set the in message payload (=body) with the name parameter
exchange.getIn().setBody(name);
// now a special header is set to instruct the file component what the output filename
// should be
exchange.getIn().setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, "incident-" + incidentId + ".txt");
// now we want to send the exchange to this endpoint and we then need a producer
// for this, so we create and start the producer.
Producer producer = endpoint.createProducer();
producer.start();
// process the exchange will send the exchange to the file component, that will process
// the exchange and yes write the payload to the given filename
producer.process(exchange);
// stop the producer, we want to be nice and cleanup
producer.stop();
} catch (Exception e) {
// we ignore any exceptions and just rethrow as runtime
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
After running our unit test again with mvn test we have a output file in the target folder:
D:\demo\part-two>type target\incident-123.txt Claus Ibsen
Fully java based configuration of endpoints
In the file example above the configuration was URI based. What if you want 100% java setter based style, well this is of course also possible. We just need to cast to the component specific endpoint and then we have all the setters available:
// create the file endpoint, we cast to FileEndpoint because then we can do
// 100% java settter based configuration instead of the URI sting based
// must pass in an empty string, or part of the URI configuration if wanted
FileEndpoint endpoint = (FileEndpoint)component.createEndpoint("");
endpoint.setFile(new File("target/subfolder"));
endpoint.setAutoCreate(true);
That's it. Now we have used the setters to configure the FileEndpoint that it should store the file in the folder target/subfolder. Of course Camel now stores the file in the subfolder.
D:\demo\part-two>type target\subfolder\incident-123.txt Claus Ibsen
Lessons learned
Okay I wanted to demonstrate how you can be in 100% control of the configuration and usage of Camel based on plain Java code with no hidden magic or special XML or other configuration files. Just add the camel-core.jar and you are ready to go.
You must have noticed that the code for sending a message to a given endpoint is the same for both the log and file, in fact any Camel endpoint. You as the client shouldn't bother with component specific code such as file stuff for file components, jms stuff for JMS messaging etc. This is what the Message Endpoint EIP pattern is all about and Camel solves this very very nice - a key pattern in Camel.
Reducing code lines
Now that you have been introduced to Camel and one of its masterpiece patterns solved elegantly with the Message Endpoint its time to give productive and show a solution in fewer code lines, in fact we can get it down to 5, 4, 3, 2 .. yes only 1 line of code.
The key is the ProducerTemplate that is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer. Meaning that it has methods to send messages to any Camel endpoints. First of all we need to get hold of such a template and this is done from the CamelContext
private ProducerTemplate template;
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception {
...
// get the ProducerTemplate thst is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer for very
// easy sending exchanges to Camel.
template = camel.createProducerTemplate();
// start Camel
camel.start();
}
Now we can use template for sending payloads to any endpoint in Camel. So all the logging gabble can be reduced to:
template.sendBody("log:com.mycompany.part2.easy", name);
And the same goes for the file, but we must also send the header to instruct what the output filename should be:
String filename = "easy-incident-" + incidentId + ".txt";
template.sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder", name, FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, filename);
Reducing even more code lines
Well we got the Camel code down to 1-2 lines for sending the message to the component that does all the heavy work of wring the message to a file etc. But we still got 5 lines to initialize Camel.
camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
camel.addComponent("log", new LogComponent());
camel.addComponent("file", new FileComponent());
template = camel.createProducerTemplate();
camel.start();
This can also be reduced. All the standard components in Camel is auto discovered on-the-fly so we can remove these code lines and we are down to 3 lines.
| Component auto discovery When an endpoint is requested with a scheme that Camel hasn't seen before it will try to look for it in the classpath. It will do so by looking for special Camel component marker files that reside in the folder META-INF/services/org/apache/camel/component. If there are files in this folder it will read them as the filename is the scheme part of the URL. For instance the log component is defined in this file META-INF/services/org/apache/component/log and its content is: class=org.apache.camel.component.log.LogComponent The class property defines the component implementation. Tip: End-users can create their 3rd party components using the same technique and have them been auto discovered on-the-fly. |
Okay back to the 3 code lines:
camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
template = camel.createProducerTemplate();
camel.start();
Later will we see how we can reduce this to ... in fact 0 java code lines. But the 3 lines will do for now.
Message Translation
Okay lets head back to the over goal of the integration. Looking at the EIP diagrams at the introduction page we need to be able to translate the incoming webservice to an email. Doing so we need to create the email body. When doing the message translation we could put up our sleeves and do it manually in pure java with a StringBuilder such as:
private String createMailBody(InputReportIncident parameters) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Incident ").append(parameters.getIncidentId());
sb.append(" has been reported on the ").append(parameters.getIncidentDate());
sb.append(" by ").append(parameters.getGivenName());
sb.append(" ").append(parameters.getFamilyName());
// and the rest of the mail body with more appends to the string builder
return sb.toString();
}
But as always it is a hardcoded template for the mail body and the code gets kinda ugly if the mail message has to be a bit more advanced. But of course it just works out-of-the-box with just classes already in the JDK.
Lets use a template language instead such as Apache Velocity. As Camel have a component for Velocity integration we will use this component. Looking at the Component List overview we can see that camel-velocity component uses the artifactId camel-velocity so therefore we need to add this to the pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-velocity</artifactId>
<version>${camel-version}</version>
</dependency>
And now we have a Spring conflict as Apache CXF is dependent on Spring 2.0.8 and camel-velocity is dependent on Spring 2.5.5. To remedy this we could wrestle with the pom.xml with excludes settings in the dependencies or just bring in another dependency camel-spring:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-spring</artifactId>
<version>${camel-version}</version>
</dependency>
In fact camel-spring is such a vital part of Camel that you will end up using it in nearly all situations - we will look into how well Camel is seamless integration with Spring in part 3. For now its just another dependency.
We create the mail body with the Velocity template and create the file src/main/resources/MailBody.vm. The content in the MailBody.vm file is:
Incident $body.incidentId has been reported on the $body.incidentDate by $body.givenName $body.familyName. The person can be contact by: - email: $body.email - phone: $body.phone Summary: $body.summary Details: $body.details This is an auto generated email. You can not reply.
Letting Camel creating the mail body and storing it as a file is as easy as the following 3 code lines:
private void generateEmailBodyAndStoreAsFile(InputReportIncident parameters) {
// generate the mail body using velocity template
// notice that we just pass in our POJO (= InputReportIncident) that we
// got from Apache CXF to Velocity.
Object response = template.sendBody("velocity:MailBody.vm", parameters);
// Note: the response is a String and can be cast to String if needed
// store the mail in a file
String filename = "mail-incident-" + parameters.getIncidentId() + ".txt";
template.sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder", response, FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, filename);
}
What is impressive is that we can just pass in our POJO object we got from Apache CXF to Velocity and it will be able to generate the mail body with this object in its context. Thus we don't need to prepare anything before we let Velocity loose and generate our mail body. Notice that the template method returns a object with out response. This object contains the mail body as a String object. We can cast to String if needed.
If we run our unit test with mvn test we can in fact see that Camel has produced the file and we can type its content:
D:\demo\part-two>type target\subfolder\mail-incident-123.txt Incident 123 has been reported on the 2008-07-16 by Claus Ibsen. The person can be contact by: - email: davsclaus@apache.org - phone: +45 2962 7576 Summary: bla bla Details: more bla bla This is an auto generated email. You can not reply.
First part of the solution
What we have seen here is actually what it takes to build the first part of the integration flow. Receiving a request from a webservice, transform it to a mail body and store it to a file, and return an OK response to the webservice. All possible within 10 lines of code. So lets wrap it up here is what it takes:
/** * The webservice we have implemented. */ public class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl implements ReportIncidentEndpoint { private CamelContext camel; private ProducerTemplate template; public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception { // create the camel context that is the "heart" of Camel camel = new DefaultCamelContext(); // get the ProducerTemplate thst is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer for very // easy sending exchanges to Camel. template = camel.createProducerTemplate(); // start Camel camel.start(); } public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) { // transform the request into a mail body Object mailBody = template.sendBody("velocity:MailBody.vm", parameters); // store the mail body in a file String filename = "mail-incident-" + parameters.getIncidentId() + ".txt"; template.sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder", mailBody, FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, filename); // return an OK reply OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident(); out.setCode("OK"); return out; } }
Okay I missed by one, its in fact only 9 lines of java code and 2 fields.
End of part 2
I know this is a bit different introduction to Camel to how you can start using it in your projects just as a plain java .jar framework that isn't invasive at all. I took you through the coding parts that requires 6 - 10 lines to send a message to an endpoint, buts it's important to show the Message Endpoint EIP pattern in action and how its implemented in Camel. Yes of course Camel also has to one liners that you can use, and will use in your projects for sending messages to endpoints. This part has been about good old plain java, nothing fancy with Spring, XML files, auto discovery, OGSi or other new technologies. I wanted to demonstrate the basic building blocks in Camel and how its setup in pure god old fashioned Java. There are plenty of eye catcher examples with one liners that does more than you can imagine - we will come there in the later parts.
Okay part 3 is about building the last pieces of the solution and now it gets interesting since we have to wrestle with the event driven consumer.
Brew a cup of coffee, tug the kids and kiss the wife, for now we will have us some fun with the Camel. See you in part 3.
Resources
-
Name Size Creator (Last Modifier) Creation Date Last Mod Date Comment 
 part-two.zip
part-two.zip17 kB Claus Ibsen Jul 19, 2008 Jul 19, 2008
Links
Part 3
Recap
Lets just recap on the solution we have now:
public class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl implements ReportIncidentEndpoint { private CamelContext camel; private ProducerTemplate template; public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception { // create the camel context that is the "heart" of Camel camel = new DefaultCamelContext(); // get the ProducerTemplate thst is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer for very // easy sending exchanges to Camel. template = camel.createProducerTemplate(); // start Camel camel.start(); } /** * This is the last solution displayed that is the most simple */ public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) { // transform the request into a mail body Object mailBody = template.sendBody("velocity:MailBody.vm", parameters); // store the mail body in a file String filename = "mail-incident-" + parameters.getIncidentId() + ".txt"; template.sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder", mailBody, FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, filename); // return an OK reply OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident(); out.setCode("OK"); return out; } }
This completes the first part of the solution: receiving the message using webservice, transform it to a mail body and store it as a text file.
What is missing is the last part that polls the text files and send them as emails. Here is where some fun starts, as this requires usage of the Event Driven Consumer EIP pattern to react when new files arrives. So lets see how we can do this in Camel. There is a saying: Many roads lead to Rome, and that is also true for Camel - there are many ways to do it in Camel.
Adding the Event Driven Consumer
We want to add the consumer to our integration that listen for new files, we do this by creating a private method where the consumer code lives. We must register our consumer in Camel before its started so we need to add, and there fore we call the method addMailSenderConsumer in the constructor below:
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception {
// create the camel context that is the "heart" of Camel
camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
// get the ProducerTemplate thst is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer for very
// easy sending exchanges to Camel.
template = camel.createProducerTemplate();
// add the event driven consumer that will listen for mail files and process them
addMailSendConsumer();
// start Camel
camel.start();
}
The consumer needs to be consuming from an endpoint so we grab the endpoint from Camel we want to consume. It's file://target/subfolder. Don't be fooled this endpoint doesn't have to 100% identical to the producer, i.e. the endpoint we used in the previous part to create and store the files. We could change the URL to include some options, and to make it more clear that it's possible we setup a delay value to 10 seconds, and the first poll starts after 2 seconds. This is done by adding ?consumer.delay=10000&consumer.initialDelay=2000 to the URL.
| URL Configuration The URL configuration in Camel endpoints is just like regular URL we know from the Internet. You use ? and & to set the options. |
When we have the endpoint we can create the consumer (just as in part 1 where we created a producer}. Creating the consumer requires a Processor where we implement the java code what should happen when a message arrives. To get the mail body as a String object we can use the getBody method where we can provide the type we want in return.
| Camel Type Converter Why don't we just cast it as we always do in Java? Well the biggest advantage when you provide the type as a parameter you tell Camel what type you want and Camel can automatically convert it for you, using its flexible Type Converter mechanism. This is a great advantage, and you should try to use this instead of regular type casting. |
Sending the email is still left to be implemented, we will do this later. And finally we must remember to start the consumer otherwise its not active and won't listen for new files.
private void addMailSendConsumer() throws Exception {
// Grab the endpoint where we should consume. Option - the first poll starts after 2 seconds
Endpoint endpint = camel.getEndpoint("file://target/subfolder?consumer.initialDelay=2000");
// create the event driven consumer
// the Processor is the code what should happen when there is an event
// (think it as the onMessage method)
Consumer consumer = endpint.createConsumer(new Processor() {
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
// get the mail body as a String
String mailBody = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class);
// okay now we are read to send it as an email
System.out.println("Sending email..." + mailBody);
}
});
// star the consumer, it will listen for files
consumer.start();
}
Before we test it we need to be aware that our unit test is only catering for the first part of the solution, receiving the message with webservice, transforming it using Velocity and then storing it as a file - it doesn't test the Event Driven Consumer we just added. As we are eager to see it in action, we just do a common trick adding some sleep in our unit test, that gives our Event Driven Consumer time to react and print to System.out. We will later refine the test:
public void testRendportIncident() throws Exception {
...
OutputReportIncident out = client.reportIncident(input);
assertEquals("Response code is wrong", "OK", out.getCode());
// give the event driven consumer time to react
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
}
We run the test with mvn clean test and have eyes fixed on the console output.
During all the output in the console, we see that our consumer has been triggered, as we want.
2008-07-19 12:09:24,140 [mponent@1f12c4e] DEBUG FileProcessStrategySupport - Locking the file: target\subfolder\mail-incident-123.txt ... Sending email...Incident 123 has been reported on the 2008-07-16 by Claus Ibsen. The person can be contact by: - email: davsclaus@apache.org - phone: +45 2962 7576 Summary: bla bla Details: more bla bla This is an auto generated email. You can not reply. 2008-07-19 12:09:24,156 [mponent@1f12c4e] DEBUG FileConsumer - Done processing file: target\subfolder\mail-incident-123.txt. Status is: OK
Sending the email
Sending the email requires access to a SMTP mail server, but the implementation code is very simple:
private void sendEmail(String body) {
// send the email to your mail server
String url = "smtp://someone@localhost?password=secret&to=incident@mycompany.com";
template.sendBodyAndHeader(url, body, "subject", "New incident reported");
}
And just invoke the method from our consumer:
// okay now we are read to send it as an email
System.out.println("Sending email...");
sendEmail(mailBody);
System.out.println("Email sent");
Unit testing mail
For unit testing the consumer part we will use a mock mail framework, so we add this to our pom.xml:
<!-- unit testing mail using mock -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jvnet.mock-javamail</groupId>
<artifactId>mock-javamail</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Then we prepare our integration to run with or without the consumer enabled. We do this to separate the route into the two parts:
- receive the webservice, transform and save mail file and return OK as repose
- the consumer that listen for mail files and send them as emails
So we change the constructor code a bit:
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception {
init(true);
}
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl(boolean enableConsumer) throws Exception {
init(enableConsumer);
}
private void init(boolean enableConsumer) throws Exception {
// create the camel context that is the "heart" of Camel
camel = new DefaultCamelContext();
// get the ProducerTemplate thst is a Spring'ish xxxTemplate based producer for very
// easy sending exchanges to Camel.
template = camel.createProducerTemplate();
// add the event driven consumer that will listen for mail files and process them
if (enableConsumer) {
addMailSendConsumer();
}
// start Camel
camel.start();
}
Then remember to change the ReportIncidentEndpointTest to pass in false in the ReportIncidentEndpointImpl constructor.
And as always run mvn clean test to be sure that the latest code changes works.
Adding new unit test
We are now ready to add a new unit test that tests the consumer part so we create a new test class that has the following code structure:
/** * Plain JUnit test of our consumer. */ public class ReportIncidentConsumerTest extends TestCase { private ReportIncidentEndpointImpl endpoint; public void testConsumer() throws Exception { // we run this unit test with the consumer, hence the true parameter endpoint = new ReportIncidentEndpointImpl(true); } }
As we want to test the consumer that it can listen for files, read the file content and send it as an email to our mailbox we will test it by asserting that we receive 1 mail in our mailbox and that the mail is the one we expect. To do so we need to grab the mailbox with the mockmail API. This is done as simple as:
public void testConsumer() throws Exception {
// we run this unit test with the consumer, hence the true parameter
endpoint = new ReportIncidentEndpointImpl(true);
// get the mailbox
Mailbox box = Mailbox.get("incident@mycompany.com");
assertEquals("Should not have mails", 0, box.size());
How do we trigger the consumer? Well by creating a file in the folder it listen for. So we could use plain java.io.File API to create the file, but wait isn't there an smarter solution? ... yes Camel of course. Camel can do amazing stuff in one liner codes with its ProducerTemplate, so we need to get a hold of this baby. We expose this template in our ReportIncidentEndpointImpl but adding this getter:
protected ProducerTemplate getTemplate() {
return template;
}
Then we can use the template to create the file in one code line:
// drop a file in the folder that the consumer listen
// here is a trick to reuse Camel! so we get the producer template and just
// fire a message that will create the file for us
endpoint.getTemplate().sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder?append=false", "Hello World",
FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, "mail-incident-test.txt");
Then we just need to wait a little for the consumer to kick in and do its work and then we should assert that we got the new mail. Easy as just:
// let the consumer have time to run
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
// get the mock mailbox and check if we got mail ;)
assertEquals("Should have got 1 mail", 1, box.size());
assertEquals("Subject wrong", "New incident reported", box.get(0).getSubject());
assertEquals("Mail body wrong", "Hello World", box.get(0).getContent());
}
The final class for the unit test is:
/** * Plain JUnit test of our consumer. */ public class ReportIncidentConsumerTest extends TestCase { private ReportIncidentEndpointImpl endpoint; public void testConsumer() throws Exception { // we run this unit test with the consumer, hence the true parameter endpoint = new ReportIncidentEndpointImpl(true); // get the mailbox Mailbox box = Mailbox.get("incident@mycompany.com"); assertEquals("Should not have mails", 0, box.size()); // drop a file in the folder that the consumer listen // here is a trick to reuse Camel! so we get the producer template and just // fire a message that will create the file for us endpoint.getTemplate().sendBodyAndHeader("file://target/subfolder?append=false", "Hello World", FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, "mail-incident-test.txt"); // let the consumer have time to run Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); // get the mock mailbox and check if we got mail ;) assertEquals("Should have got 1 mail", 1, box.size()); assertEquals("Subject wrong", "New incident reported", box.get(0).getSubject()); assertEquals("Mail body wrong", "Hello World", box.get(0).getContent()); } }
End of part 3
Okay we have reached the end of part 3. For now we have only scratched the surface of what Camel is and what it can do. We have introduced Camel into our integration piece by piece and slowly added more and more along the way. And the most important is: you as the developer never lost control. We hit a sweet spot in the webservice implementation where we could write our java code. Adding Camel to the mix is just to use it as a regular java code, nothing magic. We were in control of the flow, we decided when it was time to translate the input to a mail body, we decided when the content should be written to a file. This is very important to not lose control, that the bigger and heavier frameworks tend to do. No names mentioned, but boy do developers from time to time dislike these elephants. And Camel is no elephant.
I suggest you download the samples from part 1 to 3 and try them out. It is great basic knowledge to have in mind when we look at some of the features where Camel really excel - the routing domain language.
From part 1 to 3 we touched concepts such as::
- Endpoint
- URI configuration
- Consumer
- Producer
- Event Driven Consumer
- Component
- CamelContext
- ProducerTemplate
- Processor
- Type Converter
Resources
-
Name Size Creator (Last Modifier) Creation Date Last Mod Date Comment 
 part-three.zip
part-three.zip18 kB Claus Ibsen Jul 20, 2008 Jul 20, 2008
Links
Part 4
Introduction
This section is about regular Camel. The examples presented here in this section is much more in common of all the examples we have in the Camel documentation.
If you have been reading the previous 3 parts then, this quote applies:
So we start all over again! |
Routing
Camel is particular strong as a light-weight and agile routing and mediation framework. In this part we will introduce the routing concept and how we can introduce this into our solution.
Looking back at the figure from the Introduction page we want to implement this routing. Camel has support for expressing this routing logic using Java as a DSL (Domain Specific Language). In fact Camel also has DSL for XML and Scala. In this part we use the Java DSL as its the most powerful and all developers know Java. Later we will introduce the XML version that is very well integrated with Spring.
Before we jump into it, we want to state that this tutorial is about Developers not loosing control. In my humble experience one of the key fears of developers is that they are forced into a tool/framework where they loose control and/or power, and the possible is now impossible. So in this part we stay clear with this vision and our starting point is as follows:
- We have generated the webservice source code using the CXF wsdl2java generator and we have our ReportIncidentEndpointImpl.java file where we as a Developer feels home and have the power.
So the starting point is:
/** * The webservice we have implemented. */ public class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl implements ReportIncidentEndpoint { /** * This is the last solution displayed that is the most simple */ public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) { // WE ARE HERE !!! return null; } }
Yes we have a simple plain Java class where we have the implementation of the webservice. The cursor is blinking at the WE ARE HERE block and this is where we feel home. More or less any Java Developers have implemented webservices using a stack such as: Apache AXIS, Apache CXF or some other quite popular framework. They all allow the developer to be in control and implement the code logic as plain Java code. Camel of course doesn't enforce this to be any different. Okay the boss told us to implement the solution from the figure in the Introduction page and we are now ready to code.
RouteBuilder
RouteBuilder is the hearth in Camel of the Java DSL routing. This class does all the heavy lifting of supporting EIP verbs for end-users to express the routing. It does take a little while to get settled and used to, but when you have worked with it for a while you will enjoy its power and realize it is in fact a little language inside Java itself. Camel is the only integration framework we are aware of that has Java DSL, all the others are usually only XML based.
As an end-user you usually use the RouteBuilder as of follows:
- create your own Route class that extends RouteBuilder
- implement your routing DSL in the configure method
So we create a new class ReportIncidentRoutes and implement the first part of the routing:
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder; public class ReportIncidentRoutes extends RouteBuilder { public void configure() throws Exception { // direct:start is a internal queue to kick-start the routing in our example // we use this as the starting point where you can send messages to direct:start from("direct:start") // to is the destination we send the message to our velocity endpoint // where we transform the mail body .to("velocity:MailBody.vm"); } }
What to notice here is the configure method. Here is where all the action is. Here we have the Java DSL langauge, that is expressed using the fluent builder syntax that is also known from Hibernate when you build the dynamic queries etc. What you do is that you can stack methods separating with the dot.
In the example above we have a very common routing, that can be distilled from pseudo verbs to actual code with:
- from A to B
- From Endpoint A To Endpoint B
- from("endpointA").to("endpointB")
- from("direct:start").to("velocity:MailBody.vm");
from("direct:start") is the consumer that is kick-starting our routing flow. It will wait for messages to arrive on the direct queue and then dispatch the message.
to("velocity:MailBody.vm") is the producer that will receive a message and let Velocity generate the mail body response.
So what we have implemented so far with our ReportIncidentRoutes RouteBuilder is this part of the picture:

Adding the RouteBuilder
Now we have our RouteBuilder we need to add/connect it to our CamelContext that is the hearth of Camel. So turning back to our webservice implementation class ReportIncidentEndpointImpl we add this constructor to the code, to create the CamelContext and add the routes from our route builder and finally to start it.
private CamelContext context;
public ReportIncidentEndpointImpl() throws Exception {
// create the context
context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// append the routes to the context
context.addRoutes(new ReportIncidentRoutes());
// at the end start the camel context
context.start();
}
Okay how do you use the routes then? Well its just as before we use a ProducerTemplate to send messages to Endpoints, so we just send to the direct:start endpoint and it will take it from there.
So we implement the logic in our webservice operation:
/**
* This is the last solution displayed that is the most simple
*/
public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) {
Object mailBody = context.createProducerTemplate().sendBody("direct:start", parameters);
System.out.println("Body:" + mailBody);
// return an OK reply
OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident();
out.setCode("OK");
return out;
}
Notice that we get the producer template using the createProducerTemplate method on the CamelContext. Then we send the input parameters to the direct:start endpoint and it will route it to the velocity endpoint that will generate the mail body. Since we use direct as the consumer endpoint (=from) and its a synchronous exchange we will get the response back from the route. And the response is of course the output from the velocity endpoint.
We have now completed this part of the picture:

Unit testing
Now is the time we would like to unit test what we got now. So we call for camel and its great test kit. For this to work we need to add it to the pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
<type>test-jar</type>
</dependency>
After adding it to the pom.xml you should refresh your Java Editor so it pickups the new jar. Then we are ready to create out unit test class.
We create this unit test skeleton, where we extend this class ContextTestSupport
package org.apache.camel.example.reportincident; import org.apache.camel.ContextTestSupport; import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder; /** * Unit test of our routes */ public class ReportIncidentRoutesTest extends ContextTestSupport { }
ContextTestSupport is a supporting unit test class for much easier unit testing with Apache Camel. The class is extending JUnit TestCase itself so you get all its glory. What we need to do now is to somehow tell this unit test class that it should use our route builder as this is the one we gonna test. So we do this by implementing the createRouteBuilder method.
@Override
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception {
return new ReportIncidentRoutes();
}
That is easy just return an instance of our route builder and this unit test will use our routes.
It is quite common in Camel itself to unit test using routes defined as an anonymous inner class, such as illustrated below:
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception {
return new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() throws Exception {
// TODO: Add your routes here, such as:
from("jms:queue:inbox").to("file://target/out");
}
};
}
The same technique is of course also possible for end-users of Camel to create parts of your routes and test them separately in many test classes. |
We then code our unit test method that sends a message to the route and assert that its transformed to the mail body using the Velocity template.
public void testTransformMailBody() throws Exception {
// create a dummy input with some input data
InputReportIncident parameters = createInput();
// send the message (using the sendBody method that takes a parameters as the input body)
// to "direct:start" that kick-starts the route
// the response is returned as the out object, and its also the body of the response
Object out = context.createProducerTemplate().sendBody("direct:start", parameters);
// convert the response to a string using camel converters. However we could also have casted it to
// a string directly but using the type converters ensure that Camel can convert it if it wasn't a string
// in the first place. The type converters in Camel is really powerful and you will later learn to
// appreciate them and wonder why its not build in Java out-of-the-box
String body = context.getTypeConverter().convertTo(String.class, out);
// do some simple assertions of the mail body
assertTrue(body.startsWith("Incident 123 has been reported on the 2008-07-16 by Claus Ibsen."));
}
/**
* Creates a dummy request to be used for input
*/
protected InputReportIncident createInput() {
InputReportIncident input = new InputReportIncident();
input.setIncidentId("123");
input.setIncidentDate("2008-07-16");
input.setGivenName("Claus");
input.setFamilyName("Ibsen");
input.setSummary("bla bla");
input.setDetails("more bla bla");
input.setEmail("davsclaus@apache.org");
input.setPhone("+45 2962 7576");
return input;
}
Adding the File Backup
The next piece of puzzle that is missing is to store the mail body as a backup file. So we turn back to our route and the EIP patterns. We use the Pipes and Filters pattern here to chain the routing as:
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
.to("velocity:MailBody.vm")
// using pipes-and-filters we send the output from the previous to the next
.to("file://target/subfolder");
}
Notice that we just add a 2nd .to on the newline. Camel will default use the Pipes and Filters pattern here when there are multi endpoints chained liked this. We could have used the pipeline verb to let out stand out that its the Pipes and Filters pattern such as:
from("direct:start")
// using pipes-and-filters we send the output from the previous to the next
.pipeline("velocity:MailBody.vm", "file://target/subfolder");
But most people are using the multi .to style instead.
We re-run out unit test and verifies that it still passes:
Running org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentRoutesTest Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0, Time elapsed: 1.157 sec
But hey we have added the file producer endpoint and thus a file should also be created as the backup file. If we look in the target/subfolder we can see that something happened.
On my humble laptop it created this folder: target\subfolder\ID-claus-acer. So the file producer create a sub folder named ID-claus-acer what is this? Well Camel auto generates an unique filename based on the unique message id if not given instructions to use a fixed filename. In fact it creates another sub folder and name the file as: target\subfolder\ID-claus-acer\3750-1219148558921\1-0 where 1-0 is the file with the mail body. What we want is to use our own filename instead of this auto generated filename. This is archived by adding a header to the message with the filename to use. So we need to add this to our route and compute the filename based on the message content.
Setting the filename
For starters we show the simple solution and build from there. We start by setting a constant filename, just to verify that we are on the right path, to instruct the file producer what filename to use. The file producer uses a special header FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME to set the filename.
What we do is to send the header when we "kick-start" the routing as the header will be propagated from the direct queue to the file producer. What we need to do is to use the ProducerTemplate.sendBodyAndHeader method that takes both a body and a header. So we change out webservice code to include the filename also:
public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) {
// create the producer template to use for sending messages
ProducerTemplate producer = context.createProducerTemplate();
// send the body and the filename defined with the special header key
Object mailBody = producer.sendBodyAndHeader("direct:start", parameters, FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, "incident.txt");
System.out.println("Body:" + mailBody);
// return an OK reply
OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident();
out.setCode("OK");
return out;
}
However we could also have used the route builder itself to configure the constant filename as shown below:
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
.to("velocity:MailBody.vm")
// set the filename to a constant before the file producer receives the message
.setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, constant("incident.txt"))
.to("file://target/subfolder");
}
But Camel can be smarter and we want to dynamic set the filename based on some of the input parameters, how can we do this?
Well the obvious solution is to compute and set the filename from the webservice implementation, but then the webservice implementation has such logic and we want this decoupled, so we could create our own POJO bean that has a method to compute the filename. We could then instruct the routing to invoke this method to get the computed filename. This is a string feature in Camel, its Bean binding. So lets show how this can be done:
Using Bean Language to compute the filename
First we create our plain java class that computes the filename, and it has 100% no dependencies to Camel what so ever.
/** * Plain java class to be used for filename generation based on the reported incident */ public class FilenameGenerator { public String generateFilename(InputReportIncident input) { // compute the filename return "incident-" + input.getIncidentId() + ".txt"; } }
The class is very simple and we could easily create unit tests for it to verify that it works as expected. So what we want now is to let Camel invoke this class and its generateFilename with the input parameters and use the output as the filename. Pheeeww is this really possible out-of-the-box in Camel? Yes it is. So lets get on with the show. We have the code that computes the filename, we just need to call it from our route using the Bean Language:
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
// set the filename using the bean language and call the FilenameGenerator class.
// the 2nd null parameter is optional methodname, to be used to avoid ambiguity.
// if not provided Camel will try to figure out the best method to invoke, as we
// only have one method this is very simple
.setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, BeanLanguage.bean(FilenameGenerator.class, null))
.to("velocity:MailBody.vm")
.to("file://target/subfolder");
}
Notice that we use the bean language where we supply the class with our bean to invoke. Camel will instantiate an instance of the class and invoke the suited method. For completeness and ease of code readability we add the method name as the 2nd parameter
.setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, BeanLanguage.bean(FilenameGenerator.class, "generateFilename"))
Then other developers can understand what the parameter is, instead of null.
Now we have a nice solution, but as a sidetrack I want to demonstrate the Camel has other languages out-of-the-box, and that scripting language is a first class citizen in Camel where it etc. can be used in content based routing. However we want it to be used for the filename generation.
Using a script language to set the filenameWe could do as in the previous parts where we send the computed filename as a message header when we "kick-start" the route. But we want to learn new stuff so we look for a different solution using some of Camels many Languages. As OGNL is a favorite language of mine (used by WebWork) so we pick this baby for a Camel ride. For starters we must add it to our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-ognl</artifactId>
<version>${camel-version}</version>
</dependency>
And remember to refresh your editor so you got the new .jars. In OGNL glory this is done as:
"'mail-incident-' + request.body.incidentId + '.txt'"
where request.body.incidentId computes to:
Now we got the expression to dynamic compute the filename on the fly we need to set it on our route so we turn back to our route, where we can add the OGNL expression:
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
// we need to set the filename and uses OGNL for this
.setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, OgnlExpression.ognl("'mail-incident-' + request.body.incidentId + '.txt'"))
// using pipes-and-filters we send the output from the previous to the next
.pipeline("velocity:MailBody.vm", "file://target/subfolder");
}
And since we are on Java 1.5 we can use the static import of ognl so we have: import static org.apache.camel.language.ognl.OgnlExpression.ognl; ... .setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, ognl("'mail-incident-' + request.body.incidentId + '.txt'")) Notice the import static also applies for all the other languages, such as the Bean Language we used previously. |
Whatever worked for you we have now implemented the backup of the data files:

Sending the email
What we need to do before the solution is completed is to actually send the email with the mail body we generated and stored as a file. In the previous part we did this with a File consumer, that we manually added to the CamelContext. We can do this quite easily with the routing.
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder; public class ReportIncidentRoutes extends RouteBuilder { public void configure() throws Exception { // first part from the webservice -> file backup from("direct:start") .setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, bean(FilenameGenerator.class, "generateFilename")) .to("velocity:MailBody.vm") .to("file://target/subfolder"); // second part from the file backup -> send email from("file://target/subfolder") // set the subject of the email .setHeader("subject", constant("new incident reported")) // send the email .to("smtp://someone@localhost?password=secret&to=incident@mycompany.com"); } }
The last 3 lines of code does all this. It adds a file consumer from("file://target/subfolder"), sets the mail subject, and finally send it as an email.
The DSL is really powerful where you can express your routing integration logic.
So we completed the last piece in the picture puzzle with just 3 lines of code.
We have now completed the integration:

Conclusion
We have just briefly touched the routing in Camel and shown how to implement them using the fluent builder syntax in Java. There is much more to the routing in Camel than shown here, but we are learning step by step. We continue in part 5. See you there.
Resources
-
Name Size Creator (Last Modifier) Creation Date Last Mod Date Comment 
 part-four.zip
part-four.zip11 kB Claus Ibsen Aug 25, 2008 Aug 25, 2008
Links
Better JMS Transport for CXF Webservice using Apache Camel
Configuring JMS in Apache CXF before Version 2.1.3 is possible but not really easy or nice. This article shows how to use Apache Camel to provide a better JMS Transport for CXF.
Update: Since CXF 2.1.3 there is a new way of configuring JMS (Using the JMSConfigFeature). It makes JMS config for CXF as easy as with Camel. Using Camel for JMS is still a good idea if you want to use the rich feature of Camel for routing and other Integration Scenarios that CXF does not support.
So how to connect Apache Camel and CXF
The best way to connect Camel and CXF is using the Camel transport for CXF. This is a camel module that registers with cxf as a new transport. It is quite easy to configure.
<bean class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.transport.CamelTransportFactory"> <property name="bus" ref="cxf" /> <property name="camelContext" ref="camelContext" /> <property name="transportIds"> <list> <value>http://cxf.apache.org/transports/camel</value> </list> </property> </bean>
This bean registers with CXF and provides a new transport prefix camel:// that can be used in CXF address configurations. The bean references a bean cxf which will be already present in your config. The other refrenceis a camel context. We will later define this bean to provide the routing config.
How is JMS configured in Camel
In camel you need two things to configure JMS. A ConnectionFactory and a JMSComponent. As ConnectionFactory you can simply set up the normal Factory your JMS provider offers or bind a JNDI ConnectionFactory. In this example we use the ConnectionFactory provided by ActiveMQ.
<bean id="jmsConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616" /> </bean>
Then we set up the JMSComponent. It offers a new transport prefix to camel that we simply call jms. If we need several JMSComponents we can differentiate them by their name.
<bean id="jms" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsComponent"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory" /> <property name="useMessageIDAsCorrelationID" value="true" /> </bean>
You can find more details about the JMSComponent at the Camel Wiki. For example you find the complete configuration options and a JNDI sample there.
Setting up the CXF client
We will configure a simple CXF webservice client. It will use stub code generated from a wsdl. The webservice client will be configured to use JMS directly. You can also use a direct: Endpoint and do the routing to JMS in the Camel Context.
<client id="CustomerService" xmlns="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xmlns:customer="http://customerservice.example.com/" serviceName="customer:CustomerServiceService" endpointName="customer:CustomerServiceEndpoint" address="camel:jms:queue:CustomerService" serviceClass="com.example.customerservice.CustomerService"> </client>
We explicitly configure serviceName and endpointName so they are not read from the wsdl. The names we use are arbitrary and have no further function but we set them to look nice. The serviceclass points to the service interface that was generated from the wsdl. Now the important thing is address. Here we tell cxf to use the camel transport, use the JmsComponent who registered the prefix "jms" and use the queue "CustomerService".
Setting up the CamelContext
As we do not need additional routing an empty CamelContext bean will suffice.
<camelContext id="camelContext" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> </camelContext>
Running the Example
- Follow the readme.txt
Conclusion
As you have seen in this example you can use Camel to connect services to JMS easily while being able to also use the rich integration features of Apache Camel.
Tutorial using Axis 1.4 with Apache Camel
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses Maven 2 to setup the Camel project and for dependencies for artifacts.
Distribution
This sample is distributed with the Camel 1.5 distribution as examples/camel-example-axis.
Introduction
Apache Axis is/was widely used as a webservice framework. So in line with some of the other tutorials to demonstrate how Camel is not an invasive framework but is flexible and integrates well with existing solution.
We have an existing solution that exposes a webservice using Axis 1.4 deployed as web applications. This is a common solution. We use contract first so we have Axis generated source code from an existing wsdl file. Then we show how we introduce Spring and Camel to integrate with Axis.
This tutorial uses the following frameworks:
- Maven 2.0.9
- Apache Camel 1.5.0
- Apache Axis 1.4
- Spring 2.5.5
Setting up the project to run Axis
This first part is about getting the project up to speed with Axis. We are not touching Camel or Spring at this time.
Maven 2
Axis dependencies is available for maven 2 so we configure our pom.xml as:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.axis</groupId>
<artifactId>axis</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.axis</groupId>
<artifactId>axis-jaxrpc</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.axis</groupId>
<artifactId>axis-saaj</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>axis</groupId>
<artifactId>axis-wsdl4j</artifactId>
<version>1.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-discovery</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-discovery</artifactId>
<version>0.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.14</version>
</dependency>
Then we need to configure maven to use Java 1.5 and the Axis maven plugin that generates the source code based on the wsdl file:
<!-- to compile with 1.5 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.5</source> <target>1.5</target> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId> <artifactId>axistools-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <sourceDirectory>src/main/resources/</sourceDirectory> <packageSpace>com.mycompany.myschema</packageSpace> <testCases>false</testCases> <serverSide>true</serverSide> <subPackageByFileName>false</subPackageByFileName> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>wsdl2java</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>
wsdl
We use the same .wsdl file as the Tutorial-Example-ReportIncident and copy it to src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/wsdl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <wsdl:definitions xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:http="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/http/" xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" targetNamespace="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"> <!-- Type definitions for input- and output parameters for webservice --> <wsdl:types> <xs:schema targetNamespace="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"> <xs:element name="inputReportIncident"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="incidentId"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="incidentDate"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="givenName"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="familyName"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="summary"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="details"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="email"/> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="phone"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> <xs:element name="outputReportIncident"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element type="xs:string" name="code"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:schema> </wsdl:types> <!-- Message definitions for input and output --> <wsdl:message name="inputReportIncident"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:inputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:message name="outputReportIncident"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="tns:outputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:message> <!-- Port (interface) definitions --> <wsdl:portType name="ReportIncidentEndpoint"> <wsdl:operation name="ReportIncident"> <wsdl:input message="tns:inputReportIncident"/> <wsdl:output message="tns:outputReportIncident"/> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:portType> <!-- Port bindings to transports and encoding - HTTP, document literal encoding is used --> <wsdl:binding name="ReportIncidentBinding" type="tns:ReportIncidentEndpoint"> <soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/> <wsdl:operation name="ReportIncident"> <soap:operation soapAction="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org/ReportIncident" style="document"/> <wsdl:input> <soap:body parts="parameters" use="literal"/> </wsdl:input> <wsdl:output> <soap:body parts="parameters" use="literal"/> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> <!-- Service definition --> <wsdl:service name="ReportIncidentService"> <wsdl:port name="ReportIncidentPort" binding="tns:ReportIncidentBinding"> <soap:address location="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> </wsdl:port> </wsdl:service> </wsdl:definitions>
Configuring Axis
Okay we are now setup for the contract first development and can generate the source file. For now we are still only using standard Axis and not Spring nor Camel. We still need to setup Axis as a web application so we configure the web.xml in src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml as:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>axis</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.axis.transport.http.AxisServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>axis</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/services/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
The web.xml just registers Axis servlet that is handling the incoming web requests to its servlet mapping. We still need to configure Axis itself and this is done using its special configuration file server-config.wsdd. We nearly get this file for free if we let Axis generate the source code so we run the maven goal:
mvn axistools:wsdl2java
The tool will generate the source code based on the wsdl and save the files to the following folder:
.\target\generated-sources\axistools\wsdl2java\org\apache\camel\example\reportincident deploy.wsdd InputReportIncident.java OutputReportIncident.java ReportIncidentBindingImpl.java ReportIncidentBindingStub.java ReportIncidentService_PortType.java ReportIncidentService_Service.java ReportIncidentService_ServiceLocator.java undeploy.wsdd
This is standard Axis and so far no Camel or Spring has been touched. To implement our webservice we will add our code, so we create a new class AxisReportIncidentService that implements the port type interface where we can implement our code logic what happens when the webservice is invoked.
package org.apache.camel.example.axis; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.InputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.OutputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentService_PortType; import java.rmi.RemoteException; /** * Axis webservice */ public class AxisReportIncidentService implements ReportIncidentService_PortType { public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) throws RemoteException { System.out.println("Hello AxisReportIncidentService is called from " + parameters.getGivenName()); OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident(); out.setCode("OK"); return out; } }
Now we need to configure Axis itself and this is done using its server-config.wsdd file. We nearly get this for for free from the auto generated code, we copy the stuff from deploy.wsdd and made a few modifications:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <deployment xmlns="http://xml.apache.org/axis/wsdd/" xmlns:java="http://xml.apache.org/axis/wsdd/providers/java"> <!-- global configuration --> <globalConfiguration> <parameter name="sendXsiTypes" value="true"/> <parameter name="sendMultiRefs" value="true"/> <parameter name="sendXMLDeclaration" value="true"/> <parameter name="axis.sendMinimizedElements" value="true"/> </globalConfiguration> <handler name="URLMapper" type="java:org.apache.axis.handlers.http.URLMapper"/> <!-- this service is from deploy.wsdd --> <service name="ReportIncidentPort" provider="java:RPC" style="document" use="literal"> <parameter name="wsdlTargetNamespace" value="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> <parameter name="wsdlServiceElement" value="ReportIncidentService"/> <parameter name="schemaUnqualified" value="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> <parameter name="wsdlServicePort" value="ReportIncidentPort"/> <parameter name="className" value="org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentBindingImpl"/> <parameter name="wsdlPortType" value="ReportIncidentService"/> <parameter name="typeMappingVersion" value="1.2"/> <operation name="reportIncident" qname="ReportIncident" returnQName="retNS:outputReportIncident" xmlns:retNS="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" returnType="rtns:>outputReportIncident" xmlns:rtns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" soapAction="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org/ReportIncident" > <parameter qname="pns:inputReportIncident" xmlns:pns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" type="tns:>inputReportIncident" xmlns:tns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/> </operation> <parameter name="allowedMethods" value="reportIncident"/> <typeMapping xmlns:ns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" qname="ns:>outputReportIncident" type="java:org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.OutputReportIncident" serializer="org.apache.axis.encoding.ser.BeanSerializerFactory" deserializer="org.apache.axis.encoding.ser.BeanDeserializerFactory" encodingStyle="" /> <typeMapping xmlns:ns="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org" qname="ns:>inputReportIncident" type="java:org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.InputReportIncident" serializer="org.apache.axis.encoding.ser.BeanSerializerFactory" deserializer="org.apache.axis.encoding.ser.BeanDeserializerFactory" encodingStyle="" /> </service> <!-- part of Axis configuration --> <transport name="http"> <requestFlow> <handler type="URLMapper"/> <handler type="java:org.apache.axis.handlers.http.HTTPAuthHandler"/> </requestFlow> </transport> </deployment>
The globalConfiguration and transport is not in the deploy.wsdd file so you gotta write that yourself. The service is a 100% copy from deploy.wsdd. Axis has more configuration to it than shown here, but then you should check the Axis documentation.
What we need to do now is important, as we need to modify the above configuration to use our webservice class than the default one, so we change the classname parameter to our class AxisReportIncidentService:
<parameter name="className" value="org.apache.camel.example.axis.AxisReportIncidentService"/>
Running the Example
Now we are ready to run our example for the first time, so we use Jetty as the quick web container using its maven command:
mvn jetty:run
Then we can hit the web browser and enter this URL: http://localhost:8080/camel-example-axis/services and you should see the famous Axis start page with the text And now... Some Services.
Clicking on the .wsdl link shows the wsdl file, but what. It's an auto generated one and not our original .wsdl file. So we need to fix this ASAP and this is done by configuring Axis in the server-config.wsdd file:
<service name="ReportIncidentPort" provider="java:RPC" style="document" use="literal"> <wsdlFile>/WEB-INF/wsdl/report_incident.wsdl</wsdlFile> ...
We do this by adding the wsdlFile tag in the service element where we can point to the real .wsdl file.
Integrating Spring
First we need to add its dependencies to the pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
</dependency>
Spring is integrated just as it would like to, we add its listener to the web.xml and a context parameter to be able to configure precisely what spring xml files to use:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
classpath:axis-example-context.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
Next is to add a plain spring XML file named axis-example-context.xml in the src/main/resources folder.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> </beans>
The spring XML file is currently empty. We hit jetty again with mvn jetty:run just to make sure Spring was setup correctly.
Using Spring
We would like to be able to get hold of the Spring ApplicationContext from our webservice so we can get access to the glory spring, but how do we do this? And our webservice class AxisReportIncidentService is created and managed by Axis we want to let Spring do this. So we have two problems.
We solve these problems by creating a delegate class that Axis creates, and this delegate class gets hold on Spring and then gets our real webservice as a spring bean and invoke the service.
First we create a new class that is 100% independent from Axis and just a plain POJO. This is our real service.
package org.apache.camel.example.axis; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.InputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.OutputReportIncident; /** * Our real service that is not tied to Axis */ public class ReportIncidentService { public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) { System.out.println("Hello ReportIncidentService is called from " + parameters.getGivenName()); OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident(); out.setCode("OK"); return out; } }
So now we need to get from AxisReportIncidentService to this one ReportIncidentService using Spring. Well first of all we add our real service to spring XML configuration file so Spring can handle its lifecycle:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="incidentservice" class="org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentService"/> </beans>
And then we need to modify AxisReportIncidentService to use Spring to lookup the spring bean id="incidentservice" and delegate the call. We do this by extending the spring class org.springframework.remoting.jaxrpc.ServletEndpointSupport so the refactored code is:
package org.apache.camel.example.axis; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.InputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.OutputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentService_PortType; import org.springframework.remoting.jaxrpc.ServletEndpointSupport; import java.rmi.RemoteException; /** * Axis webservice */ public class AxisReportIncidentService extends ServletEndpointSupport implements ReportIncidentService_PortType { public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) throws RemoteException { // get hold of the spring bean from the application context ReportIncidentService service = (ReportIncidentService) getApplicationContext().getBean("incidentservice"); // delegate to the real service return service.reportIncident(parameters); } }
To see if everything is okay we run mvn jetty:run.
In the code above we get hold of our service at each request by looking up in the application context. However Spring also supports an init method where we can do this once. So we change the code to:
public class AxisReportIncidentService extends ServletEndpointSupport implements ReportIncidentService_PortType { private ReportIncidentService service; @Override protected void onInit() throws ServiceException { // get hold of the spring bean from the application context service = (ReportIncidentService) getApplicationContext().getBean("incidentservice"); } public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) throws RemoteException { // delegate to the real service return service.reportIncident(parameters); } }
So now we have integrated Axis with Spring and we are ready for Camel.
Integrating Camel
Again the first step is to add the dependencies to the maven pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
</dependency>
Now that we have integrated with Spring then we easily integrate with Camel as Camel works well with Spring.
| Camel does not require Spring Camel does not require Spring, we could easily have used Camel without Spring, but most users prefer to use Spring also. |
We choose to integrate Camel in the Spring XML file so we add the camel namespace and the schema location:
xmlns:camel="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring" http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"
CamelContext
CamelContext is the heart of Camel its where all the routes, endpoints, components, etc. is registered. So we setup a CamelContext and the spring XML files looks like:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:camel="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <bean id="incidentservice" class="org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentService"/> <camel:camelContext id="camel"> <!-- TODO: Here we can add Camel stuff --> </camel:camelContext> </beans>
Store a file backup
We want to store the web service request as a file before we return a response. To do this we want to send the file content as a message to an endpoint that produces the file. So we need to do two steps:
- configure the file backup endpoint
- send the message to the endpoint
The endpoint is configured in spring XML so we just add it as:
<camel:camelContext id="camelContext">
<!-- endpoint named backup that is configued as a file component -->
<camel:endpoint id="backup" uri="file://target?append=false"/>
</camel:camelContext>
In the CamelContext we have defined our endpoint with the id backup and configured it use the URL notation that we know from the internet. Its a file scheme that accepts a context and some options. The contest is target and its the folder to store the file. The option is just as the internet with ? and & for subsequent options. We configure it to not append, meaning than any existing file will be overwritten. See the File component for options and how to use the camel file endpoint.
Next up is to be able to send a message to this endpoint. The easiest way is to use a ProducerTemplate. A ProducerTemplate is inspired by Spring template pattern with for instance JmsTemplate or JdbcTemplate in mind. The template that all the grunt work and exposes a simple interface to the end-user where he/she can set the payload to send. Then the template will do proper resource handling and all related issues in that regard. But how do we get hold of such a template? Well the CamelContext is able to provide one. This is done by configuring the template on the camel context in the spring XML as:
<camel:camelContext id="camelContext">
<!-- producer template exposed with this id -->
<camel:template id="camelTemplate"/>
<!-- endpoint named backup that is configued as a file component -->
<camel:endpoint id="backup" uri="file://target?append=false"/>
</camel:camelContext>
Then we can expose a ProducerTemplate property on our service with a setter in the Java code as:
public class ReportIncidentService { private ProducerTemplate template; public void setTemplate(ProducerTemplate template) { this.template = template; }
And then let Spring handle the dependency inject as below:
<bean id="incidentservice" class="org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentService">
<!-- set the producer template to use from the camel context below -->
<property name="template" ref="camelTemplate"/>
</bean>
Now we are ready to use the producer template in our service to send the payload to the endpoint. The template has many sendXXX methods for this purpose. But before we send the payload to the file endpoint we must also specify what filename to store the file as. This is done by sending meta data with the payload. In Camel metadata is sent as headers. Headers is just a plain Map<String, Object>. So if we needed to send several metadata then we could construct an ordinary HashMap and put the values in there. But as we just need to send one header with the filename Camel has a convenient send method sendBodyAndHeader so we choose this one.
public OutputReportIncident reportIncident(InputReportIncident parameters) {
System.out.println("Hello ReportIncidentService is called from " + parameters.getGivenName());
String data = parameters.getDetails();
// store the data as a file
String filename = parameters.getIncidentId() + ".txt";
// send the data to the endpoint and the header contains what filename it should be stored as
template.sendBodyAndHeader("backup", data, "org.apache.camel.file.name", filename);
OutputReportIncident out = new OutputReportIncident();
out.setCode("OK");
return out;
}
The template in the code above uses 4 parameters:
- the endpoint name, in this case the id referring to the endpoint defined in Spring XML in the camelContext element.
- the payload, can be any kind of object
- the key for the header, in this case a Camel keyword to set the filename
- and the value for the header
Running the example
We start our integration with maven using mvn jetty:run. Then we open a browser and hit http://localhost:8080. Jetty is so smart that it display a frontpage with links to the deployed application so just hit the link and you get our application. Now we hit append /services to the URL to access the Axis frontpage. The URL should be http://localhost:8080/camel-example-axis/services.
You can then test it using a web service test tools such as SoapUI.
Hitting the service will output to the console
2008-09-06 15:01:41.718::INFO: Started SelectChannelConnector @ 0.0.0.0:8080 [INFO] Started Jetty Server Hello ReportIncidentService is called from Ibsen
And there should be a file in the target subfolder.
dir target /b 123.txt
Unit Testing
We would like to be able to unit test our ReportIncidentService class. So we add junit to the maven dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
And then we create a plain junit testcase for our service class.
package org.apache.camel.example.axis; import junit.framework.TestCase; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.InputReportIncident; import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.OutputReportIncident; /** * Unit test of service */ public class ReportIncidentServiceTest extends TestCase { public void testIncident() { ReportIncidentService service = new ReportIncidentService(); InputReportIncident input = createDummyIncident(); OutputReportIncident output = service.reportIncident(input); assertEquals("OK", output.getCode()); } protected InputReportIncident createDummyIncident() { InputReportIncident input = new InputReportIncident(); input.setEmail("davsclaus@apache.org"); input.setIncidentId("12345678"); input.setIncidentDate("2008-07-13"); input.setPhone("+45 2962 7576"); input.setSummary("Failed operation"); input.setDetails("The wrong foot was operated."); input.setFamilyName("Ibsen"); input.setGivenName("Claus"); return input; } }
Then we can run the test with maven using: mvn test. But we will get a failure:
Running org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentServiceTest Hello ReportIncidentService is called from Claus Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 1, Skipped: 0, Time elapsed: 0.235 sec <<< FAILURE! Results : Tests in error: testIncident(org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentServiceTest) Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 1, Skipped: 0
What is the problem? Well our service uses a CamelProducer (the template) to send a message to the file endpoint so the message will be stored in a file. What we need is to get hold of such a producer and inject it on our service, by calling the setter.
Since Camel is very light weight and embedable we are able to create a CamelContext and add the endpoint in our unit test code directly. We do this to show how this is possible:
private CamelContext context;
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
// CamelContext is just created like this
context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// then we can create our endpoint and set the options
FileEndpoint endpoint = new FileEndpoint();
// the endpoint must have the camel context set also
endpoint.setCamelContext(context);
// our output folder
endpoint.setFile(new File("target"));
// and the option not to append
endpoint.setAppend(false);
// then we add the endpoint just in java code just as the spring XML, we register it with the "backup" id.
context.addSingletonEndpoint("backup", endpoint);
// finally we need to start the context so Camel is ready to rock
context.start();
}
@Override
protected void tearDown() throws Exception {
super.tearDown();
// and we are nice boys so we stop it to allow resources to clean up
context.stop();
}
So now we are ready to set the ProducerTemplate on our service, and we get a hold of that baby from the CamelContext as:
public void testIncident() {
ReportIncidentService service = new ReportIncidentService();
// get a producer template from the camel context
ProducerTemplate template = context.createProducerTemplate();
// inject it on our service using the setter
service.setTemplate(template);
InputReportIncident input = createDummyIncident();
OutputReportIncident output = service.reportIncident(input);
assertEquals("OK", output.getCode());
}
And this time when we run the unit test its a success:
Results : Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0
We would like to test that the file exists so we add these two lines to our test method:
// should generate a file also
File file = new File("target/" + input.getIncidentId() + ".txt");
assertTrue("File should exists", file.exists());
Smarter Unit Testing with Spring
The unit test above requires us to assemble the Camel pieces manually in java code. What if we would like our unit test to use our spring configuration file axis-example-context.xml where we already have setup the endpoint. And of course we would like to test using this configuration file as this is the real file we will use. Well hey presto the xml file is a spring ApplicationContext file and spring is able to load it, so we go the spring path for unit testing. First we add the spring-test jar to our maven dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
And then we refactor our unit test to be a standard spring unit class. What we need to do is to extend AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests instead of TestCase in our unit test. Since Spring 2.5 embraces annotations we will use one as well to instruct what our xml configuration file is located:
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:axis-example-context.xml") public class ReportIncidentServiceTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests {
What we must remember to add is the classpath: prefix as our xml file is located in src/main/resources. If we omit the prefix then Spring will by default try to locate the xml file in the current package and that is org.apache.camel.example.axis. If the xml file is located outside the classpath you can use file: prefix instead. So with these two modifications we can get rid of all the setup and teardown code we had before and now we will test our real configuration.
The last change is to get hold of the producer template and now we can just refer to the bean id it has in the spring xml file:
<!-- producer template exposed with this id -->
<camel:template id="camelTemplate"/>
So we get hold of it by just getting it from the spring ApplicationContext as all spring users is used to do:
// get a producer template from the the spring context
ProducerTemplate template = (ProducerTemplate) applicationContext.getBean("camelTemplate");
// inject it on our service using the setter
service.setTemplate(template);
Now our unit test is much better, and a real power of Camel is that is fits nicely with Spring and you can use standard Spring'ish unit test to test your Camel applications as well.
Unit Test calling WebService
What if you would like to execute a unit test where you send a webservice request to the AxisReportIncidentService how do we unit test this one? Well first of all the code is merely just a delegate to our real service that we have just tested, but nevertheless its a good question and we would like to know how. Well the answer is that we can exploit that fact that Jetty is also a slim web container that can be embedded anywhere just as Camel can. So we add this to our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty</artifactId>
<version>${jetty-version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Then we can create a new class AxisReportIncidentServiceTest to unit test with Jetty. The code to setup Jetty is shown below with code comments:
public class AxisReportIncidentServiceTest extends TestCase { private Server server; private void startJetty() throws Exception { // create an embedded Jetty server server = new Server(); // add a listener on port 8080 on localhost (127.0.0.1) Connector connector = new SelectChannelConnector(); connector.setPort(8080); connector.setHost("127.0.0.1"); server.addConnector(connector); // add our web context path WebAppContext wac = new WebAppContext(); wac.setContextPath("/unittest"); // set the location of the exploded webapp where WEB-INF is located // this is a nice feature of Jetty where we can point to src/main/webapp wac.setWar("./src/main/webapp"); server.setHandler(wac); // then start Jetty server.setStopAtShutdown(true); server.start(); } @Override protected void setUp() throws Exception { super.setUp(); startJetty(); } @Override protected void tearDown() throws Exception { super.tearDown(); server.stop(); } }
Now we just need to send the incident as a webservice request using Axis. So we add the following code:
public void testReportIncidentWithAxis() throws Exception {
// the url to the axis webservice exposed by jetty
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/unittest/services/ReportIncidentPort");
// Axis stuff to get the port where we can send the webservice request
ReportIncidentService_ServiceLocator locator = new ReportIncidentService_ServiceLocator();
ReportIncidentService_PortType port = locator.getReportIncidentPort(url);
// create input to send
InputReportIncident input = createDummyIncident();
// send the webservice and get the response
OutputReportIncident output = port.reportIncident(input);
assertEquals("OK", output.getCode());
// should generate a file also
File file = new File("target/" + input.getIncidentId() + ".txt");
assertTrue("File should exists", file.exists());
}
protected InputReportIncident createDummyIncident() {
InputReportIncident input = new InputReportIncident();
input.setEmail("davsclaus@apache.org");
input.setIncidentId("12345678");
input.setIncidentDate("2008-07-13");
input.setPhone("+45 2962 7576");
input.setSummary("Failed operation");
input.setDetails("The wrong foot was operated.");
input.setFamilyName("Ibsen");
input.setGivenName("Claus");
return input;
}
And now we have an unittest that sends a webservice request using good old Axis.
Annotations
Both Camel and Spring has annotations that can be used to configure and wire trivial settings more elegantly. Camel has the endpoint annotation @EndpointInjected that is just what we need. With this annotation we can inject the endpoint into our service. The annotation takes either a name or uri parameter. The name is the bean id in the Registry. The uri is the URI configuration for the endpoint. Using this you can actually inject an endpoint that you have not defined in the camel context. As we have defined our endpoint with the id backup we use the name parameter.
@EndpointInject(name = "backup")
private ProducerTemplate template;
Camel is smart as @EndpointInjected supports different kinds of object types. We like the ProducerTemplate so we just keep it as it is.
Since we use annotations on the field directly we do not need to set the property in the spring xml file so we change our service bean:
<bean id="incidentservice" class="org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentService"/>
Running the unit test with mvn test reveals that it works nicely.
And since we use the @EndpointInjected that refers to the endpoint with the id backup directly we can loose the template tag in the xml, so its shorter:
<bean id="incidentservice" class="org.apache.camel.example.axis.ReportIncidentService"/>
<camel:camelContext id="camelContext">
<!-- producer template exposed with this id -->
<camel:template id="camelTemplate"/>
<!-- endpoint named backup that is configued as a file component -->
<camel:endpoint id="backup" uri="file://target?append=false"/>
</camel:camelContext>
And the final touch we can do is that since the endpoint is injected with concrete endpoint to use we can remove the "backup" name parameter when we send the message. So we change from:
// send the data to the endpoint and the header contains what filename it should be stored as
template.sendBodyAndHeader("backup", data, "org.apache.camel.file.name", filename);
To without the name:
// send the data to the endpoint and the header contains what filename it should be stored as
template.sendBodyAndHeader(data, "org.apache.camel.file.name", filename);
Then we avoid to duplicate the name and if we rename the endpoint name then we don't forget to change it in the code also.
The End
This tutorial hasn't really touched the one of the key concept of Camel as a powerful routing and mediation framework. But we wanted to demonstrate its flexibility and that it integrates well with even older frameworks such as Apache Axis 1.4.
Check out the other tutorials on Camel and the other examples.
Note that the code shown here also applies to Camel 1.4 so actually you can get started right away with the released version of Camel. As this time of writing Camel 1.5 is work in progress.
See Also
Tutorial on using Camel in a Web Application
Camel has been designed to work great with the Spring framework; so if you are already a Spring user you can think of Camel as just a framework for adding to your Spring XML files.
So you can follow the usual Spring approach to working with web applications; namely to add the standard Spring hook to load a /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml file. In that file you can include your usual Camel XML configuration.
Step1: Edit your web.xml
To enable spring add a context loader listener to your /WEB-INF/web.xml file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd" version="2.4"> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
This will cause Spring to boot up and look for the /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml file.
Step 2: Create a /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml file
Now you just need to create your Spring XML file and add your camel routes or configuration.
For example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:foo"/> <to uri="mock:results"/> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
Then boot up your web application and you're good to go!
Hints and Tips
If you use Maven to build your application your directory tree will look like this...
src/main/webapp/WEB-INF web.xml applicationContext.xml
To enable more rapid development we hightly recommend the jetty:run maven plugin.
Please refer to the help for more information on using jetty:run - but briefly if you add the following to your pom.xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jetty-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<webAppConfig>
<contextPath>/</contextPath>
</webAppConfig>
<scanIntervalSeconds>10</scanIntervalSeconds>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Then you can run your web application as follows
mvn jetty:run
Then Jetty will also monitor your target/classes directory and your src/main/webapp directory so that if you modify your spring XML, your web.xml or your java code the web application will be restarted, re-creating your Camel routes.
If your unit tests take a while to run, you could miss them out when running your web application via
mvn -Dtest=false jetty:run
Tutorial Business Partners
| Under Construction This tutorial is a work in progress. |
Background and Introduction
Business Background
So there's a company, which we'll call Acme. Acme sells widgets, in a fairly unusual way. Their customers are responsible for telling Acme what they purchased. The customer enters into their own systems (ERP or whatever) which widgets they bought from Acme. Then at some point, their systems emit a record of the sale which needs to go to Acme so Acme can bill them for it. Obviously, everyone wants this to be as automated as possible, so there needs to be integration between the customer's system and Acme.
Sadly, Acme's sales people are, technically speaking, doormats. They tell all their prospects, "you can send us the data in whatever format, using whatever protocols, whatever. You just can't change once it's up and running."
The result is pretty much what you'd expect. Taking a random sample of 3 customers:
- Customer 1: XML over FTP
- Customer 2: CSV over HTTP
- Customer 3: Excel via e-mail
Now on the Acme side, all this has to be converted to a canonical XML format and submitted to the Acme accounting system via JMS. Then the Acme accounting system does its stuff and sends an XML reply via JMS, with a summary of what it processed (e.g. 3 line items accepted, line item #2 in error, total invoice $123.45). Finally, that data needs to be formatted into an e-mail, and sent to a contact at the customer in question ("Dear Joyce, we received an invoice on 1/2/08. We accepted 3 line items totaling $123.45, though there was an error with line items #2 [invalid quantity ordered]. Thank you for your business. Love, Acme.").
So it turns out Camel can handle all this:
- Listen for HTTP, e-mail, and FTP files
- Grab attachments from the e-mail messages
- Convert XML, XLS, and CSV files to a canonical XML format
- read and write JMS messages
- route based on company ID
- format e-mails using Velocity templates
- send outgoing e-mail messages
Tutorial Background
This tutorial will cover all that, plus setting up tests along the way.
Before starting, you should be familiar with:
- Camel concepts including the CamelContext, Routes, Components and Endpoints, and Enterprise Integration Patterns
- Configuring Camel with the XML or Java DSL
You'll learn:
- How to set up a Maven build for a Camel project
- How to transform XML, CSV, and Excel data into a standard XML format with Camel
- How to write POJOs (Plain Old Java Objects), Velocity templates, and XSLT stylesheets that are invoked by Camel routes for message transformation
- How to configure simple and complex Routes in Camel, using either the XML or the Java DSL format
- How to set up unit tests that load a Camel configuration and test Camel routes
- How to use Camel's Data Formats to automatically convert data between Java objects and XML, CSV files, etc.
- How to send and receive e-mail from Camel
- How to send and receive JMS messages from Camel
- How to use Enterprise Integration Patterns including Message Router and Pipes and Filters
- How to use various languages to express content-based routing rules in Camel
- How to deal with Camel messages, headers, and attachments
You may choose to treat this as a hands-on tutorial, and work through building the code and configuration files yourself. Each of the sections gives detailed descriptions of the steps that need to be taken to get the components and routes working in Camel, and takes you through tests to make sure they are working as expected.
But each section also links to working copies of the source and configuration files, so if you don't want the hands-on approach, you can simply review and/or download the finished files.
High-Level Diagram
Here's more or less what the integration process looks like.
First, the input from the customers to Acme:

And then, the output from Acme to the customers:

Tutorial Tasks
To get through this scenario, we're going to break it down into smaller pieces, implement and test those, and then try to assemble the big scenario and test that.
Here's what we'll try to accomplish:
- Create a Maven build for the project
- Get sample files for the customer Excel, CSV, and XML input
- Get a sample file for the canonical XML format that Acme's accounting system uses
- Create an XSD for the canonical XML format
- Create JAXB POJOs corresponding to the canonical XSD
- Create an XSLT stylesheet to convert the Customer 1 (XML over FTP) messages to the canonical format
- Create a unit test to ensure that a simple Camel route invoking the XSLT stylesheet works
- Create a POJO that converts a List<List<String>> to the above JAXB POJOs
- Note that Camel can automatically convert CSV input to a List of Lists of Strings representing the rows and columns of the CSV, so we'll use this POJO to handle Customer 2 (CSV over HTTP)
- Create a unit test to ensure that a simple Camel route invoking the CSV processing works
- Create a POJO that converts a Customer 3 Excel file to the above JAXB POJOs (using POI to read Excel)
- Create a unit test to ensure that a simple Camel route invoking the Excel processing works
- Create a POJO that reads an input message, takes an attachment off the message, and replaces the body of the message with the attachment
- This is assuming for Customer 3 (Excel over e-mail) that the e-mail contains a single Excel file as an attachment, and the actual e-mail body is throwaway
- Build a set of Camel routes to handle the entire input (Customer -> Acme) side of the scenario.
- Build unit tests for the Camel input.
- TODO: Tasks for the output (Acme -> Customer) side of the scenario
Let's Get Started!
Step 1: Initial Maven build
We'll use Maven for this project as there will eventually be quite a few dependencies and it's nice to have Maven handle them for us. You should have a current version of Maven (e.g. 2.0.9) installed.
You can start with a pretty empty project directory and a Maven POM file, or use a simple JAR archetype to create one.
Here's a sample POM. We've added a dependency on camel-core, and set the compile version to 1.5 (so we can use annotations):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.apache.camel.tutorial</groupId> <artifactId>business-partners</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>Camel Business Partners Tutorial</name> <dependencies> <dependency> <artifactId>camel-core</artifactId> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.5</source> <target>1.5</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
Step 2: Get Sample Files
You can make up your own if you like, but here are the "off the shelf" ones. You can save yourself some time by downloading these to src/test/resources in your Maven project.
- Customer 1 (XML): input-customer1.xml
- Customer 2 (CSV): input-customer2.csv
- Customer 3 (Excel): input-customer3.xls
- Canonical Acme XML Request: canonical-acme-request.xml
- Canonical Acme XML Response: TODO
If you look at these files, you'll see that the different input formats use different field names and/or ordering, because of course the sales guys were totally OK with that. Sigh.
Step 3: XSD and JAXB Beans for the Canonical XML Format
Here's the sample of the canonical XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <invoice xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/tutorial/partners/invoice"> <partner-id>2</partner-id> <date-received>9/12/2008</date-received> <line-item> <product-id>134</product-id> <description>A widget</description> <quantity>3</quantity> <item-price>10.45</item-price> <order-date>6/5/2008</order-date> </line-item> <!-- // more line-item elements here --> <order-total>218.82</order-total> </invoice>
If you're ambitions, you can write your own XSD (XML Schema) for files that look like this, and save it to src/main/xsd.
Solution: If not, you can download mine, and save that to save it to src/main/xsd.
Generating JAXB Beans
Down the road we'll want to deal with the XML as Java POJOs. We'll take a moment now to set up those XML binding POJOs. So we'll update the Maven POM to generate JAXB beans from the XSD file.
We need a dependency:
<dependency> <artifactId>camel-jaxb</artifactId> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
And a plugin configured:
<plugin> <groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId> <artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>xjc</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>
That should do it (it automatically looks for XML Schemas in src/main/xsd to generate beans for). Run mvn install and it should emit the beans into target/generated-sources/jaxb. Your IDE should see them there, though you may need to update the project to reflect the new settings in the Maven POM.
Step 4: Initial Work on Customer 1 Input (XML over FTP)
To get a start on Customer 1, we'll create an XSLT template to convert the Customer 1 sample file into the canonical XML format, write a small Camel route to test it, and build that into a unit test. If we get through this, we can be pretty sure that the XSLT template is valid and can be run safely in Camel.
Create an XSLT template
Start with the Customer 1 sample input. You want to create an XSLT template to generate XML like the canonical XML sample above – an invoice element with line-item elements (one per item in the original XML document). If you're especially clever, you can populate the current date and order total elements too.
Solution: My sample XSLT template isn't that smart, but it'll get you going if you don't want to write one of your own.
Create a unit test
Here's where we get to some meaty Camel work. We need to:
- Set up a unit test
- That loads a Camel configuration
- That has a route invoking our XSLT
- Where the test sends a message to the route
- And ensures that some XML comes out the end of the route
The easiest way to do this is to set up a Spring context that defines the Camel stuff, and then use a base unit test class from Spring that knows how to load a Spring context to run tests against. So, the procedure is:
Set Up a Skeletal Camel/Spring Unit Test
- Add dependencies on Camel-Spring, and the Spring test JAR (which will automatically bring in JUnit 3.8.x) to your POM:
<dependency> <artifactId>camel-spring</artifactId> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <version>2.5.5</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
- Create a new unit test class in src/test/java/your-package-here, perhaps called XMLInputTest.java
- Make the test extend Spring's AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests class, so it can load a Spring context for the test
- Create a Spring context configuration file in src/test/resources, perhaps called XMLInputTest-context.xml
- In the unit test class, use the class-level @ContextConfiguration annotation to indicate that a Spring context should be loaded
- By default, this looks for a Context configuration file called TestClassName-context.xml in a subdirectory corresponding to the package of the test class. For instance, if your test class was org.apache.camel.tutorial.XMLInputTest, it would look for org/apache/camel/tutorial/XMLInputTest-context.xml
- To override this default, use the locations attribute on the @ContextConfiguration annotation to provide specific context file locations (starting each path with a / if you don't want it to be relative to the package directory). My solution does this so I can put the context file directly in src/test/resources instead of in a package directory under there.
- Add a CamelContext instance variable to the test class, with the @Autowired annotation. That way Spring will automatically pull the CamelContext out of the Spring context and inject it into our test class.
- Add a ProducerTemplate instance variable and a setUp method that instantiates it from the CamelContext. We'll use the ProducerTemplate later to send messages to the route.
protected ProducerTemplate<Exchange> template; protected void setUp() throws Exception { super.setUp(); template = camelContext.createProducerTemplate(); }
- Put in an empty test method just for the moment (so when we run this we can see that "1 test succeeded")
- Add the Spring <beans> element (including the Camel Namespace) with an empty <camelContext> element to the Spring context, like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring-1.4.0.xsd"> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> </camelContext> </beans>
Test it by running mvn install and make sure there are no build errors. So far it doesn't test much; just that your project and test and source files are all organized correctly, and the one empty test method completes successfully.
Solution: Your test class might look something like this:
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/XMLInputTest.java
- src/test/resources/XMLInputTest-context.xml (same as just above)
Flesh Out the Unit Test
So now we're going to write a Camel route that applies the XSLT to the sample Customer 1 input file, and makes sure that some XML output comes out:
- Save the input-customer1.xml file to src/test/resources
- Save your XSLT file (created in the previous step) to src/main/resources
- Write a Camel Route, either right in the Spring XML, or using the Java DSL (in another class under src/test/java somewhere). This route should use the Pipes and Filters integration pattern to:
- Start from the endpoint direct:start (which lets the test conveniently pass messages into the route)
- Call the endpoint xslt:YourXSLTFile.xsl (to transform the message with the specified XSLT template)
- Send the result to the endpoint mock:finish (which lets the test verify the route output)
- Add a test method to the unit test class that:
- Get a reference to the Mock endpoint mock:finish using code like this:
MockEndpoint finish = MockEndpoint.resolve(camelContext, "mock:finish"); - Set the expectedMessageCount on that endpoint to 1
- Get a reference to the Customer 1 input file, using code like this:
InputStream in = XMLInputTest.class.getResourceAsStream("/input-partner1.xml"); assertNotNull(in); - Send that InputStream as a message to the direct:start endpoint, using code like this:
template.sendBody("direct:start", in);Note that we can send the sample file body in several formats (File, InputStream, String, etc.) but in this case an InputStream is pretty convenient.
- Ensure that the message made it through the route to the final endpoint, by testing all configured Mock endpoints like this:
MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext);
- If you like, inspect the final message body using some code like finish.getExchanges().get(0).getIn().getBody().
- If you do this, you'll need to know what format that body is – String, byte array, InputStream, etc.
- Get a reference to the Mock endpoint mock:finish using code like this:
- Run your test with mvn install and make sure the build completes successfully.
Solution: Your finished test might look something like this:
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/XMLInputTest.java
- For XML Configuration:
- src/test/resources/XMLInputTest-context.xml
- Or, for Java DSL Configuration:
- src/test/resources/XMLInputTest-dsl-context.xml
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/routes/XMLInputTestRoute.java
| Test Base Class Once your test class is working, you might want to extract things like the @Autowired CamelContext, the ProducerTemplate, and the setUp method to a custom base class that you extend with your other tests. |
Step 5: Initial Work on Customer 2 Input (CSV over HTTP)
To get a start on Customer 2, we'll create a POJO to convert the Customer 2 sample CSV data into the JAXB POJOs representing the canonical XML format, write a small Camel route to test it, and build that into a unit test. If we get through this, we can be pretty sure that the CSV conversion and JAXB handling is valid and can be run safely in Camel.
Create a CSV-handling POJO
To begin with, CSV is a known data format in Camel. Camel can convert a CSV file to a List (representing rows in the CSV) of Lists (representing cells in the row) of Strings (the data for each cell). That means our POJO can just assume the data coming in is of type List<List<String>>, and we can declare a method with that as the argument.
Looking at the JAXB code in target/generated-sources/jaxb, it looks like an Invoice object represents the whole document, with a nested list of LineItemType objects for the line items. Therefore our POJO method will return an Invoice (a document in the canonical XML format).
So to implement the CSV-to-JAXB POJO, we need to do something like this:
- Create a new class under src/main/java, perhaps called CSVConverterBean.
- Add a method, with one argument of type List<List<String>> and the return type Invoice
- In the method, the logic should look roughly like this:
- Create a new Invoice, using the method on the generated ObjectFactory class
- Loop through all the rows in the incoming CSV (the outer List)
- Skip the first row, which contains headers (column names)
- For the other rows:
- Create a new LineItemType (using the ObjectFactory again)
- Pick out all the cell values (the Strings in the inner List) and put them into the correct fields of the LineItemType
- Not all of the values will actually go into the line item in this example
- You may hardcode the column ordering based on the sample data file, or else try to read it dynamically from the headers in the first line
- Note that you'll need to use a JAXB DatatypeFactory to create the XMLGregorianCalendar values that JAXB uses for the date fields in the XML – which probably means using a SimpleDateFormat to parse the date and setting that date on a GregorianCalendar
- Add the line item to the invoice
- Populate the partner ID, date of receipt, and order total on the Invoice
- Throw any exceptions out of the method, so Camel knows something went wrong
- Return the finished Invoice
Solution: Here's an example of what the CSVConverterBean might look like.
Create a unit test
Start with a simple test class and test Spring context like last time, perhaps based on the name CSVInputTest:
/** * A test class the ensure we can convert Partner 2 CSV input files to the * canonical XML output format, using JAXB POJOs. */ @ContextConfiguration(locations = "/CSVInputTest-context.xml") public class CSVInputTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @Autowired protected CamelContext camelContext; protected ProducerTemplate<Exchange> template; protected void setUp() throws Exception { super.setUp(); template = camelContext.createProducerTemplate(); } public void testCSVConversion() { // TODO } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring-1.4.0.xsd"> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <!-- TODO --> </camelContext> </beans>
Now the meaty part is to flesh out the test class and write the Camel routes.
- Update the Maven POM to include CSV Data Format support:
<dependency> <artifactId>camel-csv</artifactId> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
- Write the routes (right in the Spring XML context, or using the Java DSL) for the CSV conversion process, again using the Pipes and Filters pattern:
- Start from the endpoint direct:CSVstart (which lets the test conveniently pass messages into the route). We'll name this differently than the starting point for the previous test, in case you use the Java DSL and put all your routes in the same package (which would mean that each test would load the DSL routes for several tests.)
- This time, there's a little preparation to be done. Camel doesn't know that the initial input is a CSV, so it won't be able to convert it to the expected List<List<String>> without a little hint. For that, we need an unmarshal transformation in the route. The unmarshal method (in the DSL) or element (in the XML) takes a child indicating the format to unmarshal; in this case that should be csv.
- Next invoke the POJO to transform the message with a bean:CSVConverter endpoint
- As before, send the result to the endpoint mock:finish (which lets the test verify the route output)
- Finally, we need a Spring <bean> element in the Spring context XML file (but outside the <camelContext> element) to define the Spring bean that our route invokes. This Spring bean should have a name attribute that matches the name used in the bean endpoint (CSVConverter in the example above), and a class attribute that points to the CSV-to-JAXB POJO class you wrote above (such as, org.apache.camel.tutorial.CSVConverterBean). When Spring is in the picture, any bean endpoints look up Spring beans with the specified name.
- Write a test method in the test class, which should look very similar to the previous test class:
- Get the MockEndpoint for the final endpoint, and tell it to expect one message
- Load the Partner 2 sample CSV file from the ClassPath, and send it as the body of a message to the starting endpoint
- Verify that the final MockEndpoint is satisfied (that is, it received one message) and examine the message body if you like
- Note that we didn't marshal the JAXB POJOs to XML in this test, so the final message should contain an Invoice as the body. You could write a simple line of code to get the Exchange (and Message) from the MockEndpoint to confirm that.
- Run this new test with mvn install and make sure it passes and the build completes successfully.
Solution: Your finished test might look something like this:
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/CSVInputTest.java
- For XML Configuration:
- src/test/resources/CSVInputTest-context.xml
- Or, for Java DSL Configuration:
- src/test/resources/CSVInputTest-dsl-context.xml
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/routes/CSVInputTestRoute.java
Step 6: Initial Work on Customer 3 Input (Excel over e-mail)
To get a start on Customer 3, we'll create a POJO to convert the Customer 3 sample Excel data into the JAXB POJOs representing the canonical XML format, write a small Camel route to test it, and build that into a unit test. If we get through this, we can be pretty sure that the Excel conversion and JAXB handling is valid and can be run safely in Camel.
Create an Excel-handling POJO
Camel does not have a data format handler for Excel by default. We have two options – create an Excel DataFormat (so Camel can convert Excel spreadsheets to something like the CSV List<List<String>> automatically), or create a POJO that can translate Excel data manually. For now, the second approach is easier (if we go the DataFormat route, we need code to both read and write Excel files, whereas otherwise read-only will do).
So, we need a POJO with a method that takes something like an InputStream or byte[] as an argument, and returns in Invoice as before. The process should look something like this:
- Update the Maven POM to include POI support:
<dependency> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <version>3.1-FINAL</version> </dependency>
- Create a new class under src/main/java, perhaps called ExcelConverterBean.
- Add a method, with one argument of type InputStream and the return type Invoice
- In the method, the logic should look roughly like this:
- Create a new Invoice, using the method on the generated ObjectFactory class
- Create a new HSSFWorkbook from the InputStream, and get the first sheet from it
- Loop through all the rows in the sheet
- Skip the first row, which contains headers (column names)
- For the other rows:
- Create a new LineItemType (using the ObjectFactory again)
- Pick out all the cell values and put them into the correct fields of the LineItemType (you'll need some data type conversion logic)
- Not all of the values will actually go into the line item in this example
- You may hardcode the column ordering based on the sample data file, or else try to read it dynamically from the headers in the first line
- Note that you'll need to use a JAXB DatatypeFactory to create the XMLGregorianCalendar values that JAXB uses for the date fields in the XML – which probably means setting the date from a date cell on a GregorianCalendar
- Add the line item to the invoice
- Populate the partner ID, date of receipt, and order total on the Invoice
- Throw any exceptions out of the method, so Camel knows something went wrong
- Return the finished Invoice
Solution: Here's an example of what the ExcelConverterBean might look like.
Create a unit test
The unit tests should be pretty familiar now. The test class and context for the Excel bean should be quite similar to the CSV bean.
- Create the basic test class and corresponding Spring Context XML configuration file
- The XML config should look a lot like the CSV test, except:
- Remember to use a different start endpoint name if you're using the Java DSL and not use separate packages per test
- You don't need the unmarshal step since the Excel POJO takes the raw InputStream from the source endpoint
- You'll declare a <bean> and endpoint for the Excel bean prepared above instead of the CSV bean
- The test class should look a lot like the CSV test, except use the right input file name and start endpoint name.
| Logging You may notice that your tests emit a lot less output all of a sudden. The dependency on POI brought in Log4J and configured commons-logging to use it, so now we need a log4j.properties file to configure log output. You can use the attached one (snarfed from ActiveMQ) or write your own; either way save it to src/main/resources to ensure you continue to see log output. |
Solution: Your finished test might look something like this:
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/ExcelInputTest.java
- For XML Configuration:
- src/test/resources/ExcelInputTest-context.xml
- Or, for Java DSL Configuration:
- src/test/resources/ExcelInputTest-dsl-context.xml
- src/test/java/org/apache/camel/tutorial/routes/ExcelInputTestRoute.java
Step 7: Put this all together into Camel routes for the Customer Input
With all the data type conversions working, the next step is to write the real routes that listen for HTTP, FTP, or e-mail input, and write the final XML output to an ActiveMQ queue. Along the way these routes will use the data conversions we've developed above.
So we'll create 3 routes to start with, as shown in the diagram back at the beginning:
- Accept XML orders over FTP from Customer 1 (we'll assume the FTP server dumps files in a local directory on the Camel machine)
- Accept CSV orders over HTTP from Customer 2
- Accept Excel orders via e-mail from Customer 3 (we'll assume the messages are sent to an account we can access via IMAP)
...
Step 8: Create a unit test for the Customer Input Routes
Languages Supported Appendix
To support flexible and powerful Enterprise Integration Patterns Camel supports various Languages to create an Expression or Predicate within either the Routing Domain Specific Language or the Xml Configuration. The following languages are supported
Bean Language
The purpose of the Bean Language is to be able to implement an Expression or Predicate using a simple method on a bean.
So the idea is you specify a bean name which will then be resolved in the Registry such as the Spring ApplicationContext then a method is invoked to evaluate the Expression or Predicate.
If no method name is provided then one is attempted to be chosen using the rules for Bean Binding; using the type of the message body and using any annotations on the bean methods.
The Bean Binding rules are used to bind the Message Exchange to the method parameters; so you can annotate the bean to extract headers or other expressions such as XPath or XQuery from the message.
Using Bean Expressions from the Java DSL
from("activemq:topic:OrdersTopic"). filter().method("myBean", "isGoldCustomer"). to("activemq:BigSpendersQueue");
Using Bean Expressions from XML
<route> <from uri="activemq:topic:OrdersTopic"/> <filter> <method bean="myBean" method="isGoldCustomer"/> <to uri="activemq:BigSpendersQueue"/> </filter> </route>
Writing the expression bean
The bean in the above examples is just any old Java Bean with a method called isGoldCustomer() that returns some object that is easily converted to a boolean value in this case, as its used as a predicate.
So we could implement it like this...
public class MyBean { public boolean isGoldCustomer(Exchange exchange) { ... } }
We can also use the Bean Integration annotations. For example you could do...
public boolean isGoldCustomer(String body) {...}
or
public boolean isGoldCustomer(@Header(name = "foo") Integer fooHeader) {...}
So you can bind parameters of the method to the Exchange, the Message or individual headers, properties, the body or other expressions.
Non registry beans
As of Camel 1.5 the Bean Language also supports invoking beans that isn't registered in the Registry. This is usable for quickly to invoke a bean from Java DSL where you don't need to register the bean in the Registry such as the Spring ApplicationContext.
Camel can instantiate the bean and invoke the method if given a class or invoke an already existing instance. This is illustrated from the example below:
NOTE This bean DSL is supported since Camel 2.0-M2
from("activemq:topic:OrdersTopic").
filter().expression(bean(MyBean.class, "isGoldCustomer")).
to("activemq:BigSpendersQueue");
The 2nd parameter isGoldCustomer is an optional parameter to explicit set the method name to invoke. If not provided Camel will try to invoke the best suited method. If case of ambiguity Camel will thrown an Exception. In these situations the 2nd parameter can solve this problem. Also the code is more readable if the method name is provided. The 1st parameter can also be an existing instance of a Bean such as:
private MyBean my; from("activemq:topic:OrdersTopic"). filter().expression(bean(my, "isGoldCustomer")). to("activemq:BigSpendersQueue");
Other examples
We have some test cases you can look at if it'll help
- MethodFilterTest is a JUnit test case showing the Java DSL use of the bean expression being used in a filter
- aggregator.xml is a Spring XML test case for the Aggregator which uses a bean method call to test for the completion of the aggregation.
Dependencies
The Bean language is part of camel-core.
Constant Expression Language
The Constant Expression Language is really just a way to specify constant strings as a type of expression.
Available as of Camel 1.5
Example usage
The setHeader element of the Spring DSL can utilize a constant expression like:
<route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <setHeader headerName="theHeader"> <constant>the value</constant> </setHeader> <to uri="mock:b"/> </route>
in this case, the Message coming from the seda:a Endpoint will have 'theHeader' header set to the constant value 'the value'.
And the same example using Java DSL:
from("seda:a").setHeader("theHeader", constant("the value")).to("mock:b");
Dependencies
The Constant language is part of camel-core.
EL
Camel supports the unified JSP and JSF Expression Language via the JUEL to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
For example you could use EL inside a Message Filter in XML
<route> <from uri="seda:foo"/> <filter> <el>${in.headers.foo == 'bar'}</el> <to uri="seda:bar"/> </filter> </route>
You could also use slightly different syntax, e.g. if the header name is not a valid identifier:
<route> <from uri="seda:foo"/> <filter> <el>${in.headers['My Header'] == 'bar'}</el> <to uri="seda:bar"/> </filter> </route>
You could use EL to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| exchange | Exchange | the Exchange object |
| in | Message | the exchange.in message |
| out | Message | the exchange.out message |
Samples
You can use EL dot notation to invoke operations. If you for instance have a body that contains a POJO that has a getFamiliyName method then you can construct the syntax as follows:
"$in.body.familyName"
Dependencies
To use EL in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-juel which implements the EL language.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-juel</artifactId> <version>1.6.1</version> </dependency>
Header Expression Language
The Header Expression Language allows you to extract values of named headers.
Available as of Camel 1.5
Example usage
The recipientList element of the Spring DSL can utilize a header expression like:
<route> <from uri="direct:a" /> <!-- use comma as a delimiter for String based values --> <recipientList delimiter=","> <header>myHeader</header> </recipientList> </route>
In this case, the list of recipients are contained in the header 'myHeader'.
And the same example in Java DSL:
from("direct:a").recipientList(header("myHeader"));
And with a slightly different syntax where you use the builder to the fullest (i.e. avoid using parameters but using stacked operations, notice that header is not a parameter but a stacked method call)
from("direct:a").recipientList().header("myHeader");
Dependencies
The Header language is part of camel-core.
JXPath
Camel supports JXPath to allow XPath expressions to be used on beans in an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration. For example you could use JXPath to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List.
From 1.3 of Camel onwards you can use XPath expressions directly using smart completion in your IDE as follows
from("queue:foo").filter(). jxpath("/in/body/foo"). to("queue:bar")
Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| this | Exchange | the Exchange object |
| in | Message | the exchange.in message |
| out | Message | the exchange.out message |
Using XML configuration
If you prefer to configure your routes in your Spring XML file then you can use JXPath expressions as follows
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="activemq:MyQueue"/> <filter> <jxpath>in/body/name = 'James'</xpath> <to uri="mqseries:SomeOtherQueue"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
Examples
Here is a simple example using a JXPath expression as a predicate in a Message Filter
from("direct:start"). filter().jxpath("in/body/name='James'"). to("mock:result");
JXPath injection
You can use Bean Integration to invoke a method on a bean and use various languages such as JXPath to extract a value from the message and bind it to a method parameter.
For example
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@JXPath("in/body/foo") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
Dependencies
To use JXpath in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-jxpath which implements the JXpath language.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-jxpath</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
OGNL
Camel allows OGNL to be used as an Expression or Predicate the DSL or Xml Configuration.
You could use OGNL to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
You can use OGNL dot notation to invoke operations. If you for instance have a body that contains a POJO that has a getFamiliyName method then you can construct the syntax as follows:
"request.body.familyName" // or "getRequest().getBody().getFamilyName()"
Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| this | Exchange | the Exchange is the root object |
| exchange | Exchange | the Exchange object |
| exception | Throwable | the Exchange exception (if any) |
| exchangeId | String | the exchange id |
| fault | Message | the Fault message (if any) |
| request | Message | the exchange.in message |
| response | Message | the exchange.out message (if any) |
| properties | Map | the exchange properties |
| property(name) | Object | the property by the given name |
| property(name, type) | Type | the property by the given name as the given type |
Samples
For example you could use OGNL inside a Message Filter in XML
<route> <from uri="seda:foo"/> <filter> <ognl>request.headers.foo = 'bar'</ognl> <to uri="seda:bar"/> </filter> </route>
And the sample using Java DSL:
from("seda:foo").filter().ognl("request.headers.foo = 'bar'").to("seda:bar");
Dependencies
To use OGNL in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-ognl which implements the OGNL language.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-ognl</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Scripting Languages
Camel supports a number of scripting languages which can be used to create an Expression or Predicate via the standard JSR 223 which is a standard part of Java 6.
The following scripting languages are integrated into the DSL:
However any JSR 223 scripting language can be used using the generic DSL methods.
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
See Also
BeanShell
Camel supports BeanShell among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a BeanShell expression use the following Java code
... beanShell("someBeanShellExpression") ...
For example you could use the beanShell function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
JavaScript
Camel supports JavaScript/ECMAScript among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a JavaScript expression use the following Java code
... javaScript("someJavaScriptExpression") ...
For example you could use the javaScript function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
Example
In the sample below we use JavaScript to create a Predicate use in the route path, to route exchanges from admin users to a special queue.
from("direct:start")
.choice()
.when().javaScript("request.headers.get('user') == 'admin'").to("seda:adminQueue")
.otherwise()
.to("seda:regularQueue");
And a Spring DSL sample as well:
<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<choice>
<when>
<javaScript>request.headers.get('user') == 'admin'</javaScript>
<to uri="seda:adminQueue"/>
</when>
<otherwise>
<to uri="seda:regularQueue"/>
</otherwise>
</choice>
</route>
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Groovy
Camel supports Groovy among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a Groovy expression use the following Java code
... groovy("someGroovyExpression") ...
For example you could use the groovy function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
Example
// lets route if a line item is over $100 from("queue:foo").filter(groovy("request.lineItems.any { i -> i.value > 100 }")).to("queue:bar")
And the Spring DSL:
<route>
<from uri="queue:foo"/>
<filter>
<groovy>request.lineItems.any { i -> i.value > 100 }</groovy>
<to uri="queue:bar"/>
</filter>
</route>
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Python
Camel supports Python among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a Python expression use the following Java code
... python("somePythonExpression") ...
For example you could use the python function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
Example
In the sample below we use Python to create a Predicate use in the route path, to route exchanges from admin users to a special queue.
from("direct:start")
.choice()
.when().python("request.headers['user'] == 'admin'").to("seda:adminQueue")
.otherwise()
.to("seda:regularQueue");
And a Spring DSL sample as well:
<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<choice>
<when>
<python>request.headers['user'] == 'admin'</python>
<to uri="seda:adminQueue"/>
</when>
<otherwise>
<to uri="seda:regularQueue"/>
</otherwise>
</choice>
</route>
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
PHP
Camel supports PHP among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a PHP expression use the following Java code
... php("somePHPExpression") ...
For example you could use the php function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Ruby
Camel supports Ruby among other Scripting Languages to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration.
To use a Ruby expression use the following Java code
... ruby("someRubyExpression") ...
For example you could use the ruby function to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List
Example
In the sample below we use Ruby to create a Predicate use in the route path, to route exchanges from admin users to a special queue.
from("direct:start")
.choice()
.when().ruby("$request.headers['user'] == 'admin'").to("seda:adminQueue")
.otherwise()
.to("seda:regularQueue");
And a Spring DSL sample as well:
<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<choice>
<when>
<ruby>$request.headers['user'] == 'admin'</ruby>
<to uri="seda:adminQueue"/>
</when>
<otherwise>
<to uri="seda:regularQueue"/>
</otherwise>
</choice>
</route>
ScriptContext
The JSR-223 scripting languages ScriptContext is pre configured with the following attributes all set at ENGINE_SCOPE:
| Attribute | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| context | org.apache.camel.CamelContext | The Camel Context |
| exchange | org.apache.camel.Exchange | The current Exchange |
| request | org.apache.camel.Message | The IN message |
| response | org.apache.camel.Message | The OUT message |
Attributes
You can add your own attributes with the attribute(name, value) DSL method, such as:
In the sample below we add an attribute user that is an object we already have instantiated as myUser. This object has a getFirstName() method that we want to set as header on the message. We use the groovy language to concat the first and last name into a single string that is returned.
from("direct:in").setHeader("name").groovy("'$user.firstName $user.lastName'").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
Any scripting language
Camel can run any JSR-223 scripting languages using the script DSL method such as:
from("direct:in").setHeader("firstName").script("jaskel", "user.firstName").attribute("user", myUser").to("seda:users");
This is a bit different using the Spring DSL where you use the expression element that doesn't support setting attributes (yet):
<from uri="direct:in"/>
<setHeader headerName="firstName">
<expression language="jaskel">user.firstName</expression>
</setHeader>
<to uri="seda:users"/>
Dependencies
To use scripting languages in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-script which integrates the JSR-223 scripting engine.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-script</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Simple Expression Language
The Simple Expression Language is a really simple language you can use. Its primarily intended for being a really small and simple language for testing without requiring any new dependencies or knowledge of XPath; so its ideal for testing in camel-core. However for real world use cases you are generally recommended to choose a more expressive and powerful language such as:
- Bean Language
- EL
- OGNL
- one of the supported Scripting Languages
The simple language uses ${body} placeholders for complex expressions where the expression contains constant literals. The ${ } placeholders can be omitted if the expression is only the token itself.
To get the body of the in message: "body", or "in.body" or "${body}".
A complex expression must use ${ } placeholders, such as: "Hello ${in.header.name} how are you?".
You can have multiple tokens in the same expression: "Hello ${in.header.name} this is ${in.header.me} speaking".
However you can not nest tokens (i.e. having another ${ } placeholder in an existing, is not allowed).
Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | String | the input message id |
| body | Object | the input body |
| in.body | Object | the input body |
| out.body | Object | the output body |
| header.foo | Object | refer to the input foo header |
| headers.foo | Object | refer to the input foo header |
| in.header.foo | Object | refer to the input foo header |
| in.headers.foo | Object | refer to the input foo header |
| out.header.foo | Object | refer to the out header foo |
| out.headers.foo | Object | refer to the out header foo |
| property.foo | Object | refer to the foo property on the exchange |
| sys.foo | String | refer to the system property |
| exception.message | String | New in Camel 2.0. Refer to the exception.messsage on the exchange, is null if no exception set on exchange |
| date:command:pattern | String | New in Camel 1.5. Date formatting using the java.text.SimepleDataFormat patterns. Supported commands are: now for current timestamp, in.header.xxx or header.xxx to use the Date object in the IN header with the key xxx. out.header.xxx to use the Date object in the OUT header with the key xxx. |
| bean:bean expression | Object | New in Camel 1.5. Invoking a bean expression using the Bean language. Specifying a method name you must use dot as separator. In Camel 2.0 we also support the ?method=methodname syntax that is used by the Bean component. |
Operator support
Avaiable as of Camel 2.0
We added a basic set of operators supported in the simple language in Camel 2.0. The parser is limited to only support a single operator.
To enable it the left value must be enclosed in ${ }. The syntax is:
${leftValue} OP rightValue
Where the rightValue can be a String literal enclosed in ' ', null, a constant value or another expression enclosed in ${ }.
Camel will automatically type convert the rightValue type to the leftValue type, so its able to eg. convert a string into a numeric so you can use > comparison for numeric values.
The following operators is supported:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | equals |
| > | greather than |
| >= | greather than or equals |
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equals |
| != | not equals |
| contains | For testing if contains in a string based value |
| not contains | For testinf if not contains in a string based value |
| regex | For matching against a given regular expression pattern defined as a String value |
| not regex | For not matching against a given regular expression pattern defined as a String value |
| in | For matching if in a set of values, each element must be separated by comma. |
| not in | For matching if not in a set of values, each element must be separated by comma. |
| is | For matching if the left hand side type is an instanceof the value. |
| not is | For matching if the left hand side type is not an instanceof the value. |
| range | For matching if the left hand side is within a range of values defined as numbers: from..to |
| not range | For matching if the left hand side is not within a range of values defined as numbers: from..to |
And the following operators can be used to group expressions:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| and | and is used to group two expressions |
| or | or is used to group two expressions |
Notice: Currently and or or can only be used once in a simple language expression. This might change in the future.
The syntax for AND is:
${leftValue} OP rightValue and ${leftValue} OP rightValue
And the syntax for OR is:
${leftValue} OP rightValue or ${leftValue} OP rightValue
Some examples:
simple("${in.header.foo} == 'foo'") // ' ' can be omitted simple("${in.header.foo} == foo") // here Camel will type convert '100' into the type of in.header.bar and if its an Integer '100' will also be converter to an Integer simple("${in.header.bar} == '100'") simple("${in.header.bar} == 100") // 100 will be converter to the type of in.header.bar so we can do > comparison simple("${in.header.bar} > 100") // testing for null simple("${in.header.baz} == null") // testing for not null simple("${in.header.baz} != null")
And a bit more advanced example where the right value is another expression
simple("${in.header.date} == ${date:now:yyyyMMdd}") simple("${in.header.type} == ${bean:orderService?method=getOrderType}")
And an example with contains, testing if the title contains the word Camel
simple("${in.header.title} contains 'Camel'")
And an example with regex, testing if the number header is a 4 digit value:
simple("${in.header.number} regex '\d{4}'")
And finally an example if the header equals any of the values in the list. Each element must be separated by comma, and no space around.
This also works for numbers etc, as Camel will convert each element into the type of the left hand side.
simple("${in.header.type} in 'gold,silver'")
And for all the last 3 we also support the negate test using not:
simple("${in.header.type} not in 'gold,silver'")
And you can test for if the type is a certain instance, eg for instance a String
simple("${in.header.type} is 'java.lang.String'")
We have added a shorthand for all java.lang types so you can write it as:
simple("${in.header.type} is String")
Ranges is also supported. The range interval requires numbers and both from and end is inclusive. For instance to test whether a value is between 100 and 199:
simple("${in.header.number} range 100..199")
Notice we use .. in the range without spaces. Its based on the same syntax as Groovy.
| Can be used in Spring XML As the Spring XML does not have all the power as the Java DSL with all its various builder methods, you had to resort to use some other languages
<from uri="seda:orders">
<filter>
<simple>${in.header.type} == 'widget'</simple>
<to uri="bean:orderService?method=handleWidget"/>
</filter>
</from>
|
Using and / or
If you have two expressions you can combine them with the and or or operator.
For instance:
simple("${in.header.title} contains 'Camel' and ${in.header.type' == 'gold'")
And of course the or is also supported. The sample example would be:
simple("${in.header.title} contains 'Camel' or ${in.header.type' == 'gold'")
Notice: Currently and or or can only be used once in a simple language expression. This might change in the future.
So you cannot do:
simple("${in.header.title} contains 'Camel' and ${in.header.type' == 'gold' and ${in.header.number} range 100..200")
Samples
In the Spring XML sample below we filter based on a header value:
<from uri="seda:orders">
<filter>
<simple>in.header.foo</simple>
<to uri="mock:fooOrders"/>
</filter>
</from>
The Simple language can be used for the predicate test above in the Message Filter pattern, where we test if the in message has a foo header (a header with the key foo exists). If the expression evaluates to true then the message is routed to the mock:foo endpoint, otherwise its lost in the deep blue sea ![]() .
.
The same example in Java DSL:
from("seda:orders")
.filter().simple("in.header.foo").to("seda:fooOrders");
You can also use the simple language for simple text concatenations such as:
from("direct:hello").transform().simple("Hello ${in.header.user} how are you?").to("mock:reply");
Notice that we must use ${ } placeholders in the expression now to let Camel be able to parse it correctly.
And this sample uses the date command to output current date.
from("direct:hello").transform().simple("The today is ${date:now:yyyyMMdd} and its a great day.").to("mock:reply");
And in the sample below we invoke the bean language to invoke a method on a bean to be included in the returned string:
from("direct:order").transform().simple("OrderId: ${bean:orderIdGenerator}").to("mock:reply");
Where orderIdGenerator is the id of the bean registered in the Registry. If using Spring then its the Spring bean id.
If we want to declare which method to invoke on the order id generator bean we must prepend .method name such as below where we invoke the generateId method.
from("direct:order").transform().simple("OrderId: ${bean:orderIdGenerator.generateId}").to("mock:reply");
And in Camel 2.0 we can use the ?method=methodname option that we are familiar with the Bean component itself:
from("direct:order").transform().simple("OrderId: ${bean:orderIdGenerator?method=generateId}").to("mock:reply");
Dependencies
The Bean language is part of camel-core.
File Expression Language
Available as of Camel 1.5
The File Expression Language is an extension to the Simple language, adding file related capabilities. These capabilities is related to common use cases working with file path and names. The goal is to allow expression to be used with the File and FTP components for setting dynamic file patterns for both consumer and producer.
Syntax
This language is an extension to the Simple language so the Simple syntax applies also. So the table below only lists the additional.
As opposed to Simple language File Language also supports Constant expressions so you can enter a fixed filename.
All the file tokens uses the same expression name as the method on the java.io.File object, for instance file:absolute refers to the java.io.File.getAbsolute() method. Notice that not all expressions is supported by the current Exchange. For instance the FTP component supports some of the options, where as the File component support all of them.
| Expression | Type | File Consumer | File Producer | FTP Consumer | FTP Producer | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| file:name | String | yes | no | yes | no | refers to the file name (is relative to the starting directory, see note below) |
| file:name.noext | String | yes | no | yes | no | refers to the file name with no extension (is relative to the starting directory, see note below) |
| file:onlyname | String | yes | no | yes | no | Camel 2.0: refers to the file name only with no leading paths. |
| file:onlyname.noext | String | yes | no | yes | no | Camel 2.0: refers to the file name only with no extension and with no leading paths. |
| file:ext | String | yes | no | yes | no | Camel 1.6.1/Camel 2.0: refers to the file extension only |
| file:parent | String | yes | no | yes | no | refers to the file parent |
| file:path | String | yes | no | yes | no | refers to the file path |
| file:absolute | Boolean | yes | no | no | no | Camel 2.0: refers to whether the file is regarded as absolute or relative |
| file:absolute.path | String | yes | no | no | no | refers to the absolute file path |
| file:length | Long | yes | no | yes | no | refers to the file length returned as a Long type |
| file:modified | Date | yes | no | yes | no | Camel 2.0: refers to the file last modified returned as a Date type |
| date:command:pattern | String | yes | yes | yes | yes | for date formatting using the java.text.SimepleDataFormat patterns. Is an extension to the Simple language. Additional command is: file (consumers only) for the last modified timestamp of the file. Notice: all the commands from the Simple language can also be used. |
File token example
Relative paths
We have a java.io.File handle for the file hello.txt in the following relative directory: .\filelanguage\test. And we configure out endpoint to use this starting directory .\filelanguage. The the file tokens will return as:
| Expression | Returns |
|---|---|
| file:name | test\hello.txt |
| file:name.noext | test\hello |
| file:onlyname | hello.txt |
| file:onlyname.noext | hello |
| file:ext | txt |
| file:parent | filelanguage\test |
| file:path | filelanguage\test\hello.txt |
| file:absolute | false |
| file:absolute.path | \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage\test\hello.txt |
Absolute paths
We have a java.io.File handle for the file hello.txt in the following absolute directory: \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage\test. And we configure out endpoint to use the absolute starting directory \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage. The the file tokens will return as:
| Expression | Returns |
|---|---|
| file:name | test\hello.txt |
| file:name.noext | test\hello |
| file:onlyname | hello.txt |
| file:onlyname.noext | hello |
| file:ext | txt |
| file:parent | \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage\test |
| file:path | \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage\test\hello.txt |
| file:absolute | true |
| file:absolute.path | \workspace\camel\camel-core\target\filelanguage\test\hello.txt |
Samples
You can enter a fixed Constant expression such as myfile.txt:
fileName="myfile.txt"
Lets assume we use the file consumer to read files and want to move the read files to backup folder with the current date as a sub folder. This can be archived using an expression like:
fileName="backup/${date:now:yyyyMMdd}/${file:name.noext}.bak"
relative folder names is also supported so suppose the backup folder should be a sibling folder then you can append .. as:
fileName="../backup/${date:now:yyyyMMdd}/${file:name.noext}.bak"
As this is an extension to the Simple language we have access to all the goodies from this language also, so in this use case we want to use the in.header.type as a parameter in the dynamic expression:
fileName="../backup/${date:now:yyyyMMdd}/type-${in.header.type}/backup-of-${file:name.noext}.bak"
If you have a custom Date you want to use in the expression then Camel supports retrieving dates from the message header.
fileName="orders/order-${in.header.customerId}-${date:in.header.orderDate:yyyyMMdd}.xml"
And finally we can also use a bean expression to invoke a POJO class that generates some String output (or convertible to String) to be used:
fileName="uniquefile-${bean:myguidgenerator.generateid}.txt"
And of course all this can be combined in one expression where you can use the File Language, Simple and the Bean language in one combined expression. This is pretty powerful for those common file path patterns.
Dependencies
The File language is part of camel-core.
SQL
The SQL support is added by JoSQL and is primarily used for performing SQL queries on in-memory objects. If you prefer to perform actual database queries then check out the JPA component.
Camel supports SQL to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration. For example you could use SQL to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List.
from("queue:foo").setBody().sql("select * from MyType").to("queue:bar")
And the spring DSL:
<from uri="queue:foo"/> <setBody> <sql>select * from MyType</sql> </setBody> <to uri="queue:bar"/>
Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| exchange | Exchange | the Exchange object |
| in | Message | the exchange.in message |
| out | Message | the exchange.out message |
| the property key | Object | the Exchange properties |
| the header key | Object | the exchange.in headers |
| the variable key | Object | if any additional variables is added using setVariables method |
Dependencies
To use SQL in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-josql which implements the SQL language.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-josql</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
XPath
Camel supports XPath to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration. For example you could use XPath to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List.
from("queue:foo"). filter().xpath("//foo")). to("queue:bar")
from("queue:foo"). choice().xpath("//foo")).to("queue:bar"). otherwise().to("queue:others");
Namespaces
In 1.3 onwards you can easily use namespaces with XPath expressions using the Namespaces helper class.
Namespaces ns = new Namespaces("c", "http://acme.com/cheese"); from("direct:start").filter(). xpath("/c:person[@name='James']", ns). to("mock:result");
Variables
Variables in XPath is defined in different namespaces. The default namespace is http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring.
| Namespace URI | Local part | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| http://camel.apache.org/xml/in/ | in | Message | the exchange.in message |
| http://camel.apache.org/xml/out/ | out | Message | the exchange.out message |
| http://camel.apache.org/xml/variables/environment-variables | env | Object | OS environment variables |
| http://camel.apache.org/xml/variables/system-properties | system | Object | Java System properties |
| http://camel.apache.org/xml/variables/exchange-property | Object | the exchange property |
Camel will resolve variables according to either:
- namespace given
- no namespace given
Namespace given
If the namespace is given then Camel is instructed exactly what to return. However when resolving either in or out Camel will try to resolve a header with the given local part first, and return it. If the local part has the value body then the body is returned instead.
No namespace given
If there is no namespace given then Camel resolves only based on the local part. Camel will try to resolve a variable in the following steps:
- from variables that has been set using the variable(name, value) fluent builder
- from message.in.header if there is a header with the given key
- from exchange.properties if there is a property with the given key
Functions
Camel adds the following XPath functions that can be used to access the exchange:
| Function | Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in:body | none | Object | Will return the in message body. |
| in:header | the header name | Object | Will return the in message header. |
| out:body | none | Object | Will return the out message body. |
| out:header | the header name | Object | Will return the out message header. |
Here's an example showing some of these functions in use.
from("direct:start").choice() .when().xpath("in:header('foo') = 'bar'").to("mock:x") .when().xpath("in:body() = '<two/>'").to("mock:y") .otherwise().to("mock:z");
Using XML configuration
If you prefer to configure your routes in your Spring XML file then you can use XPath expressions as follows
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring" xmlns:foo="http://example.com/person"> <route> <from uri="activemq:MyQueue"/> <filter> <xpath>/foo:person[@name='James']</xpath> <to uri="mqseries:SomeOtherQueue"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
Notice how we can reuse the namespace prefixes, foo in this case, in the XPath expression for easier namespace based XPath expressions!
See also this discussion on the mailinglist about using your own namespaces with xpath
Setting result type
The XPath expression will return a result type using native XML objects such as org.w3c.dom.NodeList. But many times you want a result type to be a String. To do this you have to instruct the XPath which result type to use.
In Java DSL:
xpath("/foo:person/@id", String.class)
In Spring DSL you use the resultType attribute to provide a fully qualified classname:
<xpath resultType="java.lang.String">/foo:person/@id</xpath>
In @XPath:
Available as of Camel 2.1
@XPath(value = "concat('foo-',//order/name/)", resultType = String.class) String name)
Where we use the xpath function concat to prefix the order name with foo-. In this case we have to specify that we want a String as result type so the concat function works.
Examples
Here is a simple example using an XPath expression as a predicate in a Message Filter
from("direct:start"). filter().xpath("/person[@name='James']"). to("mock:result");
If you have a standard set of namespaces you wish to work with and wish to share them across many different XPath expressions you can use the NamespaceBuilder as shown in this example
// lets define the namespaces we'll need in our filters Namespaces ns = new Namespaces("c", "http://acme.com/cheese") .add("xsd", "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"); // now lets create an xpath based Message Filter from("direct:start"). filter(ns.xpath("/c:person[@name='James']")). to("mock:result");
In this sample we have a choice construct. The first choice evaulates if the message has a header key type that has the value Camel.
The 2nd choice evaluates if the message body has a name tag <name> which values is Kong.
If neither is true the message is routed in the otherwise block:
from("direct:in").choice() // using $headerName is special notation in Camel to get the header key .when().xpath("$type = 'Camel'") .to("mock:camel") // here we test for the body name tag .when().xpath("//name = 'Kong'") .to("mock:donkey") .otherwise() .to("mock:other") .end();
And the spring XML equivalent of the route:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:in"/> <choice> <when> <xpath>$type = 'Camel'</xpath> <to uri="mock:camel"/> </when> <when> <xpath>//name = 'Kong'</xpath> <to uri="mock:donkey"/> </when> <otherwise> <to uri="mock:other"/> </otherwise> </choice> </route> </camelContext>
XPath injection
You can use Bean Integration to invoke a method on a bean and use various languages such as XPath to extract a value from the message and bind it to a method parameter.
The default XPath annotation has SOAP and XML namespaces available. If you want to use your own namespace URIs in an XPath expression you can use your own copy of the XPath annotation to create whatever namespace prefixes you want to use.
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import org.apache.camel.component.bean.XPathAnnotationExpressionFactory; import org.apache.camel.language.LanguageAnnotation; import org.apache.camel.language.NamespacePrefix; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER}) @LanguageAnnotation(language = "xpath", factory = XPathAnnotationExpressionFactory.class) public @interface MyXPath { String value(); // You can add the namespaces as the default value of the annotation NamespacePrefix[] namespaces() default { @NamespacePrefix(prefix = "n1", uri = "http://example.org/ns1"), @NamespacePrefix(prefix = "n2", uri = "http://example.org/ns2")}; Class<?> resultType() default NodeList.class; }
i.e. cut and paste upper code to your own project in a different package and/or annotation name then add whatever namespace prefix/uris you want in scope when you use your annotation on a method parameter. Then when you use your annotation on a method parameter all the namespaces you want will be available for use in your XPath expression.
NOTE this feature is supported from Camel 1.6.1.
For example
public class Foo { @MessageDriven(uri = "activemq:my.queue") public void doSomething(@Path("/foo/bar/text()") String correlationID, @Body String body) { // process the inbound message here } }
Dependencies
The XPath language is part of camel-core.
XQuery
Camel supports XQuery to allow an Expression or Predicate to be used in the DSL or Xml Configuration. For example you could use XQuery to create an Predicate in a Message Filter or as an Expression for a Recipient List.
from("queue:foo").filter(). xquery("//foo")). to("queue:bar")
You can also use functions inside your query, in which case you need an explicit type conversion (or you will get a org.w3c.dom.DOMException: HIERARCHY_REQUEST_ERR) by passing the Class as a second argument to the xquery() method.
from("direct:start"). recipientList().xquery("concat('mock:foo.', /person/@city)", String.class);
Variables
The IN message body will be set as the contextItem. Besides this these Variables is also added as parameters:
| Variable | Type | Description | Support version |
|---|---|---|---|
| exchange | Exchange | The current Exchange | |
| in.body | Object | The In message's body | >= 1.6.1 |
| out.body | Object | The OUT message's body (if any) | >= 1.6.1 |
| in.headers.* | Object | You can access the value of exchange.in.headers with key foo by using the variable which name is in.headers.foo | >=1.6.1 |
| out.headers.* | Object | You can access the value of exchange.out.headers with key foo by using the variable which name is out.headers.foo variable | >=1.6.1 |
| key name | Object | Any exchange.properties and exchange.in.headers (exchange.in.headers support was removed since camel 1.6.1) and any additional parameters set using setParameters(Map). These parameters is added with they own key name, for instance if there is an IN header with the key name foo then its added as foo. |
Using XML configuration
If you prefer to configure your routes in your Spring XML file then you can use XPath expressions as follows
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:foo="http://example.com/person" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="activemq:MyQueue"/> <filter> <xquery>/foo:person[@name='James']</xquery> <to uri="mqseries:SomeOtherQueue"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
Notice how we can reuse the namespace prefixes, foo in this case, in the XPath expression for easier namespace based XQuery expressions!
When you use functions in your XQuery expression you need an explicit type conversion which is done in the xml configuration via the @type attribute:
<xquery type="java.lang.String">concat('mock:foo.', /person/@city)</xquery>
Using XQuery as an endpoint
Sometimes an XQuery expression can be quite large; it can essentally be used for Templating. So you may want to use an XQuery Endpoint so you can route using XQuery templates.
The following example shows how to take a message of an ActiveMQ queue (MyQueue) and transform it using XQuery and send it to MQSeries.
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="activemq:MyQueue"/> <to uri="xquery:com/acme/someTransform.xquery"/> <to uri="mqseries:SomeOtherQueue"/> </route> </camelContext>
Examples
Here is a simple example using an XQuery expression as a predicate in a Message Filter
from("direct:start").filter().xquery("/person[@name='James']").to("mock:result");
This example uses XQuery with namespaces as a predicate in a Message Filter
Namespaces ns = new Namespaces("c", "http://acme.com/cheese"); from("direct:start"). filter().xquery("/c:person[@name='James']", ns). to("mock:result");
Learning XQuery
XQuery is a very powerful language for querying, searching, sorting and returning XML. For help learning XQuery try these tutorials
- Mike Kay's XQuery Primer
- the W3Schools XQuery Tutorial
You might also find the XQuery function reference useful
Dependencies
To use XQuery in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-saxon which implements the XQuery language.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-saxon</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency>
Pattern Appendix
There now follows a breakdown of the various Enterprise Integration Patterns that Camel supports
Messaging Systems
Message Channel
Camel supports the Message Channel from the EIP patterns. The Message Channel is an internal implementation detail of the Endpoint interface and all interactions with the Message Channel are via the Endpoint interfaces.
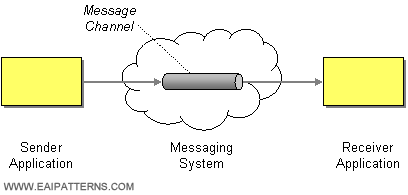
For more details see
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message
Camel supports the Message from the EIP patterns using the Message interface.
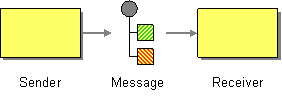
To support various message exchange patterns like one way Event Message and Request Reply messages Camel uses an Exchange interface which has a pattern property which can be set to InOnly for an Event Message which has a single inbound Message, or InOut for a Request Reply where there is an inbound and outbound message.
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Pipes and Filters
Camel supports the Pipes and Filters from the EIP patterns in various ways.
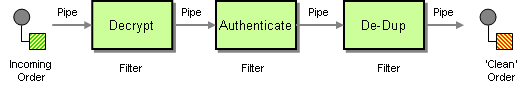
With Camel you can split your processing across multiple independent Endpoint instances which can then be chained together.
Using Routing Logic
You can create pipelines of logic using multiple Endpoint or Message Translator instances as follows
from("direct:a").pipeline("direct:x", "direct:y", "direct:z", "mock:result");
Though pipeline is the default mode of operation when you specify multiple outputs in Camel. The opposite to pipeline is multicast; which fires the same message into each of its outputs. (See the example below).
In Spring XML you can use the <pipeline/> element as of 1.4.0 onwards
<route> <from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/> <pipeline> <bean ref="foo"/> <bean ref="bar"/> <to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/> </pipeline> </route>
In the above the pipeline element is actually unnecessary, you could use this...
<route> <from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/> <bean ref="foo"/> <bean ref="bar"/> <to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/> </route>
Its just a bit more explicit. However if you wish to use <multicast/> to avoid a pipeline - to send the same message into multiple pipelines - then the <pipeline/> element comes into its own.
<route> <from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/> <multicast> <pipeline> <bean ref="something"/> <to uri="log:Something"/> </pipeline> <pipeline> <bean ref="foo"/> <bean ref="bar"/> <to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/> </pipeline> </multicast> </route>
In the above example we are routing from a single Endpoint to a list of different endpoints specified using URIs. If you find the above a bit confusing, try reading about the Architecture or try the Examples
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Router
The Message Router from the EIP patterns allows you to consume from an input destination, evaluate some predicate then choose the right output destination.
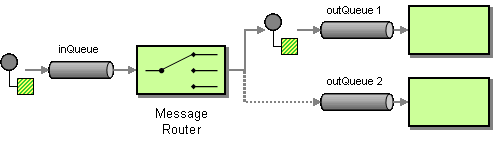
The following example shows how to route a request from an input queue:a endpoint to either queue:b, queue:c or queue:d depending on the evaluation of various Predicate expressions
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").choice().when(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b") .when(header("foo").isEqualTo("cheese")).to("seda:c").otherwise().to("seda:d"); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <choice> <when> <xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath> <to uri="seda:b"/> </when> <when> <xpath>$foo = 'cheese'</xpath> <to uri="seda:c"/> </when> <otherwise> <to uri="seda:d"/> </otherwise> </choice> </route> </camelContext>
Choice without otherwise
If you use a choice without adding an otherwise, any unmatched exchanges will be dropped by default. If you prefer to have an exception for an unmatched exchange, you can add a throwFault to the otherwise.
....otherwise().throwFault("No matching when clause found on choice block");
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Translator
Camel supports the Message Translator from the EIP patterns by using an arbitrary Processor in the routing logic, by using a bean to perform the transformation, or by using transform() in the DSL. You can also use a Data Format to marshal and unmarshal messages in different encodings.
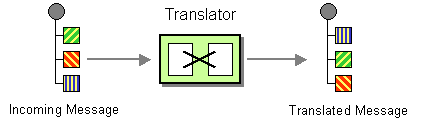
Using the Fluent Builders
You can transform a message using Camel's Bean Integration to call any method on a bean in your Registry such as your Spring XML configuration file as follows
from("activemq:SomeQueue"). beanRef("myTransformerBean", "myMethodName"). to("mqseries:AnotherQueue");
Where the "myTransformerBean" would be defined in a Spring XML file or defined in JNDI etc. You can omit the method name parameter from beanRef() and the Bean Integration will try to deduce the method to invoke from the message exchange.
or you can add your own explicit Processor to do the transformation
from("direct:start").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) { Message in = exchange.getIn(); in.setBody(in.getBody(String.class) + " World!"); } }).to("mock:result");
or you can use the DSL to explicitly configure the transformation
from("direct:start").transform(body().append(" World!")).to("mock:result");
Use Spring XML
You can also use Spring XML Extensions to do a transformation. Basically any Expression language can be substituted inside the transform element as shown below
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <transform> <simple>${in.body} extra data!</simple> </transform> <to uri="mock:end"/> </route> </camelContext>
Or you can use the Bean Integration to invoke a bean
<route> <from uri="activemq:Input"/> <bean ref="myBeanName" method="doTransform"/> <to uri="activemq:Output"/> </route>
You can also use Templating to consume a message from one destination, transform it with something like Velocity or XQuery and then send it on to another destination. For example using InOnly (one way messaging)
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
If you want to use InOut (request-reply) semantics to process requests on the My.Queue queue on ActiveMQ with a template generated response, then sending responses back to the JMSReplyTo Destination you could use this.
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm");
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the JUnit tests
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Endpoint
Camel supports the Message Endpoint from the EIP patterns using the Endpoint interface.
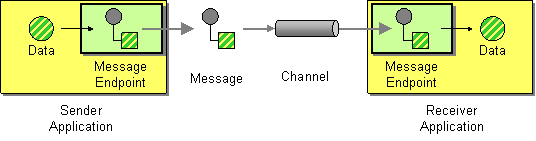
When using the DSL to create Routes you typically refer to Message Endpoints by their URIs rather than directly using the Endpoint interface. Its then a responsibility of the CamelContext to create and activate the necessary Endpoint instances using the available Component implementations.
For more details see
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Messaging Channels
Point to Point Channel
Camel supports the Point to Point Channel from the EIP patterns using the following components
- SEDA for in-VM seda based messaging
- JMS for working with JMS Queues for high performance, clustering and load balancing
- JPA for using a database as a simple message queue
- XMPP for point-to-point communication over XMPP (Jabber)
- and others
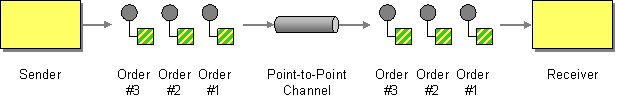
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Publish Subscribe Channel
Camel supports the Publish Subscribe Channel from the EIP patterns using the following components
- JMS for working with JMS Topics for high performance, clustering and load balancing
- XMPP when using rooms for group communication
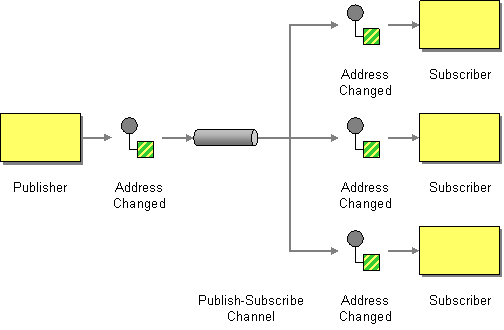
Using Routing Logic
Another option is to explicitly list the publish-subscribe relationship in your routing logic; this keeps the producer and consumer decoupled but lets you control the fine grained routing configuration using the DSL or Xml Configuration.
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").multicast().to("seda:b", "seda:c", "seda:d"); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <multicast> <to uri="seda:b"/> <to uri="seda:c"/> <to uri="seda:d"/> </multicast> </route> </camelContext>
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Dead Letter Channel
Camel supports the Dead Letter Channel from the EIP patterns using the DeadLetterChannel processor which is an Error Handler.
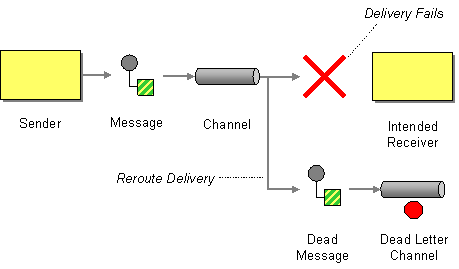
| Difference between Dead Letter Channel and Default Error Handler The major difference is that Dead Letter Channel has a dead letter queue that whenever an Exchange could not be processed is moved to. It will always moved failed exchanges to this queue. Unlike the Default Error Handler that does not have a dead letter queue. So whenever an Exchange could not be processed the error is propagated back to the client. Notice: You can adjust this behavior of whether the client should be notified or not with the handled option. |
Redelivery
It is common for a temporary outage or database deadlock to cause a message to fail to process; but the chances are if its tried a few more times with some time delay then it will complete fine. So we typically wish to use some kind of redelivery policy to decide how many times to try redeliver a message and how long to wait before redelivery attempts.
The RedeliveryPolicy defines how the message is to be redelivered. You can customize things like
- how many times a message is attempted to be redelivered before it is considered a failure and sent to the dead letter channel
- the initial redelivery timeout
- whether or not exponential backoff is used (i.e. the time between retries increases using a backoff multiplier)
- whether to use collision avoidance to add some randomness to the timings
- delay pattern a new option in Camel 2.0, see below for details.
Once all attempts at redelivering the message fails then the message is forwarded to the dead letter queue.
About moving Exchange to dead letter queue and using handled
Handled on Dead Letter Channel was introduced in Camel 2.0, this feature does not exist in Camel 1.x
When all attempts of redelivery have failed the Exchange is moved to the dead letter queue (the dead letter endpoint). The exchange is then complete and from the client point of view it was processed. As such the Dead Letter Channel have handled the Exchange.
For instance configuring the dead letter channel as:
errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("jms:queue:dead").maximumRedeliveries(3).redeliverDealy(5000));
The Dead Letter Channel above will clear the caused exception when the Exchange is moved to the jms:queue:dead destination and the client will not notice the failure.
By default handled is true.
How to let the client notice the error?
If you want to move the message to the dead letter queue and also let the client notice the error, then you can configure the Dead Letter Channel to not handle the error. For example:
errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("jms:queue:dead").maximumRedeliveries(3).redeliverDealy(5000).handled(false));
When all attempts of redelivery have failed the Exchange is moved to the dead letter queue (the dead letter endpoint). As the Dead Letter Channel
is configured to not handle it, it will mark the Exchange as failed so the client will be notified of this error.
| Handled See also Exception Clause for more details on the handled policy as this feature was first introduced here and thus we have more docuemntation and samples there. |
About moving Exchange to dead letter queue and using the original message
Available as of Camel 2.0
The option useOriginalMessage is used for routing the original input message instead of the current message that potentially is modified during routing.
For instance if you have this route:
from("jms:queue:order:input") .to("bean:validateOrder"); .to("bean:transformOrder") .to("bean:handleOrder");
The route listen for JMS messages and validates, transforms and handle it. During this the Exchange payload is transformed/modified. So in case something goes wrong and we want to move the message to another JMS destination, then we can configure our Dead Letter Channel with the useOriginalBody option. But when we move the Exchange to this destination we do not know in which state the message is in. Did the error happen in before the transformOrder or after? So to be sure we want to move the original input message we received from jms:queue:order:input. So we can do this by enabling the useOriginalMessage option as shown below:
// will use original body
errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("jms:queue:dead")
.useOriginalMessage().mamimumRedeliveries(5).redeliverDelay(5000);
Then the messages routed to the jms:queue:dead is the original input. If we want to manually retry we can move the JMS message from the failed to the input queue, with no problem as the message is the same as the original we received.
OnRedelivery
Available in Camel 1.6.0 onwards
When Dead Letter Channel is doing redeliver its possible to configure a Processor that is executed just before every redelivery attempt. This can be used for the situations where you need to alter the message before its redelivered. See below for sample.
| onException and onRedeliver In Camel 2.0 we also added support for per onException to set a onRedeliver. That means you can do special on redelivery for different exceptions, as opposed to onRedelivery set on Dead Letter Channel can be viewed as a global scope. |
Redelivery default values
In Camel 2.0 redelivery is disabled by default, as opposed to Camel 1.x in which Dead Letter Channel is configured with maximumRedeliveries=5.
The default redeliver policy will use the following values:
- maximumRedeliveries=0 (in Camel 1.x the default value is 5)
- redeliverDelay=1000L (1 second, new as of Camel 2.0)
- use initialRedeliveryDelay for previous versions
- maximumRedeliveryDelay = 60 * 1000L (60 seconds)
- And the exponential backoff and collision avoidance is turned off.
- The retriesExhaustedLogLevel and retryAttemptedLogLevel are set to LoggingLevel.DEBUG
- Stack traces is not logged
The maximum redeliver delay ensures that a delay is never longer than the value, default 1 minute. This can happen if you turn on the exponential backoff.
The maximum redeliveries is the number of re delivery attempts. By default Camel will try to process the exchange 1 + 5 times. 1 time for the normal attempt and then 5 attempts as redeliveries.
Setting the maximumRedeliveries to a negative value such as -1 will then always redelivery (unlimited).
Setting the maximumRedeliveries to 0 will disable any re delivery attempt.
Camel will log delivery failures at the DEBUG logging level by default. You can change this by specifying retriesExhaustedLogLevel and/or retryAttemptedLogLevel. See ExceptionBuilderWithRetryLoggingLevelSetTest for an example.
In Camel 2.0 you can turn logging of stack traces on/off. If turned off Camel will still log the redelivery attempt. Its just much less verbose.
Redeliver Delay Pattern
Available as of Camel 2.0
Delay pattern is used as a single option to set a range pattern for delays. If used then the following options does not apply: (delay, backOffMultiplier, useExponentialBackOff, useCollisionAvoidance, maximumRedeliveryDelay).
The idea is to set groups of ranges using the following syntax: limit:delay;limit 2:delay 2;limit 3:delay 3;...;limit N:delay N
Each group has two values separated with colon
- limit = upper limit
- delay = delay in millis
And the groups is again separated with semi colon.
The rule of thumb is that the next groups should have a higher limit than the previous group.
Lets clarify this with an example:
delayPattern=5:1000;10:5000;20:20000
That gives us 3 groups:
- 5:1000
- 10:5000
- 20:20000
Resulting in these delays for redelivery attempt:
- Attempt number 0..4 = 0 millis (as the first group start with 5)
- Attempt number 5..9 = 1000 millis (the first group)
- Attempt number 10..19 = 5000 millis (the second group)
- Attempt number 20.. = 20000 millis (the last group)
You can start a group with limit 0 to eg have a starting delay: delayPattern=0:1000;5:5000
- Attempt number 0..4 = 1000 millis (the first group)
- Attempt number 5.. = 5000 millis (the last group)
There is no requirement that the next delay should be higher than the previous. You can use any delay value you like. For example with delayPattern=0:5000;3:1000 we start with 5 sec delay and then later reduce that to 1 second.
Redelivery header
When a message is redelivered the DeadLetterChannel will append a customizable header to the message to indicate how many times its been redelivered.
In Camel 1.x: The header is org.apache.camel.redeliveryCount.
In Camel 2.0: The header is CamelRedeliveryCount.
And a boolean flag whether it is being redelivered or not (first attempt)
In Camel 1.x: The header org.apache.camel.Redelivered contains a boolean if the message is redelivered or not.
In Camel 2.0: The header CamelRedelivered contains a boolean if the message is redelivered or not.
Which endpoint failed
Available as of Camel 2.1
When Camel routes messages it will decorate the Exchange with a property that contains the last endpoint Camel send the Exchange to:
String lastEndpointUri = exchange.getProperty(Exchange.TO_ENDPOINT, String.class);
The Exchange.TO_ENDPOINT have the constant value CamelToEndpoint.
This information is updated when Camel sends a message to any endpoint. So if it exists its the last endpoint which Camel send the Exchange to.
When for example processing the Exchange at a given Endpoint and the message is to be moved into the dead letter queue, then Camel also decorates the Exchange with another property that contains that last endpoint:
String failedEndpointUri = exchange.getProperty(Exchange.FAILURE_ENDPOINT, String.class);
The Exchange.FAILURE_ENDPOINT have the constant value CamelFailureEndpoint.
This allows for example you to fetch this information in your dead letter queue and use that for error reporting.
This is useable if the Camel route is a bit dynamic such as the dynamic Recipient List so you know which endpoints failed.
Notice: These information is kept on the Exchange even if the message was successfully processed by a given endpoint, and then later fails for example in a local Bean processing instead. So beware that this is a hint that helps pinpoint errors.
from("activemq:queue:foo") .to("http://someserver/somepath") .beanRef("foo");
Now suppose the route above and a failure happens in the foo bean. Then the Exchange.TO_ENDPOINT and Exchange.FAILURE_ENDPOINT will still contain the value of http://someserver/somepath.
Samples
The following example shows how to configure the Dead Letter Channel configuration using the DSL
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { // using dead letter channel with a seda queue for errors errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("seda:errors")); // here is our route from("seda:a").to("seda:b"); } };
You can also configure the RedeliveryPolicy as this example shows
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { // configures dead letter channel to use seda queue for errors and use at most 2 redelveries // and exponential backoff errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("seda:errors").maximumRedeliveries(2).useExponentialBackOff()); // here is our route from("seda:a").to("seda:b"); } };
How can I modify the Exchange before redelivery?
In Camel 1.6.0 we added support directly in Dead Letter Channel to set a Processor that is executed before each redelivery attempt.
When Dead Letter Channel is doing redeliver its possible to configure a Processor that is executed just before every redelivery attempt. This can be used for the situations where you need to alter the message before its redelivered.
Here we configure the Dead Letter Channel to use our processor MyRedeliveryProcessor to be executed before each redelivery.
// we configure our Dead Letter Channel to invoke // MyRedeliveryProcessor before a redelivery is // attempted. This allows us to alter the message before errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error").maximumRedeliveries(5) .onRedelivery(new MyRedeliverPrcessor()) // setting delay to zero is just to make unit teting faster .redeliverDelay(0L));
And this is the processor MyRedeliveryProcessor where we alter the message.
// This is our processor that is executed before every redelivery attempt // here we can do what we want in the java code, such as altering the message public class MyRedeliverPrcessor implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { // the message is being redelivered so we can alter it // we just append the redelivery counter to the body // you can of course do all kind of stuff instead String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); int count = exchange.getIn().getHeader("CamelRedeliveryCounter", Integer.class); exchange.getIn().setBody(body + count); } }
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Guaranteed Delivery
Camel supports the Guaranteed Delivery from the EIP patterns using the following components
- File for using file systems as a persistent store of messages
- JMS when using persistent delivery (the default) for working with JMS Queues and Topics for high performance, clustering and load balancing
- JPA for using a database as a persistence layer
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Bus
Camel supports the Message Bus from the EIP patterns. You could view Camel as a Message Bus itself as it allows producers and consumers to be decoupled.
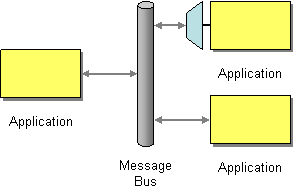
Folks often assume that a Message Bus is a JMS though so you may wish to refer to the JMS component for traditional MOM support.
Also worthy of node is the XMPP component for supporting messaging over XMPP (Jabber)
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Routing
Content Based Router
The Content Based Router from the EIP patterns allows you to route messages to the correct destination based on the contents of the message exchanges.
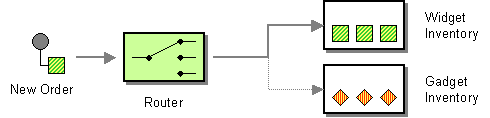
The following example shows how to route a request from an input seda:a endpoint to either seda:b, seda:c or seda:d depending on the evaluation of various Predicate expressions
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").choice().when(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b") .when(header("foo").isEqualTo("cheese")).to("seda:c").otherwise().to("seda:d"); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <choice> <when> <xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath> <to uri="seda:b"/> </when> <when> <xpath>$foo = 'cheese'</xpath> <to uri="seda:c"/> </when> <otherwise> <to uri="seda:d"/> </otherwise> </choice> </route> </camelContext>
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at the junit test case
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Filter
The Message Filter from the EIP patterns allows you to filter messages
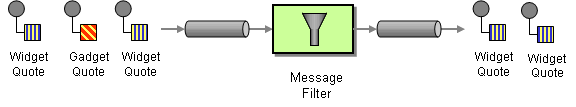
The following example shows how to create a Message Filter route consuming messages from an endpoint called queue:a which if the Predicate is true will be dispatched to queue:b
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b"); } };
You can of course use many different Predicate languages such as XPath, XQuery, SQL or various Scripting Languages. Here is an XPath example
from("direct:start"). filter().xpath("/person[@name='James']"). to("mock:result");
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <filter> <xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath> <to uri="seda:b"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext>
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at the junit test case
Using stop
Available as of Camel 2.0
Stop is a bit different than a message filter as it will filter out all messages. Stop is convenient to use in a Content Based Router when you for example need to stop further processing in one of the predicates.
In the example below we do not want to route messages any further that has the word Bye in the message body. Notice how we prevent this in the when predicate by using the .stop().
from("direct:start") .choice() .when(body().contains("Hello")).to("mock:hello") .when(body().contains("Bye")).to("mock:bye").stop() .otherwise().to("mock:other") .end() .to("mock:result");
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Recipient List
The Recipient List from the EIP patterns allows you to route messages to a number of dynamically specified recipients.
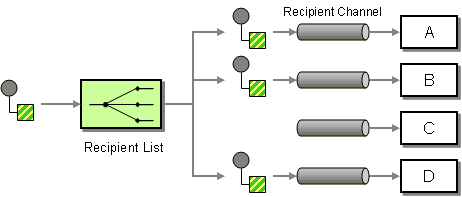
Static Recipient List
The following example shows how to route a request from an input queue:a endpoint to a static list of destinations
Using Annotations
You can use the RecipientList Annotation on a POJO to create a Dynamic Recipient List. For more details see the Bean Integration.
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").multicast().to("seda:b", "seda:c", "seda:d"); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <multicast> <to uri="seda:b"/> <to uri="seda:c"/> <to uri="seda:d"/> </multicast> </route> </camelContext>
Dynamic Recipient List
Usually one of the main reasons for using the Recipient List pattern is that the list of recipients is dynamic and calculated at runtime. The following example demonstrates how to create a dynamic recipient list using an Expression (which in this case it extracts a named header value dynamically) to calculate the list of endpoints which are either of type Endpoint or are converted to a String and then resolved using the endpoint URIs.
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").recipientList(header("foo")); } };
The above assumes that the header contains a list of endpoint URIs. The following takes a single string header and tokenizes it
from("direct:a").recipientList( header("recipientListHeader").tokenize(","));
Iteratable value
The dynamic list of recipients that are defined in the header must be iteratable such as:
- java.util.Collection
- java.util.Iterator
- arrays
- org.w3c.dom.NodeList
- Camel 1.5.1: a single String with values separated with comma
- any other type will be regarded as a single value
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <recipientList> <xpath>$foo</xpath> </recipientList> </route> </camelContext>
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the junit test case
Using delimiter in Spring XML
Available as of Camel 1.5.1
In Spring DSL you can set the delimiter attribute for setting a delimiter to be used if the header value is a single String with multiple separated endpoints. By default Camel uses comma as delimiter, but this option lets you specify a customer delimiter to use instead.
<route> <from uri="direct:a" /> <!-- use comma as a delimiter for String based values --> <recipientList delimiter=","> <header>myHeader</header> </recipientList> </route>
So if myHeader contains a String with the value "activemq:queue:foo, activemq:topic:hello , log:bar" then Camel will split the String using the delimiter given in the XML that was comma, resulting into 3 endpoints to send to. You can use spaces between the endpoints as Camel will trim the value when it lookup the endpoint to send to.
Note: In Java DSL you use the tokenizer to archive the same. The route above in Java DSL:
from("direct:a").recipientList(header("myHeader").tokenize(","));
In Camel 2.1 its a bit easier as you can pass in the delimiter as 2nd parameter:
from("direct:a").recipientList(header("myHeader"), "#");
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Splitter
The Splitter from the EIP patterns allows you split a message into a number of pieces and process them individually
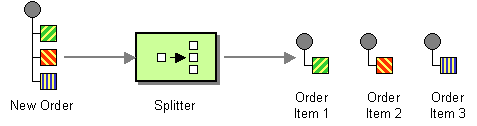
As of Camel 2.0, you need to specify a Splitter as split(). In earlier versions of Camel, you need to use splitter().
| What does the splitter return? The Splitter will by default return the last splitted message. You can override this by suppling your own strategy as an AggregationStrategy. There is a sample on this page (Split aggregate request/reply sample). Notice its the same strategy as the Aggregator supports. This Splitter can be viewed as having a build in light weight Aggregator. |
Example
The following example shows how to take a request from the queue:a endpoint the split it into pieces using an Expression, then forward each piece to queue:b
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").split(body(String.class).tokenize("\n")).to("seda:b"); } };
The splitter can use any Expression language so you could use any of the Languages Supported such as XPath, XQuery, SQL or one of the Scripting Languages to perform the split. e.g.
from("activemq:my.queue").split(xpath("//foo/bar")).convertBodyTo(String.class).to("file://some/directory")
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <split> <xpath>/invoice/lineItems</xpath> <to uri="seda:b"/> </split> </route> </camelContext>
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the junit test case
Using Tokenizer from Spring XML Extensions
Avaiaible as of Camel 2.0
You can use the tokenizer expression in the Spring DSL to split bodies or headers using a token. This is a common use-case, so we provided a special tokenizer tag for this.
In the sample below we split the body using a @ as separator. You can of course use comma or space or even a regex pattern, also set regex=true.
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <split> <tokenize token="@"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </split> </route> </camelContext>
Splitting the body in Spring XML is a bit harder as you need to use the Simple language to dictate this
<split> <simple>${body}</simple> <to uri="mock:result"/> </split>
Message Headers
The following headers is set on each Exchange that are split:
| header | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.splitCounter | int | Camel 1.x: A split counter that increases for each Exchange being split. The counter starts from 0. |
| org.apache.camel.splitSize | int | Camel 1.x: The total number of Exchanges that was splitted. This header is not applied for stream based splitting. |
Exchange properties
The following properties is set on each Exchange that are split:
| header | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.splitCounter | int | Camel 1.6.2: A split counter that increases for each Exchange being split. The counter starts from 0. |
| org.apache.camel.splitSize | int | Camel 1.6.2: The total number of Exchanges that was splitted. This header is not applied for stream based splitting. |
| CamelSplitIndex | int | Camel 2.0: A split counter that increases for each Exchange being split. The counter starts from 0. |
| CamelSplitSize | int | Camel 2.0: The total number of Exchanges that was splitted. This header is not applied for stream based splitting. |
Parallel execution of distinct 'parts'
If you want to execute all parts in parallel you can use special notation of split() with two arguments, where the second one is a boolean flag if processing should be parallel. e.g.
XPathBuilder xPathBuilder = new XPathBuilder("//foo/bar"); from("activemq:my.queue").split(xPathBuilder, true).to("activemq:my.parts");
In Camel 2.0 the boolean option has been refactored into a builder method parallelProcessing so its easier to understand what the route does when we use a method instead of true|false.
XPathBuilder xPathBuilder = new XPathBuilder("//foo/bar"); from("activemq:my.queue").split(xPathBuilder).parallelProcessing().to("activemq:my.parts");
Stream based
Available as of Camel 1.5
You can split streams by enabling the streaming mode using the streaming builder method.
from("direct:streaming").split(body().tokenize(",")).streaming().to("activemq:my.parts");
Specifying a custom aggregation strategy
Available as of Camel 2.0
This is specified similar to the Aggregator.
Specifying a custom ThreadPoolExecutor
You can customize the underlying ThreadPoolExecutor used in the parallel splitter. In the Java DSL try something like this:
XPathBuilder xPathBuilder = new XPathBuilder("//foo/bar"); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(8, 16, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue()); from("activemq:my.queue").split(xPathBuilder, true, threadPoolExecutor).to("activemq:my.parts");
In the Spring DSL try this:
Available as of Camel 1.6.0
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:parallel-custom-pool"/> <split executorServiceRef="threadPoolExecutor"> <xpath>/invoice/lineItems</xpath> <to uri="mock:result"/> </split> </route> </camelContext> <!-- There's an easier way of specifying constructor args, just can't remember it at the moment... old Spring syntax will do for now! --> <bean id="threadPoolExecutor" class="java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="8"/> <constructor-arg index="1" value="16"/> <constructor-arg index="2" value="0"/> <constructor-arg index="3" value="MILLISECONDS"/> <constructor-arg index="4"><bean class="java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue"/></constructor-arg> </bean>
Using a Pojo to do the splitting
As the Splitter can use any Expression to do the actual splitting we leverage this fact and use a method expression to invoke a Bean to get the splitted parts.
The Bean should return a value that is iterable such as: java.util.Collection, java.util.Iterator or an array.
In the route we define the Expression as a method call to invoke our Bean that we have registered with the id mySplitterBean in the Registry.
from("direct:body") // here we use a POJO bean mySplitterBean to do the split of the payload .split().method("mySplitterBean", "splitBody") .to("mock:result"); from("direct:message") // here we use a POJO bean mySplitterBean to do the split of the message // with a certain header value .split().method("mySplitterBean", "splitMessage") .to("mock:result");
And the logic for our Bean is as simple as. Notice we use Camel Bean Binding to pass in the message body as a String object.
public class MySplitterBean { /** * The split body method returns something that is iteratable such as a java.util.List. * * @param body the payload of the incoming message * @return a list containing each part splitted */ public List<String> splitBody(String body) { // since this is based on an unit test you can of couse // use different logic for splitting as Camel have out // of the box support for splitting a String based on comma // but this is for show and tell, since this is java code // you have the full power how you like to split your messages List<String> answer = new ArrayList<String>(); String[] parts = body.split(","); for (String part : parts) { answer.add(part); } return answer; } /** * The split message method returns something that is iteratable such as a java.util.List. * * @param header the header of the incoming message with the name user * @param body the payload of the incoming message * @return a list containing each part splitted */ public List<Message> splitMessage(@Header(value = "user") String header, @Body String body) { // we can leverage the Parameter Binding Annotations // http://camel.apache.org/parameter-binding-annotations.html // to access the message header and body at same time, // then create the message that we want, splitter will // take care rest of them. // *NOTE* this feature requires Camel version >= 1.6.1 List<Message> answer = new ArrayList<Message>(); String[] parts = header.split(","); for (String part : parts) { DefaultMessage message = new DefaultMessage(); message.setHeader("user", part); message.setBody(body); answer.add(message); } return answer; } }
Split aggregate request/reply sample
This sample shows how you can split an Exchange, process each splitted message, aggregate and return a combined response to the original caller using request/reply.
The route below illustrates this and how the split supports a aggregationStrategy to hold the in progress processed messages:
// this routes starts from the direct:start endpoint // the body is then splitted based on @ separator // the splitter in Camel supports InOut as well and for that we need // to be able to aggregate what response we need to send back, so we provide our // own strategy with the class MyOrderStrategy. from("direct:start") .split(body().tokenize("@"), new MyOrderStrategy()) // each splitted message is then send to this bean where we can process it .to("bean:MyOrderService?method=handleOrder") // this is important to end the splitter route as we do not want to do more routing // on each splitted message .end() // after we have splitted and handled each message we want to send a single combined // response back to the original caller, so we let this bean build it for us // this bean will receive the result of the aggregate strategy: MyOrderStrategy .to("bean:MyOrderService?method=buildCombinedResponse")
And the OrderService bean is as follows:
public static class MyOrderService { private static int counter; /** * We just handle the order by returning a id line for the order */ public String handleOrder(String line) { LOG.debug("HandleOrder: " + line); return "(id=" + ++counter + ",item=" + line + ")"; } /** * We use the same bean for building the combined response to send * back to the original caller */ public String buildCombinedResponse(String line) { LOG.debug("BuildCombinedResponse: " + line); return "Response[" + line + "]"; } }
And our custom aggregationStrategy that is responsible for holding the in progress aggregated message that after the splitter is ended will be sent to the buildCombinedResponse method for final processing before the combined response can be returned to the waiting caller.
/** * This is our own order aggregation strategy where we can control * how each splitted message should be combined. As we do not want to * loos any message we copy from the new to the old to preserve the * order lines as long we process them */ public static class MyOrderStrategy implements AggregationStrategy { public Exchange aggregate(Exchange oldExchange, Exchange newExchange) { // put order together in old exchange by adding the order from new exchange if (oldExchange == null) { // the first time we aggregate we only have the new exchange, // so we just return it return newExchange; } String orders = oldExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); String newLine = newExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); LOG.debug("Aggregate old orders: " + orders); LOG.debug("Aggregate new order: " + newLine); // put orders together separating by semi colon orders = orders + ";" + newLine; // put combined order back on old to preserve it oldExchange.getIn().setBody(orders); // return old as this is the one that has all the orders gathered until now return oldExchange; } }
So lets run the sample and see how it works.
We send an Exchange to the direct:start endpoint containing a IN body with the String value: A@B@C. The flow is:
HandleOrder: A HandleOrder: B Aggregate old orders: (id=1,item=A) Aggregate new order: (id=2,item=B) HandleOrder: C Aggregate old orders: (id=1,item=A);(id=2,item=B) Aggregate new order: (id=3,item=C) BuildCombinedResponse: (id=1,item=A);(id=2,item=B);(id=3,item=C) Response to caller: Response[(id=1,item=A);(id=2,item=B);(id=3,item=C)]
Stop processing in case of exception
Available as of Camel 2.1
The Splitter will by default continue to process the entire Exchange even in case of one of the splitted message will thrown an exception during routing.
For example if you have an Exchange with 1000 rows that you split and route each sub message. During processing of these sub messages an exception is thrown at the 17th. What Camel does by default is to process the remainder 983 messages. You have the chance to remedy or handle this in the AggregationStrategy.
But sometimes you just want Camel to stop and let the exception be propagated back, and let the Camel error handler handle it. You can do this in Camel 2.1 by specifying that it should stop in case of an exception occurred. This is done by the stopOnException option as shown below:
from("direct:start")
.split(body().tokenize(",")).stopOnException()
.process(new MyProcessor())
.to("mock:split");
And using XML DSL you specify it as follows:
<route>
<from uri="direct:start"/>
<split stopOnException="true">
<tokenize token=","/>
<process ref="myProcessor"/>
<to uri="mock:split"/>
</split>
</route>
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Resequencer
The Resequencer from the EIP patterns allows you to reorganise messages based on some comparator. By default in Camel we use an Expression to create the comparator; so that you can compare by a message header or the body or a piece of a message etc.
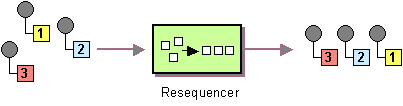
Camel supports two resequencing algorithms:
- Batch resequencing collects messages into a batch, sorts the messages and sends them to their output.
- Stream resequencing re-orders (continuous) message streams based on the detection of gaps between messages.
Batch Resequencing
The following example shows how to use the batch-processing resequencer so that messages are sorted in order of the body() expression. That is messages are collected into a batch (either by a maximum number of messages per batch or using a timeout) then they are sorted in order and then sent out to their output.
Using the Fluent Builders
from("direct:start").resequencer(body()).to("mock:result");
This is equvalent to
from("direct:start").resequencer(body()).batch().to("mock:result");
The batch-processing resequencer can be further configured via the size() and timeout() methods.
from("direct:start").resequencer(body()).batch().size(300).timeout(4000L).to("mock:result")
This sets the batch size to 300 and the batch timeout to 4000 ms (by default, the batch size is 100 and the timeout is 1000 ms). Alternatively, you can provide a configuration object.
from("direct:start").resequencer(body()).batch(new BatchResequencerConfig(300, 4000L)).to("mock:result")
So the above example will reorder messages from endpoint direct:a in order of their bodies, to the endpoint mock:result. Typically you'd use a header rather than the body to order things; or maybe a part of the body. So you could replace this expression with
resequencer(header("JMSPriority"))
for example to reorder messages using their JMS priority.
You can of course use many different Expression languages such as XPath, XQuery, SQL or various Scripting Languages.
You can also use multiple expressions; so you could for example sort by priority first then some other custom header
resequencer(header("JMSPriority"), header("MyCustomerRating"))
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start" /> <resequencer> <simple>body</simple> <to uri="mock:result" /> <!-- batch-config can be ommitted for default (batch) resequencer settings --> <batch-config batchSize="300" batchTimeout="4000" /> </resequencer> </route> </camelContext>
Stream Resequencing
The next example shows how to use the stream-processing resequencer. Messages are re-ordered based on their sequence numbers given by a seqnum header using gap detection and timeouts on the level of individual messages.
Using the Fluent Builders
from("direct:start").resequencer(header("seqnum")).stream().to("mock:result");
The stream-processing resequencer can be further configured via the capacity() and timeout() methods.
from("direct:start").resequencer(header("seqnum")).stream().capacity(5000).timeout(4000L).to("mock:result")
This sets the resequencer's capacity to 5000 and the timeout to 4000 ms (by default, the capacity is 100 and the timeout is 1000 ms). Alternatively, you can provide a configuration object.
from("direct:start").resequencer(header("seqnum")).stream(new StreamResequencerConfig(5000, 4000L)).to("mock:result")
The stream-processing resequencer algorithm is based on the detection of gaps in a message stream rather than on a fixed batch size. Gap detection in combination with timeouts removes the constraint of having to know the number of messages of a sequence (i.e. the batch size) in advance. Messages must contain a unique sequence number for which a predecessor and a successor is known. For example a message with the sequence number 3 has a predecessor message with the sequence number 2 and a successor message with the sequence number 4. The message sequence 2,3,5 has a gap because the sucessor of 3 is missing. The resequencer therefore has to retain message 5 until message 4 arrives (or a timeout occurs).
If the maximum time difference between messages (with successor/predecessor relationship with respect to the sequence number) in a message stream is known, then the resequencer's timeout parameter should be set to this value. In this case it is guaranteed that all messages of a stream are delivered in correct order to the next processor. The lower the timeout value is compared to the out-of-sequence time difference the higher is the probability for out-of-sequence messages delivered by this resequencer. Large timeout values should be supported by sufficiently high capacity values. The capacity parameter is used to prevent the resequencer from running out of memory.
By default, the stream resequencer expects long sequence numbers but other sequence numbers types can be supported as well by providing a custom comparator via the comparator() method
ExpressionResultComparator<Exchange> comparator = new MyComparator(); from("direct:start").resequencer(header("seqnum")).stream().comparator(comparator).to("mock:result");
or via a StreamResequencerConfig object.
ExpressionResultComparator<Exchange> comparator = new MyComparator(); StreamResequencerConfig config = new StreamResequencerConfig(100, 1000L, comparator); from("direct:start").resequencer(header("seqnum")).stream(config).to("mock:result");
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <resequencer> <simple>in.header.seqnum</simple> <to uri="mock:result" /> <stream-config capacity="5000" timeout="4000"/> </resequencer> </route> </camelContext>
Further Examples
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at the batch-processing resequencer junit test case and the stream-processing resequencer junit test case
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Transformation
Content Enricher
Camel supports the Content Enricher from the EIP patterns using a Message Translator, an artibrary Processor in the routing logic or using the enrich DSL element to enrich the message.
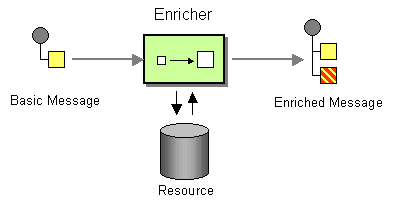
Content enrichment using a Message Translator or a Processor
Using the Fluent Builders
You can use Templating to consume a message from one destination, transform it with something like Velocity or XQuery and then send it on to another destination. For example using InOnly (one way messaging)
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
If you want to use InOut (request-reply) semantics to process requests on the My.Queue queue on ActiveMQ with a template generated response, then sending responses back to the JMSReplyTo Destination you could use this.
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm");
Here is a simple example using the DSL directly to transform the message body
from("direct:start").setBody(body().append(" World!")).to("mock:result");
In this example we add our own Processor using explicit Java code
from("direct:start").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) { Message in = exchange.getIn(); in.setBody(in.getBody(String.class) + " World!"); } }).to("mock:result");
Finally we can use Bean Integration to use any Java method on any bean to act as the transformer
from("activemq:My.Queue"). beanRef("myBeanName", "myMethodName"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the JUnit tests
Using Spring XML
<route> <from uri="activemq:Input"/> <bean ref="myBeanName" method="doTransform"/> <to uri="activemq:Output"/> </route>
Content enrichment using the enrich DSL element
Camel comes with two flavors of content enricher in the DSL
- enrich
- pollEnrich
enrich is using a [Producer] to obtain the additional data. It is usually used for Request Reply messaging, for instance to invoke an external web service.
poolEnrich on the other hand is using a Polling Consumer to obtain the additional data. It is usually used for Event Message messaging, for instance to read a file or download a FTP file.
This feature is available since Camel 2.0
Using the Fluent Builders
AggregationStrategy aggregationStrategy = ... from("direct:start") .enrich("direct:resource", aggregationStrategy) .to("direct:result"); from("direct:resource") ...
The content enricher (enrich) retrieves additional data from a resource endpoint in order to enrich an incoming message (contained in the orginal exchange). An aggregation strategy is used to combine the original exchange and the resource exchange. The first parameter of the AggregationStrategy.aggregate(Exchange, Exchange) method corresponds to the the original exchange, the second parameter the resource exchange. The results from the resource endpoint are stored in the resource exchange's out-message. Here's an example template for implementing an aggregation strategy.
public class ExampleAggregationStrategy implements AggregationStrategy { public Exchange aggregate(Exchange original, Exchange resource) { Object originalBody = original.getIn().getBody(); Object resourceResponse = resource.getOut().getBody(); Object mergeResult = ... // combine original body and resource response if (original.getPattern().isOutCapable()) { original.getOut().setBody(mergeResult); } else { original.getIn().setBody(mergeResult); } return original; } }
Using this template the original exchange can be of any pattern. The resource exchange created by the enricher is always an in-out exchange.
Using Spring XML
The same example in the Spring DSL
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <enrich uri="direct:resource" strategyRef="aggregationStrategy"/> <to uri="direct:result"/> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:resource"/> ... </route> </camelContext> <bean id="aggregationStrategy" class="..." />
Aggregation strategy is optional
The aggregation strategy is optional. If you do not provide it Camel will by default just use the body obtained from the resource.
from("direct:start") .enrich("direct:resource") .to("direct:result");
In the route above the message send to the direct:result endpoint will contain the output from the direct:resource as we do not use any custom aggregation.
And in Spring DSL you just omit the strategyRef attribute:
<route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <enrich uri="direct:resource"/> <to uri="direct:result"/> </route>
Content enrich using pollEnrich
The pollEnrich works just as the enrich however as it uses a Polling Consumer we have 3 methods when polling
- receive
- receiveNoWait
- receive(timeout)
By default Camel will use the receiveNoWait.
If there is no data then the newExchange in the aggregation strategy is null.
You can pass in a timeout value that determines which method to use
- timeout is -1 or negative then receive is selected
- timeout is 0 then receiveNoWait is selected
- otherwise receive(timeout) is selected
The timeout values is in millis.
The sample below reads a file based on a JMS message that contains a header with the filename.
from("activemq:queue:order") .setHeader(Exchange.FILE_NAME, header("orderId")) .pollEnrich("file://order/data/additional") .to("bean:processOrder");
And if we want to wait at most 20 seconds for the file to be ready we can use a timeout:
from("activemq:queue:order") .setHeader(Exchange.FILE_NAME, header("orderId")) .pollEnrich("file://order/data/additional", 20000) .to("bean:processOrder");
And yes pollEnrich also supports the aggregation strategy so we can pass it in as an argument too:
.pollEnrich("file://order/data/additional", 20000, aggregationStrategy)
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Content Filter
Camel supports the Content Filter from the EIP patterns using one of the following mechanisms in the routing logic to transform content from the inbound message.
- Message Translator
- invoking a Java bean
- Processor object
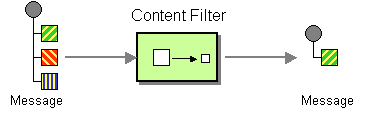
A common way to filter messages is to use an Expression in the DSL like XQuery, SQL or one of the supported Scripting Languages.
Using the Fluent Builders
Here is a simple example using the DSL directly
from("direct:start").setBody(body().append(" World!")).to("mock:result");
In this example we add our own Processor
from("direct:start").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) { Message in = exchange.getIn(); in.setBody(in.getBody(String.class) + " World!"); } }).to("mock:result");
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the JUnit tests
Using Spring XML
<route> <from uri="activemq:Input"/> <bean ref="myBeanName" method="doTransform"/> <to uri="activemq:Output"/> </route>
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Normalizer
Camel supports the Normalizer from the EIP patterns by using a Message Router in front of a number of Message Translator instances.
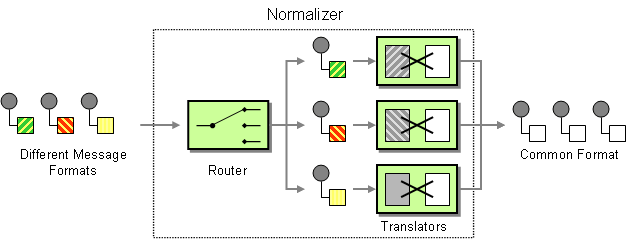
Example
This example shows a Message Normalizer that converts two types of XML messages into a common format. Messages in this common format are then filtered.
Using the Fluent Builders
// we need to normalize two types of incoming messages from("direct:start") .choice() .when().xpath("/employee").to("bean:normalizer?method=employeeToPerson") .when().xpath("/customer").to("bean:normalizer?method=customerToPerson") .end() .to("mock:result");
In this case we're using a Java bean as the normalizer. The class looks like this
public class MyNormalizer { public void employeeToPerson(Exchange exchange, @XPath("/employee/name/text()") String name) { exchange.getOut().setBody(createPerson(name)); } public void customerToPerson(Exchange exchange, @XPath("/customer/@name") String name) { exchange.getOut().setBody(createPerson(name)); } private String createPerson(String name) { return "<person name=\"" + name + "\"/>"; } }
Using the Spring XML Extensions
The same example in the Spring DSL
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <choice> <when> <xpath>/employee</xpath> <to uri="bean:normalizer?method=employeeToPerson"/> </when> <when> <xpath>/customer</xpath> <to uri="bean:normalizer?method=customerToPerson"/> </when> </choice> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext> <bean id="normalizer" class="org.apache.camel.processor.MyNormalizer"/>
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Messaging Endpoints
Messaging Mapper
Camel supports the Messaging Mapper from the EIP patterns by using either Message Translator pattern or the Type Converter module.

See also
- Message Translator
- Type Converter
- CXF for JAX-WS support for binding business logic to messaging & web services
- Pojo
- Bean
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Event Driven Consumer
Camel supports the Event Driven Consumer from the EIP patterns. The default consumer model is event based (i.e. asynchronous) as this means that the Camel container can then manage pooling, threading and concurrency for you in a declarative manner.
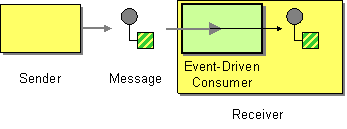
The Event Driven Consumer is implemented by consumers implementing the Processor interface which is invoked by the Message Endpoint when a Message is available for processing.
For more details see
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Polling Consumer
Camel supports implementing the Polling Consumer from the EIP patterns using the PollingConsumer interface which can be created via the Endpoint.createPollingConsumer() method.
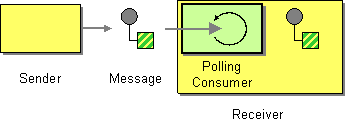
So in your Java code you can do
Endpoint endpoint = context.getEndpoint("activemq:my.queue");
PollingConsumer consumer = endpoint.createPollingConsumer();
Exchange exchange = consumer.receive();
Notice in Camel 2.0 we have introduced the ConsumerTemplate.
There are 3 main polling methods on PollingConsumer
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
| receive() | Waits until a message is available and then returns it; potentially blocking forever |
| receive(long) | Attempts to receive a message exchange, waiting up to the given timeout and returning null if no message exchange could be received within the time available |
| receiveNoWait() | Attempts to receive a message exchange immediately without waiting and returning null if a message exchange is not available yet |
ConsumerTemplate
Available as of Camel 2.0
The ConsumerTemplate is a template much like Spring's JmsTemplate or JdbcTemplate supporting the Polling Consumer EIP. With the template you can consume Exchanges from an Endpoint.
The template supports the 3 operations above, but also including convenient methods for returning the body, etc consumeBody.
The example from above using ConsumerTemplate is:
Exchange exchange = consumerTemplate.receive("activemq:my.queue");
Or to extract and get the body you can do:
Object body = consumerTemplate.receiveBody("activemq:my.queue");
And you can provide the body type as a parameter and have it returned as the type:
String body = consumerTemplate.receiveBody("activemq:my.queue", String.class);
You get hold of a ConsumerTemplate from the CamelContext with the createConsumerTemplate operation:
ConsumerTemplate consumer = context.createConsumerTemplate();
Using ConsumerTemplate with Spring DSL
With the Spring DSL we can declare the consumer in the CamelContext with the consumerTemplate tag, just like the ProducerTemplate. The example below illustrates this:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <!-- define a producer template --> <template id="producer"/> <!-- define a consumer template --> <consumerTemplate id="consumer"/> <route> <from uri="seda:foo"/> <to id="result" uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext>
Then we can get leverage Spring to inject the ConsumerTemplate in our java class. The code below is part of an unit test but it shows how the consumer and producer can work together.
@ContextConfiguration public class SpringConsumerTemplateTest extends AbstractJUnit38SpringContextTests { @Autowired private ProducerTemplate producer; @Autowired private ConsumerTemplate consumer; @EndpointInject(name = "result") private MockEndpoint mock; public void testConsumeTemplate() throws Exception { // we expect Hello World received in our mock endpoint mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Hello World"); // we use the producer template to send a message to the seda:start endpoint producer.sendBody("seda:start", "Hello World"); // we consume the body from seda:start String body = consumer.receiveBody("seda:start", String.class); assertEquals("Hello World", body); // and then we send the body again to seda:foo so it will be routed to the mock // endpoint so our unit test can complete producer.sendBody("seda:foo", body); // assert mock received the body mock.assertIsSatisfied(); } }
Timer based polling consumer
In this sample we use a Timer to schedule a route to be started every 5th second and invoke our bean MyCoolBean where we implement the business logic for the Polling Consumer. Here we want to consume all messages from a JMS queue, process the message and send them to the next queue.
First we setup our route as:
MyCoolBean cool = new MyCoolBean(); cool.setProducer(template); cool.setConsumer(consumer); from("timer://foo?period=5000").bean(cool, "someBusinessLogic"); from("activemq:queue.foo").to("mock:result");
And then we have out logic in our bean:
public static class MyCoolBean { private int count; private ConsumerTemplate consumer; private ProducerTemplate producer; public void setConsumer(ConsumerTemplate consumer) { this.consumer = consumer; } public void setProducer(ProducerTemplate producer) { this.producer = producer; } public void someBusinessLogic() { // loop to empty queue while (true) { // receive the message from the queue, wait at most 3 sec String msg = consumer.receiveBody("activemq:queue.inbox", 3000, String.class); if (msg == null) { // no more messages in queue break; } // do something with body msg = "Hello " + msg; // send it to the next queue producer.sendBodyAndHeader("activemq:queue.foo", msg, "number", count++); } } }
Scheduled Poll Components
Quite a few inbound Camel endpoints use a scheduled poll pattern to receive messages and push them through the Camel processing routes. That is to say externally from the client the endpoint appears to use an Event Driven Consumer but internally a scheduled poll is used to monitor some kind of state or resource and then fire message exchanges.
Since this a such a common pattern, polling components can extend the ScheduledPollConsumer base class which makes it simpler to implement this pattern.
There is also the Quartz Component which provides scheduled delivery of messages using the Quartz enterprise scheduler.
For more details see:
- PollingConsumer
- Scheduled Polling Components
ScheduledPollConsumer Options
The ScheduledPollConsumer supports the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| pollStrategy | Camel 2.0: A pluggable org.apache.camel.PollingConsumerPollStrategy allowing you to provide your custom implementation to control error handling usually occurred during the poll operation before an Exchange have been created and being routed in Camel. In other words the error occurred while the polling was gathering information, for instance access to a file network failed so Camel cannot access it to scan for files. The default implementation will log the caused exception at WARN level and ignore it. |
About error handling and scheduled polling consumers
ScheduledPollConsumer is scheduled based and its run method is invoked periodically based on schedule settings. But errors can also occur when a poll being executed. For instance if Camel should poll a file network, and this network resource is not available then a java.io.IOException could occur. As this error happens before any Exchange has been created and prepared for routing, then the regular Error handling in Camel does not apply. So what does the consumer do then? Well the exception is propagated back to the run method where its handled. Camel will by default log the exception at WARN level and then ignore it. At next schedule the error could have been resolved and thus being able to poll the endpoint successfully.
Controlling the error handling using PollingConsumerPollStrategy
Available as of Camel 2.0
org.apache.camel.PollingConsumerPollStrategy is a pluggable strategy that you can configure on the ScheduledPollConsumer. The default implementation org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultPollingConsumerPollStrategy will log the caused exception at WARN level and then ignore this issue.
The strategy interface provides the following 3 methods
- begin
- void begin(Consumer consumer, Endpoint endpoint)
- commit
- void commit(Consumer consumer, Endpoint endpoint)
- rollback
- boolean rollback(Consumer consumer, Endpoint endpoint, int retryCounter, Exception e) throws Exception
The most interesting is the rollback as it allows you do handle the caused exception and decide what to do.
For instance if we want to provide a retry feature to a scheduled consumer we can implement the PollingConsumerPollStrategy method and put the retry logic in the rollback method. Lets just retry up till 3 times:
public boolean rollback(Consumer consumer, Endpoint endpoint, int retryCounter, Exception e) throws Exception {
if (retryCounter < 3) {
// return true to tell Camel that it should retry the poll immediately
return true;
}
// okay we give up do not retry anymore
return false;
}
Notice that we are given the Consumer as a parameter. We could use this to restart the consumer as we can invoke stop and start:
// error occurred lets restart the consumer, that could maybe resolve the issue
consumer.stop();
consumer.start();
Notice: If you implement the begin operation make sure to avoid throwing exceptions as in such a case the poll operation is not invoked and Camel will invoke the rollback directly.
Configuring an Endpoint to use PollingConsumerPollStrategy
To configure an Endpoint to use a custom PollingConsumerPollStrategy you use the option pollStrategy. For example in the file consumer below we want to use our custom strategy defined in the Registry with the bean id myPoll:
from("file://inbox/?pollStrategy=#myPoll").to("activemq:queue:inbox")
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
See Also
Competing Consumers
Camel supports the Competing Consumers from the EIP patterns using a few different components.
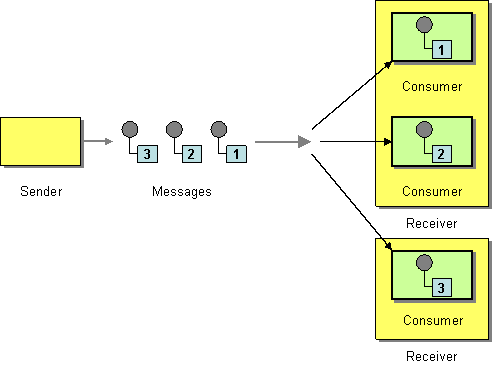
You can use the following components to implement competing consumers:-
- SEDA for SEDA based concurrent processing using a thread pool
- JMS for distributed SEDA based concurrent processing with queues which support reliable load balancing, failover and clustering.
Enabling Competing Consumers with JMS
To enable Competing Consumers you just need to set the concurrentConsumers property on the JMS endpoint.
For example
from("jms:MyQueue?concurrentConsumers=5").bean(SomeBean.class);
Or just run multiple JVMs of any ActiveMQ or JMS route ![]()
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Message Dispatcher
Camel supports the Message Dispatcher from the EIP patterns using various approaches.
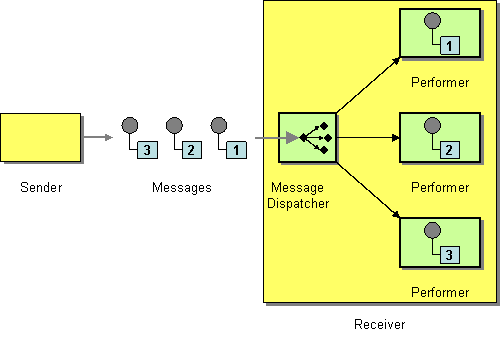
You can use a component like JMS with selectors to implement a Selective Consumer as the Message Dispatcher implementation. Or you can use an Endpoint as the Message Dispatcher itself and then use a Content Based Router as the Message Dispatcher.
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Selective Consumer
The Selective Consumer from the EIP patterns can be implemented in two ways
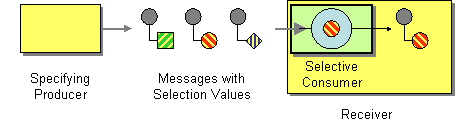
The first solution is to provide a Message Selector to the underlying URIs when creating your consumer. For example when using JMS you can specify a selector parameter so that the message broker will only deliver messages matching your criteria.
The other approach is to use a Message Filter which is applied; then if the filter matches the message your consumer is invoked as shown in the following example
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).process(myProcessor); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<bean id="myProcessor" class="org.apache.camel.builder.MyProcessor"/> <camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <filter> <xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath> <process ref="myProcessor"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext>
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Durable Subscriber
Camel supports the Durable Subscriber from the EIP patterns using the JMS component which supports publish & subscribe using Topics with support for non-durable and durable subscribers.
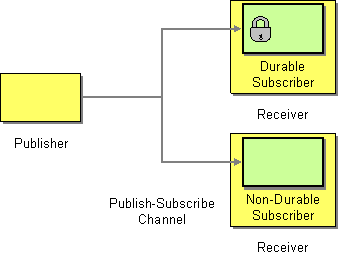
Another alternative is to combine the Message Dispatcher or Content Based Router with File or JPA components for durable subscribers then something like Queue for non-durable.
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Idempotent Consumer
The Idempotent Consumer from the EIP patterns is used to filter out duplicate messages.
This pattern is implemented using the IdempotentConsumer class. This uses an Expression to calculate a unique message ID string for a given message exchange; this ID can then be looked up in the MessageIdRepository to see if it has been seen before; if it has the message is consumed; if its not then the message is processed and the ID is added to the repository.
The Idempotent Consumer essentially acts like a Message Filter to filter out duplicates.
Camel will add the message id eagerly to the repository to detect duplication also for Exchanges currently in progress.
On completion Camel will remove the message id from the repository if the Exchange failed, otherwise it stays there.
Options
The Idempotent Consumer has the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| eager | true | Camel 2.0: Eager controls whether Camel adds the message to the repository before or after the exchange has been processed. If enabled before then Camel will be able to detect duplicate messages even when messages are currently in progress. By disabling Camel will only detect duplicates when a message has successfully been processed. |
Using the Fluent Builders
The following example will use the header myMessageId to filter out duplicates
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").idempotentConsumer(header("myMessageId"), MemoryIdempotentRepository.memoryIdempotentRepository(200)) .to("seda:b"); } };
The above example will use an in-memory based MessageIdRepository which can easily run out of memory and doesn't work in a clustered environment. So you might prefer to use the JPA based implementation which uses a database to store the message IDs which have been processed
from("direct:start").idempotentConsumer( header("messageId"), jpaMessageIdRepository(lookup(JpaTemplate.class), PROCESSOR_NAME) ).to("mock:result");
In the above example we are using the header messageId to filter out duplicates and using the collection myProcessorName to indicate the Message ID Repository to use. This name is important as you could process the same message by many different processors; so each may require its own logical Message ID Repository.
For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at the junit test case
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Transactional Client
Camel recommends supporting the Transactional Client from the EIP patterns using spring transactions.
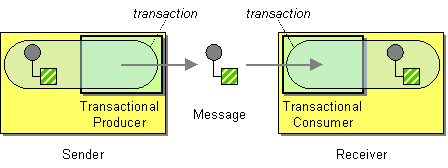
Transaction Oriented Endpoints (Camel Toes) like JMS support using a transaction for both inbound and outbound message exchanges. Endpoints that support transactions will participate in the current transaction context that they are called from.
| Convention over configuration In Camel 2.0 onwards we have improved the default configuration reducing the number of Spring XML gobble you need to configure. |
| Configuration of Redelivery The redelivery in transacted mode is not handled by Camel but by the backing system (the transaction manager). In such cases you should resort to the backing system how to configure the redelivery. |
You should use the SpringRouteBuilder to setup the routes since you will need to setup the spring context with the TransactionTemplates that will define the transaction manager configuration and policies.
For inbound endpoint to be transacted, they normally need to be configured to use a Spring PlatformTransactionManager. In the case of the JMS component, this can be done by looking it up in the spring context.
You first define needed object in the spring configuration.
<bean id="jmsTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.JmsTransactionManager"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="jmsConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/> </bean>
Then you look them up and use them to create the JmsComponent.
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = (PlatformTransactionManager) spring.getBean("jmsTransactionManager"); ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = (ConnectionFactory) spring.getBean("jmsConnectionFactory"); JmsComponent component = JmsComponent.jmsComponentTransacted(connectionFactory, transactionManager); component.getConfiguration().setConcurrentConsumers(1); ctx.addComponent("activemq", component);
Transaction Policies
Outbound endpoints will automatically enlist in the current transaction context. But what if you do not want your outbound endpoint to enlist in the same transaction as your inbound endpoint? The solution is to add a Transaction Policy to the processing route. You first have to define transaction policies that you will be using. The policies use a spring TransactionTemplate under the covers for declaring the transaction demarcation to use. So you will need to add something like the following to your spring xml:
<bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.SpringTransactionPolicy"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> </bean> <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.SpringTransactionPolicy"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> <property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW"/> </bean>
Then in your SpringRouteBuilder, you just need to create new SpringTransactionPolicy objects for each of the templates.
public void configure() { ... Policy requried = bean(SpringTransactionPolicy.class, "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED")); Policy requirenew = bean(SpringTransactionPolicy.class, "PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW")); ... }
Once created, you can use the Policy objects in your processing routes:
// Send to bar in a new transaction from("activemq:queue:foo").policy(requirenew).to("activemq:queue:bar"); // Send to bar without a transaction. from("activemq:queue:foo").policy(notsupported ).to("activemq:queue:bar");
Camel 1.x - Database Sample
In this sample we want to ensure that two endpoints is under transaction control. These two endpoints inserts data into a database.
The sample is in its full as a unit test.
First of all we setup the usual spring stuff in its configuration file. Here we have defined a DataSource to the HSQLDB and a most importantly
the Spring DataSoruce TransactionManager that is doing the heavy lifting of ensuring our transactional policies. You are of course free to use any
of the Spring based TransactionMananger, eg. if you are in a full blown J2EE container you could use JTA or the WebLogic or WebSphere specific managers.
We use the required transaction policy that we define as the PROPOGATION_REQUIRED spring bean. And as last we have our book service bean that does the business logic
and inserts data in the database as our core business logic.
<!-- datasource to the database --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:camel"/> <property name="username" value="sa"/> <property name="password" value=""/> </bean> <!-- spring transaction manager --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- policy for required transaction used in our Camel routes --> <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.SpringTransactionPolicy"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="txManager"/> </bean> <!-- bean for book business logic --> <bean id="bookService" class="org.apache.camel.spring.interceptor.BookService"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>
In our Camel route that is Java DSL based we setup the transactional policy, wrapped as a Policy.
// Notice that we use the SpringRouteBuilder that has a few more features than // the standard RouteBuilder return new SpringRouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { // lookup the transaction policy SpringTransactionPolicy required = lookup("PROPAGATION_REQUIRED", SpringTransactionPolicy.class); // use this error handler instead of DeadLetterChannel that is the default // Notice: transactionErrorHandler is in SpringRouteBuilder if (useTransactionErrorHandler) { // useTransactionErrorHandler is only used for unit testing to reuse code // for doing a 2nd test without this transaction error handler, so ignore // this. For spring based transaction, end users are encouraged to use the // transaction error handler instead of the default DeadLetterChannel. errorHandler(transactionErrorHandler(required)); }
Then we are ready to define our Camel routes. We have two routes: 1 for success conditions, and 1 for a forced rollback condition.
This is after all based on a unit test.
// set the required policy for this route from("direct:okay").policy(required). setBody(constant("Tiger in Action")).beanRef("bookService"). setBody(constant("Elephant in Action")).beanRef("bookService"); // set the required policy for this route from("direct:fail").policy(required). setBody(constant("Tiger in Action")).beanRef("bookService"). setBody(constant("Donkey in Action")).beanRef("bookService");
As its a unit test we need to setup the database and this is easily done with Spring JdbcTemplate
// create database and insert dummy data final DataSource ds = getMandatoryBean(DataSource.class, "dataSource"); jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(ds); jdbc.execute("create table books (title varchar(50))"); jdbc.update("insert into books (title) values (?)", new Object[] {"Camel in Action"});
And our core business service, the book service, will accept any books except the Donkeys.
public class BookService { private SimpleJdbcTemplate jdbc; public BookService() { } public void setDataSource(DataSource ds) { jdbc = new SimpleJdbcTemplate(ds); } public void orderBook(String title) throws Exception { if (title.startsWith("Donkey")) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("We don't have Donkeys, only Camels"); } // create new local datasource to store in DB jdbc.update("insert into books (title) values (?)", title); } }
Then we are ready to fire the tests. First to commit condition:
public void testTransactionSuccess() throws Exception { template.sendBody("direct:okay", "Hello World"); int count = jdbc.queryForInt("select count(*) from books"); assertEquals("Number of books", 3, count); }
And lastly the rollback condition since the 2nd book is a Donkey book:
public void testTransactionRollback() throws Exception { try { template.sendBody("direct:fail", "Hello World"); } catch (RuntimeCamelException e) { // expeced as we fail assertIsInstanceOf(TransactedRuntimeCamelException.class, e.getCause()); assertTrue(e.getCause().getCause() instanceof IllegalArgumentException); assertEquals("We don't have Donkeys, only Camels", e.getCause().getCause().getMessage()); } int count = jdbc.queryForInt("select count(*) from books"); assertEquals("Number of books", 1, count); }
Camel 1.x - JMS Sample
In this sample we want to listen for messages on a queue and process the messages with our business logic java code and send them along. Since its based on a unit test the destination is a mock endpoint.
This time we want to setup the camel context and routes using the Spring XML syntax.
<!-- here we define our camel context --> <camel:camelContext id="myroutes"> <!-- and now our route using the XML syntax --> <camel:route errorHandlerRef="errorHandler"> <!-- 1: from the jms queue --> <camel:from uri="activemq:queue:okay"/> <!-- 2: setup the transactional boundaries to require a transaction --> <camel:policy ref="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/> <!-- 3: call our business logic that is myProcessor --> <camel:process ref="myProcessor"/> <!-- 4: if success then send it to the mock --> <camel:to uri="mock:result"/> </camel:route> </camel:camelContext> <!-- this bean is our business logic --> <bean id="myProcessor" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.tx.JMSTransactionalClientTest$MyProcessor"/>
Since the rest is standard XML stuff its nothing fancy now for the reader:
<!-- the transactional error handler --> <bean id="errorHandler" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.TransactionErrorHandlerBuilder"> <property name="springTransactionPolicy" ref="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/> </bean> <bean id="jmsConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false&broker.useJmx=false"/> </bean> <bean id="jmsTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.JmsTransactionManager"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory"/> </bean> <bean id="jmsConfig" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsConfiguration"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory"/> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> <property name="transacted" value="true"/> <property name="concurrentConsumers" value="1"/> </bean> <bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent"> <property name="configuration" ref="jmsConfig"/> </bean> <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.SpringTransactionPolicy"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> </bean>
Our business logic is set to handle the incomming messages and fail the first two times. When its a success it responds with a Bye World message.
public static class MyProcessor implements Processor { private int count; public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { if (++count <= 2) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Forced Exception number " + count + ", please retry"); } exchange.getIn().setBody("Bye World"); exchange.getIn().setHeader("count", count); } }
And our unit test is tested with this java code. Notice that we expect the Bye World message to be delivered at the 3rd attempt.
MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Bye World"); // success at 3rd attempt mock.message(0).header("count").isEqualTo(3); template.sendBody("activemq:queue:okay", "Hello World"); mock.assertIsSatisfied();
Camel 1.x - Spring based configuration
In Camel 1.4 we have introduced the concept of configuration of the error handlers using spring XML configuration. The sample below demonstrates that you can configure transaction error handlers in Spring XML as spring beans. These can then be set as global, per route based or per policy based error handler. The latter has been demonstrated in the samples above. This sample is the database sample configured in Spring XML.
Notice that we have defined two error handler, one per route. The first route uses the transaction error handler, and the 2nd uses no error handler at all.
<!-- here we define our camel context --> <camel:camelContext id="myroutes"> <!-- first route with transaction error handler --> <!-- here we refer to our transaction error handler we define in this Spring XML file --> <!-- in this route the transactionErrorHandler is used --> <camel:route errorHandlerRef="transactionErrorHandler"> <!-- 1: from the jms queue --> <camel:from uri="activemq:queue:okay"/> <!-- 2: setup the transactional boundaries to require a transaction --> <camel:policy ref="required"/> <!-- 3: call our business logic that is myProcessor --> <camel:process ref="myProcessor"/> <!-- 4: if success then send it to the mock --> <camel:to uri="mock:result"/> </camel:route> <!-- 2nd route with no error handling --> <!-- this route doens't use error handler, in fact the spring bean with id noErrorHandler --> <camel:route errorHandlerRef="noErrorHandler"> <camel:from uri="activemq:queue:bad"/> <camel:to uri="log:bad"/> </camel:route> </camel:camelContext>
The following snippet is the Spring XML configuration to setup the error handlers in pure spring XML:
<!-- camel policy we refer to in our route --> <bean id="required" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.SpringTransactionPolicy"> <property name="transactionTemplate" ref="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/> </bean> <!-- the standard spring transaction template for required --> <bean id="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> </bean> <!-- the transaction error handle we refer to from the route --> <bean id="transactionErrorHandler" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.TransactionErrorHandlerBuilder"> <property name="transactionTemplate" ref="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/> </bean> <!-- the no error handler --> <bean id="noErrorHandler" class="org.apache.camel.builder.NoErrorHandlerBuilder"/>
DelayPolicy (@deprecated)
DelayPolicy is a new policy introduced in Camel 1.5, to replaces the RedeliveryPolicy used in Camel 1.4. Notice the transactionErrorHandler can be configured with a DelayPolicy to set a fixed delay in millis between each redelivery attempt. Camel does this by sleeping the delay until transaction is marked for rollback and the caused exception is rethrown.
This allows a simple redelivery interval that can be configured for development mode or light production to avoid a rapid redelivery strategy that can exhaust a system that constantly fails.
The DelayPolicy is @deprecated and removed in Camel 2.0. All redelivery configuration should be configured on the back system.
We strongly recommend that you configure the backing system for correct redelivery policy in your environment.
Camel 2.0 - Database Sample
In this sample we want to ensure that two endpoints is under transaction control. These two endpoints inserts data into a database.
The sample is in its full as a unit test.
First of all we setup the usual spring stuff in its configuration file. Here we have defined a DataSource to the HSQLDB and a most importantly
the Spring DataSoruce TransactionManager that is doing the heavy lifting of ensuring our transactional policies. You are of course free to use any
of the Spring based TransactionMananger, eg. if you are in a full blown J2EE container you could use JTA or the WebLogic or WebSphere specific managers.
As we use the new convention over configuration we do not need to configure a transaction policy bean, so we do not have any PROPAGATION_REQUIRED beans.
All the beans needed to be configured is standard Spring beans only, eg. there are no Camel specific configuration at all.
<!-- this example uses JDBC so we define a data source --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:camel"/> <property name="username" value="sa"/> <property name="password" value=""/> </bean> <!-- spring transaction manager --> <!-- this is the transaction manager Camel will use for transacted routes --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- bean for book business logic --> <bean id="bookService" class="org.apache.camel.spring.interceptor.BookService"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>
Then we are ready to define our Camel routes. We have two routes: 1 for success conditions, and 1 for a forced rollback condition.
This is after all based on a unit test. Notice that we mark each route as transacted using the transacted tag.
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:okay"/> <!-- we mark this route as transacted. Camel will lookup the spring transaction manager and use it by default. We can optimally pass in arguments to specify a policy to use that is configured with a spring transaction manager of choice. However Camel supports convention over configuration as we can just use the defaults out of the box and Camel that suites in most situations --> <transacted/> <setBody> <constant>Tiger in Action</constant> </setBody> <bean ref="bookService"/> <setBody> <constant>Elephant in Action</constant> </setBody> <bean ref="bookService"/> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:fail"/> <!-- we mark this route as transacted. See comments above. --> <transacted/> <setBody> <constant>Tiger in Action</constant> </setBody> <bean ref="bookService"/> <setBody> <constant>Donkey in Action</constant> </setBody> <bean ref="bookService"/> </route> </camelContext>
That is all that is needed to configure a Camel route as being transacted. Just remember to use the transacted DSL. The rest is standard Spring XML to setup the transaction manager.
Camel 2.0 - JMS Sample
In this sample we want to listen for messages on a queue and process the messages with our business logic java code and send them along. Since its based on a unit test the destination is a mock endpoint.
First we configure the standard Spring XML to declare a JMS connection factory, a JMS transaction manager and our ActiveMQ component that we use in our routing.
<!-- setup JMS connection factory --> <bean id="jmsConnectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false&broker.useJmx=false"/> </bean> <!-- setup spring jms TX manager --> <bean id="jmsTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jms.connection.JmsTransactionManager"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory"/> </bean> <!-- define our activemq component --> <bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory"/> <!-- define the jms consumer/producer as transacted --> <property name="transacted" value="true"/> <!-- setup the transaction manager to use --> <!-- if not provided then Camel will automatic use a JmsTransactionManager, however if you for instance use a JTA transaction manager then you must configure it --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="jmsTransactionManager"/> </bean>
And then we configure our routes. Notice that all we have to do is mark the route as transacted using the transacted tag.
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <!-- 1: from the jms queue --> <from uri="activemq:queue:okay"/> <!-- 2: mark this route as transacted --> <transacted/> <!-- 3: call our business logic that is myProcessor --> <process ref="myProcessor"/> <!-- 4: if success then send it to the mock --> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext> <bean id="myProcessor" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.tx.JMSTransactionalClientTest$MyProcessor"/>
| Transaction error handler When a route is marked as transacted using transacted Camel will automatic use the TransactionErrorHandler as Error Handler. It supports basically the same feature set as the DefaultErrorHandler, so you can for instance use Exception Clause as well. |
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Messaging Gateway
Camel has several endpoint components that support the Messaging Gateway from the EIP patterns.
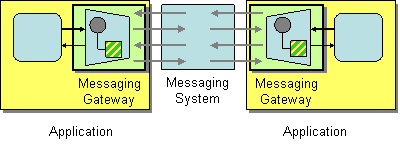
Components like Bean, CXF and Pojo provide a a way to bind a Java interface to the message exchange.
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Service Activator
Camel has several endpoint components that support the Service Activator from the EIP patterns.
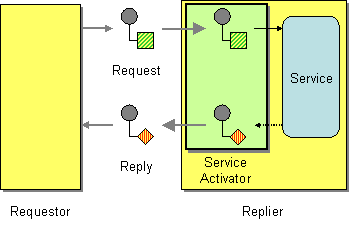
Components like Bean, CXF and Pojo provide a a way to bind the message exchange to a Java interface/service where the route defines the endpoints and wires it up to the bean.
In addition you can use the Bean Integration to wire messages to a bean using annotation.
See Also
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
System Management
Wire Tap
The Wire Tap from the EIP patterns allows you to route messages to a separate tap location while it is forwarded to the ultimate destination.
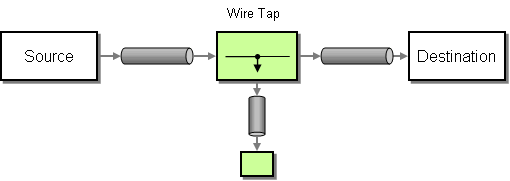
WireTap node
Available as of Camel 2.0
In Camel 2.0 we have introduced a new wireTap node for properly doing wire taps. Camel will copy the original Exchange and set its Exchange Pattern to InOnly as we want the tapped Exchange to be sent as a fire and forget style. The tapped Exchange is then send in a separate thread so it can run in parallel with the original
We have extended the wireTap to support two flavors when tapping an Exchange
- send a copy of the original Exchange (the traditional wire tap)
- send a new Exchange, allowing you to populate the Exchange beforehand
Sending a copy (traditional wire tap)
Using the Fluent Builders
from("direct:start") .to("log:foo") .wireTap("direct:tap") .to("mock:result");
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <to uri="log:foo"/> <wireTap uri="direct:tap"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route>
Sending a new Exchange
Using the Fluent Builders
Camel supports either a processor or an Expression to populate the new Exchange. Using processor gives you full power how the Exchange is populated as you can set properties, headers etc. The Expression can only be used to set the IN body.
Below is the processor variation shown:
from("direct:start") .wireTap("direct:foo", new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.getIn().setBody("Bye World"); exchange.getIn().setHeader("foo", "bar"); } }).to("mock:result"); from("direct:foo").to("mock:foo");
And the Expression variation:
from("direct:start") .wireTap("direct:foo", constant("Bye World")) .to("mock:result"); from("direct:foo").to("mock:foo");
Using the Spring XML Extensions
The processor variation, notice we use a processorRef attribute to refer to a spring bean with this id:
<route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <wireTap uri="direct:foo"> <body><constant>Bye World</constant></body> </wireTap> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route>
And the Expression variation, where the expression is defined in the body tag:
<route> <from uri="direct:start2"/> <wireTap uri="direct:foo" processorRef="myProcessor"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route>
Camel 1.x
The following example shows how to route a request from an input queue:a endpoint to the wire tap location queue:tap it is received by queue:b
Using the Fluent Builders
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("mock:error")); from("seda:a").multicast().to("seda:tap", "seda:b"); } };
Using the Spring XML Extensions
<camelContext errorHandlerRef="errorHandler" streamCache="false" id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="seda:a"/> <multicast> <to uri="seda:tap"/> <to uri="seda:b"/> </multicast> </route> </camelContext>
Further Example
For another example of this pattern in use you could look at the wire tap test case.
Using This Pattern
If you would like to use this EIP Pattern then please read the Getting Started, you may also find the Architecture useful particularly the description of Endpoint and URIs. Then you could try out some of the Examples first before trying this pattern out.
Component Appendix
There now follows the documentation on each Camel component.
ActiveMQ Component
The ActiveMQ component allows messages to be sent to a JMS Queue or Topic; or messages to be consumed from a JMS Queue or Topic using Apache ActiveMQ.
This component is based on the JMS Component and uses Spring's JMS support for declarative transactions, using Spring's JmsTemplate for sending and a MessageListenerContainer for consuming. All the options from the JMS component also applies for this component.
To use this component make sure you have the activemq.jar or activemq-core.jar on your classpath along with any Camel dependencies such as camel-core.jar, camel-spring.jar and camel-jms.jar.
URI format
activemq:[queue:|topic:]destinationName
Where destinationName is an ActiveMQ queue or topic name. By default, the destinationName is interpreted as a queue name. For example, to connect to the queue, FOO.BAR, use:
activemq:FOO.BAR
You can include the optional queue: prefix, if you prefer:
activemq:queue:FOO.BAR
To connect to a topic, you must include the topic: prefix. For example, to connect to the topic, Stocks.Prices, use:
activemq:topic:Stocks.Prices
Options
See Options on the JMS component as all these options also apply for this component.
Configuring the Connection Factory
The following test case shows how to add an ActiveMQComponent to the CamelContext using the activeMQComponent() method while specifying the brokerURL used to connect to ActiveMQ
camelContext.addComponent("activemq", activeMQComponent("vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false"));
Configuring the Connection Factory using Spring XML
You can configure the ActiveMQ broker URL on the ActiveMQComponent as follows
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> </camelContext> <bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent"> <property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://somehost:61616"/> </bean> </beans>
Using connection pooling
When sending to an AcitveMQ broker using Camel its recommended to use a JMS connection pooling such as Jencks. See more here Jencks Connection Pooling
You can grab Jencks AMQ pool with maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jencks</groupId>
<artifactId>jencks-amqpool</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
</dependency>
And then setup the activemq Camel component as follows:
<!-- use jencks connection pooling so its more effecient to send JMS messages -->
<amqpool:pool id="jmsConnectionFactory" xmlns:amqpool="http://jencks.org/amqpool/2.0"
brokerURL="tcp://localhost:61616"
maxConnections="8"/>
<bean id="jmsConfig" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsConfiguration">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="jmsConnectionFactory"/>
<property name="transacted" value="false"/>
<property name="concurrentConsumers" value="10"/>
</bean>
<bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent">
<property name="configuration" ref="jmsConfig"/>
</bean>
Invoking MessageListener POJOs in a Camel route
The ActiveMQ component also provides a helper Type Converter from a JMS MessageListener to a Processor. This means that the Bean component is capable of invoking any JMS MessageListener bean directly inside any route.
So for example you can create a MessageListener in JMS like this....
public class MyListener implements MessageListener { public void onMessage(Message jmsMessage) { // ... } }
Then use it in your Camel route as follows
from("file://foo/bar").
bean(MyListener.class);
That is, you can reuse any of the Camel Components and easily integrate them into your JMS MessageListener POJO!
Getting Component JAR
You need these dependencies
- camel-jms
- activemq-camel
camel-jms
You must have the camel-jms as dependency as ActiveMQ is an extension to the JMS component.
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-jms</artifactId> <version>1.6.0</version> </dependency>
The ActiveMQ Camel component is released with the ActiveMQ project itself.
For Maven 2 users you simply just need to add the following dependency to your project.
ActiveMQ 5.2 or later
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId> <artifactId>activemq-camel</artifactId> <version>5.2.0</version> </dependency>
ActiveMQ 5.1.0
For 5.1.0 its in the activemq-core library
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId> <artifactId>activemq-core</artifactId> <version>5.1.0</version> </dependency>
Alternatively you can download the component jar directly from the Maven repository:
ActiveMQ 4.x
For this version you must use the JMS component instead. Please be careful to use a pooling connection factory as described in the JmsTemplate Gotchas
See Also
ActiveMQ Journal Component
The ActiveMQ Journal Component allows messages to be stored in a rolling log file and then consumed from that log file. The journal aggregates and batches up concurrent writes so that to overhead of writing and waiting for the disk sync is relatively constant regardless of how many concurrent writes are being done. Therefore, this component supports and encourages you to use multiple concurrent producers to the same journal endpoint.
Each journal endpoint uses a different log file and therefore write batching (and the associated performance boost) does not occur between multiple endpoints.
This component only supports 1 active consumer on the endpoint. After the message is processed by the consumer's processor, the log file is marked and only subsequent messages in the log file will get delivered to consumers.
URI format
activemq.journal:directoryName[?options]
So for example, to send to the journal located in the /tmp/data directory you would use the following URI:
activemq.journal:/tmp/data
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| syncConsume | false | If set to true, when the journal is marked after a message is consumed, wait till the Operating System has verified the mark update is safely stored on disk. |
| syncProduce | true | If set to true, wait till the Operating System has verified the message is safely stored on disk. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Expected Exchange Data Types
The consumer of a Journal endpoint generates DefaultExchange objects with the in message :
- header "journal" : set to the endpoint uri of the journal the message came from
- header "location" : set to a Location which identifies where the recored was stored on disk
- body : set to ByteSequence which contains the byte array data of the stored message
The producer to a Journal endpoint expects an Exchange with an In message where the body can be converted to a ByteSequence or a byte[].
See Also
AMQP
The AMQP component supports the AMQP protocol via the Qpid project.
URI format
amqp:[queue:|topic:]destinationName[?options]
You can specify all of the various configuration options of the JMS component after the destination name.
See Also
Atom Component
The atom: component is used for polling atom feeds.
Camel will default poll the feed every 60th seconds.
Note: The component currently only supports polling (consuming) feeds.
URI format
atom://atomUri[?options]
Where atomUri is the URI to the atom feed to poll.
Options
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| splitEntries | true | If true Camel will poll the feed and for the subsequent polls return each entry poll by poll. If the feed contains 7 entries then Camel will return the first entry on the first poll, the 2nd entry on the next poll, until no more entries where as Camel will do a new update on the feed. If false then Camel will poll a fresh feed on every invocation. |
| filter | true | Is only used by the split entries to filter the entries to return. Camel will default use the UpdateDateFilter that only return new entries from the feed. So the client consuming from the feed never receives the same entry more than once. The filter will return the entries ordered by the newest last. |
| lastUpdate | null | Is only used by the filter, as the starting timestamp for selection never entries (uses the entry.updated timestamp). Syntax format is: yyyy-MM-ddTHH:MM:ss. Example: 2007-12-24T17:45:59. |
| feedHeader | true | Sets whether to add the Abdera Feed object as a header. |
| sortEntries | false | If splitEntries is true, this sets whether to sort those entries by updated date. |
| consumer.delay | 60000 | Delay in millis between each poll. |
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | Millis before polling starts. |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | false | If true, use fixed delay between pools, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Exchange data format
Camel will set the In body on the returned Exchange with the entries. Depending on the splitEntries flag Camel will either return one Entry or a List<Entry>.
| Option | Value | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| splitEntries | true | Only a single entry from the currently being processed feed is set: exchange.in.body(Entry) |
| splitEntries | false | The entire list of entries from the feed is set: exchange.in.body(List<Entry>) |
Camel can set the Feed object on the In header (see feedHeader option to disable this):
Message Headers
Camel atom uses these headers.
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.component.atom.feed | Camel 1.x: When consuming the org.apache.abdera.model.Feed object is set to this header. |
| CamelAtomFeed | Camel 2.0: When consuming the org.apache.abdera.model.Feed object is set to this header. |
Samples
In this sample we poll James Strachan's blog.
from("atom://http://macstrac.blogspot.com/feeds/posts/default").to("seda:feeds");
In this sample we want to filter only good blogs we like to a SEDA queue. The sample also shows how to setup Camel standalone, not running in any Container or using Spring.
// This is the CamelContext that is the heart of Camel private CamelContext context; // We use a simple Hashtable for our bean registry. For more advanced usage Spring is supported out-of-the-box private Hashtable beans = new Hashtable(); // We initialize Camel private void setupCamel() throws Exception { // First we register a blog service in our bean registry beans.put("blogService", new BlogService()); // Then we create the camel context with our bean registry context = new DefaultCamelContext(new CamelInitialContextFactory().getInitialContext(beans)); // Then we add all the routes we need using the route builder DSL syntax context.addRoutes(createRouteBuilder()); // And finally we must start Camel to let the magic routing begins context.start(); } /** * This is the route builder where we create our routes in the advanced Camel DSL syntax */ protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { // We pool the atom feeds from the source for further processing in the seda queue // we set the delay to 1 second for each pool as this is a unit test also and we can // not wait the default poll interval of 60 seconds. // Using splitEntries=true will during polling only fetch one Atom Entry at any given time. // As the feed.atom file contains 7 entries, using this will require 7 polls to fetch the entire // content. When Camel have reach the end of entries it will refresh the atom feed from URI source // and restart - but as Camel by default uses the UpdatedDateFilter it will only deliver new // blog entries to "seda:feeds". So only when James Straham updates his blog with a new entry // Camel will create an exchange for the seda:feeds. from("atom:file:src/test/data/feed.atom?splitEntries=true&consumer.delay=1000").to("seda:feeds"); // From the feeds we filter each blot entry by using our blog service class from("seda:feeds").filter().method("blogService", "isGoodBlog").to("seda:goodBlogs"); // And the good blogs is moved to a mock queue as this sample is also used for unit testing // this is one of the strengths in Camel that you can also use the mock endpoint for your // unit tests from("seda:goodBlogs").to("mock:result"); } }; } /** * This is the actual junit test method that does the assertion that our routes is working * as expected */ @Test public void testFiltering() throws Exception { // Get the mock endpoint MockEndpoint mock = context.getEndpoint("mock:result", MockEndpoint.class); // There should be two good blog entries from the feed mock.expectedMessageCount(2); // Asserts that the above expectations is true, will throw assertions exception if it failed // Camel will default wait max 20 seconds for the assertions to be true, if the conditions // is true sooner Camel will continue mock.assertIsSatisfied(); } /** * Services for blogs */ public class BlogService { /** * Tests the blogs if its a good blog entry or not */ public boolean isGoodBlog(Exchange exchange) { Entry entry = exchange.getIn().getBody(Entry.class); String title = entry.getTitle(); // We like blogs about Camel boolean good = title.toLowerCase().contains("camel"); return good; } }
See Also
Bean Component
The bean: component binds beans to Camel message exchanges.
URI format
bean:beanID[?options]
Where beanID can be any string which is used to look up the bean in the Registry
Options
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| method | String | null | The method name that bean will be invoked. If not provided, Camel will try to pick the method itself. In case of ambiguity an exception is thrown. See Bean Binding for more details. |
| cache | boolean | false | If enabled, Camel will cache the result of the first Registry look-up. Cache can be enabled if the bean in the Registry is defined as a singleton scope. |
| multiParameterArray | boolean | false | Camel 1.5: How to treat the parameters which are passed from the message body; if it is true, the In message body should be an array of parameters. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Using
The object instance that is used to consume messages must be explicitly registered with the Registry. For example, if you are using Spring you must define the bean in the Spring configuration, spring.xml; or if you don't use Spring, put the bean in JNDI.
// lets populate the context with the services we need // note that we could just use a spring.xml file to avoid this step JndiContext context = new JndiContext(); context.bind("bye", new SayService("Good Bye!")); CamelContext camelContext = new DefaultCamelContext(context);
Once an endpoint has been registered, you can build Camel routes that use it to process exchanges.
// lets add simple route camelContext.addRoutes(new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:hello").to("bean:bye"); } });
A bean: endpoint cannot be defined as the input to the route; i.e. you cannot consume from it, you can only route from some inbound message Endpoint to the bean endpoint as output. So consider using a direct: or queue: endpoint as the input.
You can use the createProxy() methods on ProxyHelper to create a proxy that will generate BeanExchanges and send them to any endpoint:
Endpoint endpoint = camelContext.getEndpoint("direct:hello"); ISay proxy = ProxyHelper.createProxy(endpoint, ISay.class); String rc = proxy.say(); assertEquals("Good Bye!", rc);
And the same route using Spring DSL:
<route>
<from uri="direct:hello">
<to uri="bean:bye"/>
</route>
Bean as endpoint
Camel also supports invoking Bean as an Endpoint. In the route below:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <to uri="myBean"/> <to uri="mock:results"/> </route> </camelContext> <bean id="myBean" class="org.apache.camel.spring.bind.ExampleBean"/>
What happens is that when the exchange is routed to the myBean Camel will use the Bean Binding to invoke the bean.
The source for the bean is just a plain POJO:
public class ExampleBean { public String sayHello(String name) { return "Hello " + name + "!"; } }
Camel will use Bean Binding to invoke the sayHello method, by converting the Exchange's In body to the String type and storing the output of the method on the Exchange Out body.
Bean Binding
How bean methods to be invoked are chosen (if they are not specified explicitly through the method parameter) and how parameter values are constructed from the Message are all defined by the Bean Binding mechanism which is used throughout all of the various Bean Integration mechanisms in Camel.
See Also
Browse Component
Available as of Camel 2.0
The Browse component provides a simple BrowsableEndpoint which can be useful for testing, visualisation tools or debugging. The exchanges sent to the endpoint are all available to be browsed.
URI format
browse:someName
Where someName can be any string to uniquely identify the endpoint.
Sample
In the route below, we insert a browse: component to be able to browse the Exchanges that are passing through:
from("activemq:order.in").to("browse:orderReceived").to("bean:processOrder");
We can now inspect the received exchanges from within the Java code:
private CamelContext context;
public void inspectRecievedOrders() {
BrowsableEndpoint browse = context.getEndpoint("browse:orderReceived", BrowsableEndpoint.class);
List<Exchange> exchanges = browse.getExchanges();
...
// then we can inspect the list of received exchanges from Java
for (Exchange exchange : exchanges) {
String payload = exchange.getIn().getBody();
...
}
}
See Also
Cometd Component
The cometd: component is a transport for working with the jetty implementation of the cometd/bayeux protocol.
Using this component in combination with the dojo toolkit library it's possible to push Camel messages directly into the browser using an AJAX based mechanism.
URI format
cometd://host:port/channelName[?options]
The channelName represents a topic that can be subscribed to by the Camel endpoints.
Examples
cometd://localhost:8080/service/mychannel cometds://localhost:8443/service/mychannel
where cometds: represents an SSL configured endpoint.
See this blog entry by David Greco who contributed this component to Apache Camel, for a full sample.
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| resourceBase | The root directory for the web resources | |
| timeout | 240000 | The server side poll timeout in milliseconds. This is how long the server will hold a reconnect request before responding. |
| interval | 0 | The client side poll timeout in milliseconds. How long a client will wait between reconnects |
| maxInterval | 30000 | The max client side poll timeout in milliseconds. A client will be removed if a connection is not received in this time. |
| multiFrameInterval | 1500 | The client side poll timeout, if multiple connections are detected from the same browser. |
| jsonCommented | true | If true, the server will accept JSON wrapped in a comment and will generate JSON wrapped in a comment. This is a defence against Ajax Hijacking. |
| logLevel | 1 | 0=none, 1=info, 2=debug. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
See Also
Cache Component
Available as of Camel 2.1
The cache component enables you to perform caching operations using EHCache as the Cache Implementation. The cache itself is created on demand or if a cache of that name already exists then it is simply utilized with its original settings.
This component supports producer and event based consumer endpoints.
The Cache consumer is an event based consumer and can be used to listen and respond to specific cache activities. If you need to perform selections from a pre-existing cache, used the processors defined for the cache component.
URI format
cache://cacheName[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| maxElementsInMemory | 1000 | The numer of elements that may be stored in the defined cache |
| memoryStoreEvictionPolicy | MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy.LFU | The number of elements that may be stored in the defined cache. Options include
|
| overflowToDisk | true | Specifies whether cache may overflow to disk |
| eternal | false | Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element is never expired. |
| timeToLiveSeconds | 300 | The maximum time between creation time and when an element expires. Is only used if the element is not eternal |
| timeToIdleSeconds | 300 | The maximum amount of time between accesses before an element expires |
| diskPersistent | true | Whether the disk store persists between restarts of the Virtual Machine. The default value is false. |
| diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds | 120 | The number of seconds between runs of the disk expiry thread. The default value is 120 seconds |
Sending/Receiving Messages to/from the cache
Message Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| CACHE_OPERATION | The operation to be performed on the cache. The valid options are
|
| CACHE_KEY | The cache key used to store the Message in the cache. The cache key is optional if the CACHE_OPERATION is DELETEALL |
Cache Producer
Sending data to the cache involves the ability to direct payloads in exchanges to be stored in a pre-existing or created-on- demand cache. The mechanics of doing this involve
- setting the Message Exchange Headers shown above.
- ensuring that the Message Exchange Body contains the message directed to the cache
Cache Consumer
Receiving data from the cache involves the ability of the CacheConsumer to listen on a pre-existing or created-on-demand Cache using an event Listener and receive automatic notifications when any cache activity take place (i.e ADD/UPDATE/DELETE/DELETEALL). Upon such an activity taking place
- an exchange containing Message Exchange Headers and a Message Exchange Body containing the just added/updated payload is placed and sent.
- in case of a DELETEALL operation, the Message Exchange Header CACHE_KEY and the Message Exchange Body are not populated.
Cache Processors
There are a set of nice processors with the ability to perform cache lookups and selectively replace payload content at the
- body
- token
- xpath level
Cache Usage Samples
Example 1: Configuring the cache
from("cache://MyApplicationCache" + "?maxElementsInMemory=1000" + "&memoryStoreEvictionPolicy=" + "MemoryStoreEvictionPolicy.LFU" + "&overflowToDisk=true" + "&eternal=true" + "&timeToLiveSeconds=300" + "&timeToIdleSeconds=true" + "&diskPersistent=true" + "&diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds=300")
Example 2: Adding keys to the cache
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start") .setHeader("CACHE_OPERATION", constant("ADD")) .setHeader("CACHE_KEY", constant("Ralph_Waldo_Emerson")) .to("cache://TestCache1") } };
Example 2: Updating existing keys in a cache
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start") .setHeader("CACHE_OPERATION", constant("UPDATE")) .setHeader("CACHE_KEY", constant("Ralph_Waldo_Emerson")) .to("cache://TestCache1") } };
Example 3: Deleting existing keys in a cache
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start") .setHeader("CACHE_OPERATION", constant("DELETE")) .setHeader("CACHE_KEY", constant("Ralph_Waldo_Emerson")) .to("cache://TestCache1") } };
Example 4: Deleting all existing keys in a cache
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:start") .setHeader("CACHE_OPERATION", constant("DELETEALL")) .to("cache://TestCache1"); } };
Example 5: Notifying any changes registering in a Cache to Processors and other Producers
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("cache://TestCache1") .process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { String operation = (String) exchange.getIn().getHeader("CACHE_OPERATION"); String key = (String) exchange.getIn().getHeader("CACHE_KEY"); Object body = exchange.getIn().getBody(); // Do something } }) } };
Example 6: Using Processors to selectively replace payload with cache values
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { //Message Body Replacer from("cache://TestCache1") .filter(header("CACHE_KEY").isEqualTo("greeting")) .process(new CacheBasedMessageBodyReplacer("cache://TestCache1","farewell")) .to("direct:next"); //Message Token replacer from("cache://TestCache1") .filter(header("CACHE_KEY").isEqualTo("quote")) .process(new CacheBasedTokenReplacer("cache://TestCache1","novel","#novel#")) .process(new CacheBasedTokenReplacer("cache://TestCache1","author","#author#")) .process(new CacheBasedTokenReplacer("cache://TestCache1","number","#number#")) .to("direct:next"); //Message XPath replacer from("cache://TestCache1"). .filter(header("CACHE_KEY").isEqualTo("XML_FRAGMENT")) .process(new CacheBasedXPathReplacer("cache://TestCache1","book1","/books/book1")) .process (new CacheBasedXPathReplacer("cache://TestCache1","book2","/books/book2")) .to("direct:next"); } };
CXF Component
The cxf: component provides integration with Apache CXF for connecting to JAX-WS services hosted in CXF.
Maven users will need to add the following dependency to their pom.xml for this component:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-cxf</artifactId>
<version>x.x.x</version>
<!-- use the same version as your Camel core version -->
</dependency>
URI format
cxf:bean:cxfEndpoint[?options]
Where cxfEndpoint represents a bean ID that references a bean in the Spring bean registry. With this URI format, most of the endpoint details are specified in the bean definition.
cxf://someAddress[?options]
Where someAddress specifies the CXF endpoint's address. With this URI format, most of the endpoint details are specified using options.
For either style above, you can append options to the URI as follows:
cxf:bean:cxfEndpoint?wsdlURL=wsdl/hello_world.wsdl&dataFormat=PAYLOAD
Options
| Name | Description | Example | Required? | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wsdlURL | The location of the WSDL. | file://local/wsdl/hello.wsdl or wsdl/hello.wsdl | No | WSDL is obtained from endpoint address by default. |
| serviceClass | The name of the SEI (Service Endpoint Interface) class. This class can have, but does not require, JSR181 annotations. Since 2.0, this option is only required by POJO mode. If the wsdlURL option is provided, serviceClass is not required for PAYLOAD and MESSAGE mode. When wsdlURL option is used without serviceClass, the serviceName and portName (endpointName for Spring configuration) options MUST be provided. Since 2.0, it is possible to use # notation to reference a serviceClass object instance from the registry. E.g. serviceClass=#beanName. Please be advised that the referenced object cannot be a Proxy (Spring AOP Proxy is OK) as it relies on Object.getClass().getName() method for non Spring AOP Proxy. | org.apache.camel.Hello | Yes | |
| serviceClassInstance | In 1.6 or later (will be deprecated in 2.0), serviceClassInstance works like serviceClass=#beanName, which looks up a serviceObject instance from the registry. | serviceClassInstance=beanName | No (use either serviceClass or serviceClassInstance) | |
| serviceName | The service name this service is implementing, it maps to the wsdl:service@name. | {http://org.apache.camel}ServiceName | Only if more than one serviceName in WSDL present | |
| portName | The port name this service is implementing, it maps to the wsdl:port@name. | {http://org.apache.camel}PortName | Only if more than one portName under the serviceName is present | |
| dataFormat | Which data type messages the CXF endpoint supports | POJO, PAYLOAD, MESSAGE | No | POJO |
| relayHeaders | Available since 1.6.1. Please see the Description of relayHeaders option section for this option in 2.0. Should a CXF endpoint relay headers along the route. Currently only available when dataFormat=POJO | true, false | No | true |
| wrapped | Which kind of operation that CXF endpoint producer will invoke | true, false | No | false |
| setDefaultBus | Will set the default bus when CXF endpoint create a bus by itself | true, false | No | false |
| bus | New in 2.0, use # notation to reference a bus object from the registry. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.cxf.Bus. | bus=#busName | No | Default bus created by CXF Bus Factory |
| cxfBinding | New in 2.0, use # notation to reference a CXF binding object from the registry. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfBinding. | cxfBinding=#bindingName | No | An instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.DefaultCxfBinding |
| headerFilterStrategy | New in 2.0, use # notation to reference a header filter strategy object from the registry. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.camel.spi.HeaderFilterStrategy. | headerFilterStrategy=#strategyName | No | An instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfHeaderFilterStrategy |
The serviceName and portName are QNames, so if you provide them be sure to prefix them with their {namespace} as shown in the examples above.
NOTE From CAMEL 1.5.1 , the serviceClass for a CXF producer (that is, the to endpoint) should be a Java interface.
The descriptions of the dataformats
| DataFormat | Description |
|---|---|
| POJO | POJOs (Plain old Java objects) are the Java parameters to the method being invoked on the target server. Both Protocol and Logical JAX-WS handlers are supported. |
| PAYLOAD | PAYLOAD is the message payload (the contents of the soap:body) after message configuration in the CXF endpoint is applied. Only Protocol JAX-WS handler is supported. Logical JAX-WS handler is not supported. |
| MESSAGE | MESSAGE is the raw message that is received from the transport layer. JAX-WS handler is not supported. |
You can determine the data format mode of an exchange by retrieving the exchange property, CamelCXFDataFormat. The exchange key constant is defined in org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfConstants.DATA_FORMAT_PROPERTY.
How to enable CXF's LoggingOutInterceptor in MESSAGE mode
CXF's LoggingOutInterceptor outputs outbound message that goes on the wire to logging system (Java Util Logging). Since the LoggingOutInterceptor is in PRE_STREAM phase (but PRE_STREAM phase is removed in MESSAGE mode), you have to configure LoggingOutInterceptor to be run during the WRITE phase. The following is an example.
<bean id="loggingOutInterceptor" class="org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingOutInterceptor"> <!-- it really should have been user-prestream but CXF does have such phase! --> <constructor-arg value="write"/> </bean> <cxf:cxfEndpoint id="serviceEndpoint" address="http://localhost:9002/helloworld" serviceClass="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.HelloService"> <cxf:outInterceptors> <ref bean="loggingOutInterceptor"/> </cxf:outInterceptors> <cxf:properties> <entry key="dataFormat" value="MESSAGE"/> </cxf:properties> </cxf:cxfEndpoint>
Description of relayHeaders option
There are in-band and out-of-band on-the-wire headers from the perspective of a JAXWS WSDL-first developer.
The in-band headers are headers that are explicitly defined as part of the WSDL binding contract for an endpoint such as SOAP headers.
The out-of-band headers are headers that are serialized over the wire, but are not explicitly part of the WSDL binding contract.
Headers relaying/filtering is bi-directional.
When a route has a CXF endpoint and the developer needs to have on-the-wire headers, such as SOAP headers, be relayed along the route to be consumed say by another JAXWS endpoint, then relayHeaders should be set to true, which is the default value.
Available in Release 1.6.1 and after (only in POJO mode)
The relayHeaders=true express an intent to relay the headers. The actual decision on whether a given header is relayed is delegated to a pluggable instance that implements the MessageHeadersRelay interface. A concrete implementation of MessageHeadersRelay will be consulted to decide if a header needs to be relayed or not. There is already an implementation of SoapMessageHeadersRelay which binds itself to well-known SOAP name spaces. Currently only out-of-band headers are filtered, and in-band headers will always be relayed when relayHeaders=true. If there is a header on the wire, whose name space is unknown to the runtime, then a fall back DefaultMessageHeadersRelay will be used, which simply allows all headers to be relayed.
The relayHeaders=false setting asserts that all headers in-band and out-of-band will be dropped.
You can plugin your own MessageHeadersRelay implementations overriding or adding additional ones to the list of relays. In order to override a preloaded relay instance just make sure that your MessageHeadersRelay implementation services the same name spaces as the one you looking to override. Also note, that the overriding relay has to service all of the name spaces as the one you looking to override, or else a runtime exception on route start up will be thrown as this would introduce an ambiguity in name spaces to relay instance mappings.
<cxf:cxfEndpoint ...> <cxf:properties> <entry key="org.apache.camel.cxf.message.headers.relays"> <list> <ref bean="customHeadersRelay"/> </list> </entry> </cxf:properties> </cxf:cxfEndpoint> <bean id="customHeadersRelay" class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.soap.headers.CustomHeadersRelay"/>
Take a look at the tests that show how you'd be able to relay/drop headers here:
Changes since Release 2.0
- POJO and PAYLOAD modes are supported. In POJO mode, only out-of-band message headers are available for filtering as the in-band headers have been processed and removed from header list by CXF. The in-band headers are incorporated into the MessageContentList in POJO mode. The camel-cxf component does make any attempt to remove the in-band headers from the MessageContentList as it does in 1.6.1. If filtering of in-band headers is required, please use PAYLOAD mode or plug in a (pretty straightforward) CXF interceptor/JAXWS Handler to the CXF endpoint.
- The Message Header Relay mechanism has been merged into CxfHeaderFilterStrategy. The relayHeaders option, its semantics, and default value remain the same, but it is a property of CxfHeaderFilterStrategy.
Here is an example of configuring it.<bean id="dropAllMessageHeadersStrategy" class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfHeaderFilterStrategy"> <!-- Set relayHeaders to false to drop all SOAP headers --> <property name="relayHeaders" value="false"/> </bean>
Then, your endpoint can reference the CxfHeaderFilterStrategy.
<route> <from uri="cxf:bean:routerNoRelayEndpoint?headerFilterStrategy=#dropAllMessageHeadersStrategy"/> <to uri="cxf:bean:serviceNoRelayEndpoint?headerFilterStrategy=#dropAllMessageHeadersStrategy"/> </route>
- The MessageHeadersRelay interface has changed slightly and has been renamed to MessageHeaderFilter. It is a property of CxfHeaderFilterStrategy. Here is an example of configuring user defined Message Header Filters:
<bean id="customMessageFilterStrategy" class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfHeaderFilterStrategy"> <property name="messageHeaderFilters"> <list> <!-- SoapMessageHeaderFilter is the built in filter. It can be removed by omitting it. --> <bean class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.SoapMessageHeaderFilter"/> <!-- Add custom filter here --> <bean class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.soap.headers.CustomHeaderFilter"/> </list> </property> </bean>
- Other than relayHeaders, there are new properties that can be configured in CxfHeaderFilterStrategy.
Name Description type Required? Default value relayHeaders All message headers will be processed by Message Header Filters boolean No true (1.6.1 behavior) relayAllMessageHeaders All message headers will be propagated (without processing by Message Header Filters) boolean No false (1.6.1 behavior) allowFilterNamespaceClash If two filters overlap in activation namespace, the property control how it should be handled. If the value is true, last one wins. If the value is false, it will throw an exception boolean No false (1.6.1 behavior)
Configure the CXF endpoints with Spring
You can configure the CXF endpoint with the Spring configuration file shown below, and you can also embed the endpoint into the camelContext tags. When you are invoking the service endpoint, you can set the operationName and operationNameSpace headers to explicitly state which operation you are calling.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:cxf="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/cxfEndpoint" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/cxfEndpoint http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/cxf/camel-cxf-1.6.0.xsd http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd "> <cxf:cxfEndpoint id="routerEndpoint" address="http://localhost:9003/CamelContext/RouterPort" serviceClass="org.apache.hello_world_soap_http.GreeterImpl"/> <cxf:cxfEndpoint id="serviceEndpoint" address="http://localhost:9000/SoapContext/SoapPort" wsdlURL="testutils/hello_world.wsdl" serviceClass="org.apache.hello_world_soap_http.Greeter" endpointName="s:SoapPort" serviceName="s:SOAPService" xmlns:s="http://apache.org/hello_world_soap_http" /> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="cxf:bean:routerEndpoint" /> <to uri="cxf:bean:serviceEndpoint" /> </route> </camelContext> </beans>
NOTE In Camel 2.x we change to use {{http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf}} as the CXF endpoint's target namespace.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:cxf="http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf/camel-cxf.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd "> ...
Be sure to include the JAX-WS schemaLocation attribute specified on the root beans element. This allows CXF to validate the file and is required. Also note the namespace declarations at the end of the <cxf:cxfEndpoint/> tag--these are required because the combined {namespace}localName syntax is presently not supported for this tag's attribute values.
The cxf:cxfEndpoint element supports many additional attributes:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| PortName | The endpoint name this service is implementing, it maps to the wsdl:port@name. In the format of ns:PORT_NAME where ns is a namespace prefix valid at this scope. |
| serviceName | The service name this service is implementing, it maps to the wsdl:service@name. In the format of ns:SERVICE_NAME where ns is a namespace prefix valid at this scope. |
| wsdlURL | The location of the WSDL. Can be on the classpath, file system, or be hosted remotely. |
| bindingId | The bindingId for the service model to use. |
| address | The service publish address. |
| bus | The bus name that will be used in the JAX-WS endpoint. |
| serviceClass | The class name of the SEI (Service Endpoint Interface) class which could have JSR181 annotation or not. |
It also supports many child elements:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| cxf:inInterceptors | The incoming interceptors for this endpoint. A list of <bean> or <ref>. |
| cxf:inFaultInterceptors | The incoming fault interceptors for this endpoint. A list of <bean> or <ref>. |
| cxf:outInterceptors | The outgoing interceptors for this endpoint. A list of <bean> or <ref>. |
| cxf:outFaultInterceptors | The outgoing fault interceptors for this endpoint. A list of <bean> or <ref>. |
| cxf:properties | A properties map which should be supplied to the JAX-WS endpoint. See below. |
| cxf:handlers | A JAX-WS handler list which should be supplied to the JAX-WS endpoint. See below. |
| cxf:dataBinding | You can specify the which DataBinding will be use in the endpoint. This can be supplied using the Spring <bean class="MyDataBinding"/> syntax. |
| cxf:binding | You can specify the BindingFactory for this endpoint to use. This can be supplied using the Spring <bean class="MyBindingFactory"/> syntax. |
| cxf:features | The features that hold the interceptors for this endpoint. A list of {{<bean>}}s or {{<ref>}}s |
| cxf:schemaLocations | The schema locations for endpoint to use. A list of {{<schemaLocation>}}s |
| cxf:serviceFactory | The service factory for this endpoint to use. This can be supplied using the Spring <bean class="MyServiceFactory"/> syntax |
You can find more advanced examples which show how to provide interceptors , properties and handlers here:
http://cwiki.apache.org/CXF20DOC/jax-ws-configuration.html
NOTE
You can use cxf:properties to set the camel-cxf endpoint's dataFormat and setDefaultBus properties from spring configuration file.
<cxf:cxfEndpoint id="testEndpoint" address="http://localhost:9000/router" serviceClass="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.HelloService" endpointName="s:PortName" serviceName="s:ServiceName" xmlns:s="http://www.example.com/test"> <cxf:properties> <entry key="dataFormat" value="MESSAGE"/> <entry key="setDefaultBus" value="true"/> </cxf:properties> </cxf:cxfEndpoint>
How to make the camel-cxf component use log4j instead of java.util.logging
CXF's default logger is java.util.logging. If you want to change it to log4j, proceed as follows. Create a file, in the classpath, named META-INF/cxf/org.apache.cxf.logger. This file should contain the fully-qualified name of the class, org.apache.cxf.common.logging.Log4jLogger, with no comments, on a single line.
How to consume a message from a camel-cxf endpoint in POJO data format
The camel-cxf endpoint consumer POJO data format is based on the cxf invoker, so the message header has a property with the name of CxfConstants.OPERATION_NAME and the message body is a list of the SEI method parameters.
public class PersonProcessor implements Processor { private static final transient Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(PersonProcessor.class); public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { LOG.info("processing exchange in camel"); BindingOperationInfo boi = (BindingOperationInfo)exchange.getProperty(BindingOperationInfo.class.toString()); if (boi != null) { LOG.info("boi.isUnwrapped" + boi.isUnwrapped()); } // Get the parameters list which element is the holder. MessageContentsList msgList = (MessageContentsList)exchange.getIn().getBody(); Holder<String> personId = (Holder<String>)msgList.get(0); Holder<String> ssn = (Holder<String>)msgList.get(1); Holder<String> name = (Holder<String>)msgList.get(2); if (personId.value == null || personId.value.length() == 0) { LOG.info("person id 123, so throwing exception"); // Try to throw out the soap fault message org.apache.camel.wsdl_first.types.UnknownPersonFault personFault = new org.apache.camel.wsdl_first.types.UnknownPersonFault(); personFault.setPersonId(""); org.apache.camel.wsdl_first.UnknownPersonFault fault = new org.apache.camel.wsdl_first.UnknownPersonFault("Get the null value of person name", personFault); // Since camel has its own exception handler framework, we can't throw the exception to trigger it // We just set the fault message in the exchange for camel-cxf component handling and return exchange.getOut().setFault(true); exchange.getOut().setBody(fault); return; } name.value = "Bonjour"; ssn.value = "123"; LOG.info("setting Bonjour as the response"); // Set the response message, first element is the return value of the operation, // the others are the holders of method parameters exchange.getOut().setBody(new Object[] {null, personId, ssn, name}); } }
How to prepare the message for the camel-cxf endpoint in POJO data format
The camel-cxf endpoint producer is based on the cxf client API. First you need to specify the operation name in the message header, then add the method parameters to a list, and initialize the message with this parameter list. The response message's body is a messageContentsList, you can get the result from that list.
NOTE After Camel 1.5 , we change the message body from object array to message content list. If you still want to get the object array from the message body, you can get the body using message.getbody(Object[].class), as follows:
Exchange senderExchange = new DefaultExchange(context, ExchangePattern.InOut); final List<String> params = new ArrayList<String>(); // Prepare the request message for the camel-cxf procedure params.add(TEST_MESSAGE); senderExchange.getIn().setBody(params); senderExchange.getIn().setHeader(CxfConstants.OPERATION_NAME, ECHO_OPERATION); Exchange exchange = template.send("direct:EndpointA", senderExchange); org.apache.camel.Message out = exchange.getOut(); // The response message's body is an MessageContentsList which first element is the return value of the operation, // If there are some holder parameters, the holder parameter will be filled in the reset of List. // The result will be extract from the MessageContentsList with the String class type MessageContentsList result = (MessageContentsList)out.getBody(); LOG.info("Received output text: " + result.get(0)); Map<String, Object> responseContext = CastUtils.cast((Map)out.getHeader(Client.RESPONSE_CONTEXT)); assertNotNull(responseContext); assertEquals("We should get the response context here", "UTF-8", responseContext.get(org.apache.cxf.message.Message.ENCODING)); assertEquals("Reply body on Camel is wrong", "echo " + TEST_MESSAGE, result.get(0));
How to deal with the message for a camel-cxf endpoint in PAYLOAD data format
PAYLOAD means that you process the payload message from the SOAP envelope. You can use the Header.HEADER_LIST as the key to set or get the SOAP headers and use the List<Element> to set or get SOAP body elements.
Camel 1.x branch, you can get the List<Element> and header from the CXF Message, but if you want to set the response message, you need to create the CXF message using the CXF API.
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from(SIMPLE_ENDPOINT_URI + "&dataFormat=PAYLOAD").to("log:info").process(new Processor() { public void process(final Exchange exchange) throws Exception { Message inMessage = exchange.getIn(); if (inMessage instanceof CxfMessage) { CxfMessage cxfInMessage = (CxfMessage) inMessage; CxfMessage cxfOutMessage = (CxfMessage) exchange.getOut(); List<Element> inElements = cxfInMessage.getMessage().get(List.class); List<Element> outElements = new ArrayList<Element>(); XmlConverter converter = new XmlConverter(); String documentString = ECHO_RESPONSE; if (inElements.get(0).getLocalName().equals("echoBoolean")) { documentString = ECHO_BOOLEAN_RESPONSE; } org.apache.cxf.message.Exchange ex = ((CxfExchange)exchange).getExchange(); Endpoint ep = ex.get(Endpoint.class); org.apache.cxf.message.Message response = ep.getBinding().createMessage(); Document outDocument = converter.toDOMDocument(documentString); outElements.add(outDocument.getDocumentElement()); response.put(List.class, outElements); cxfOutMessage.setMessage(response); } } }); } }; }
Change in 2.0, CxfMessage.getBody() will return an org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfPayload object, which has getters for SOAP message headers and Body elements. This change enables decoupling the native CXF message from the Camel message.
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from(SIMPLE_ENDPOINT_URI + "&dataFormat=PAYLOAD").to("log:info").process(new Processor() { public void process(final Exchange exchange) throws Exception { CxfPayload<SoapHeader> requestPayload = exchange.getIn().getBody(CxfPayload.class); List<Element> inElements = requestPayload.getBody(); List<Element> outElements = new ArrayList<Element>(); XmlConverter converter = new XmlConverter(); String documentString = ECHO_RESPONSE; if (inElements.get(0).getLocalName().equals("echoBoolean")) { documentString = ECHO_BOOLEAN_RESPONSE; } Document outDocument = converter.toDOMDocument(documentString); outElements.add(outDocument.getDocumentElement()); // set the payload header with null CxfPayload<SoapHeader> responsePayload = new CxfPayload<SoapHeader>(null, outElements); exchange.getOut().setBody(responsePayload); } }); } }; }
How to get and set SOAP headers in POJO mode
POJO means that the data format is a "list of Java objects" when the Camel-cxf endpoint produces or consumes Camel exchanges. Even though Camel expose message body as POJOs in this mode, Camel-cxf still provides access to read and write SOAP headers. However, since CXF interceptors remove in-band SOAP headers from Header list after they have been processed, only out-of-band SOAP headers are available to Camel-cxf in POJO mode.
The following example illustrate how to get/set SOAP headers. Suppose we have a route that forwards from one Camel-cxf endpoint to another. That is, SOAP Client -> Camel -> CXF service. We can attach two processors to obtain/insert SOAP headers at (1) before request goes out to the CXF service and (2) before response comes back to the SOAP Client. Processor (1) and (2) in this example are InsertRequestOutHeaderProcessor and InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor. Our route looks like this:
<route> <from uri="cxf:bean:routerRelayEndpointWithInsertion"/> <process ref="InsertRequestOutHeaderProcessor" /> <to uri="cxf:bean:serviceRelayEndpointWithInsertion"/> <process ref="InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor" /> </route>
In 2.x SOAP headers are propagated to and from Camel Message headers. The Camel message header name is "org.apache.cxf.headers.Header.list" which is a constant defined in CXF (org.apache.cxf.headers.Header.HEADER_LIST). The header value is a List of CXF SoapHeader objects (org.apache.cxf.binding.soap.SoapHeader). The following snippet is the InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor (that insert a new SOAP header in the response message). The way to access SOAP headers in both InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor and InsertRequestOutHeaderProcessor are actually the same. The only difference between the two processors is setting the direction of the inserted SOAP header.
public static class InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { List<SoapHeader> soapHeaders = (List)exchange.getIn().getHeader(Header.HEADER_LIST); // Insert a new header String xml = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?><outofbandHeader " + "xmlns=\"http://cxf.apache.org/outofband/Header\" hdrAttribute=\"testHdrAttribute\" " + "xmlns:soap=\"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/\" soap:mustUnderstand=\"1\">" + "<name>New_testOobHeader</name><value>New_testOobHeaderValue</value></outofbandHeader>"; SoapHeader newHeader = new SoapHeader(soapHeaders.get(0).getName(), DOMUtils.readXml(new StringReader(xml)).getDocumentElement()); // make sure direction is OUT since it is a response message. newHeader.setDirection(Direction.DIRECTION_OUT); //newHeader.setMustUnderstand(false); soapHeaders.add(newHeader); } }
In 1.x SOAP headers are not propagated to and from Camel Message headers. Users have to go deeper into CXF APIs to access SOAP headers. Also, accessing the SOAP headers in a request message is slight different than in a response message. The InsertRequestOutHeaderProcessor and InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor are as follow.
public static class InsertRequestOutHeaderProcessor implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { CxfMessage message = exchange.getIn().getBody(CxfMessage.class); Message cxf = message.getMessage(); List<SoapHeader> soapHeaders = (List)cxf.get(Header.HEADER_LIST); // Insert a new header String xml = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?><outofbandHeader " + "xmlns=\"http://cxf.apache.org/outofband/Header\" hdrAttribute=\"testHdrAttribute\" " + "xmlns:soap=\"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/\" soap:mustUnderstand=\"1\">" + "<name>New_testOobHeader</name><value>New_testOobHeaderValue</value></outofbandHeader>"; SoapHeader newHeader = new SoapHeader(soapHeaders.get(0).getName(), DOMUtils.readXml(new StringReader(xml)).getDocumentElement()); // make sure direction is IN since it is a request message. newHeader.setDirection(Direction.DIRECTION_IN); //newHeader.setMustUnderstand(false); soapHeaders.add(newHeader); } } public static class InsertResponseOutHeaderProcessor implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { CxfMessage message = exchange.getIn().getBody(CxfMessage.class); Map responseContext = (Map)message.getMessage().get(Client.RESPONSE_CONTEXT); List<SoapHeader> soapHeaders = (List)responseContext.get(Header.HEADER_LIST); // Insert a new header String xml = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?><outofbandHeader " + "xmlns=\"http://cxf.apache.org/outofband/Header\" hdrAttribute=\"testHdrAttribute\" " + "xmlns:soap=\"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/\" soap:mustUnderstand=\"1\">" + "<name>New_testOobHeader</name><value>New_testOobHeaderValue</value></outofbandHeader>"; SoapHeader newHeader = new SoapHeader(soapHeaders.get(0).getName(), DOMUtils.readXml(new StringReader(xml)).getDocumentElement()); // make sure direction is OUT since it is a response message. newHeader.setDirection(Direction.DIRECTION_OUT); //newHeader.setMustUnderstand(false); soapHeaders.add(newHeader); } }
How to get and set SOAP headers in PAYLOAD mode
We've already shown how to access SOAP message (CxfPayload object) in PAYLOAD mode (See "How to deal with the message for a camel-cxf endpoint in PAYLOAD data format").
In 2.x Once you obtain a CxfPayload object, you can invoke the CxfPayload.getHeaders() method that returns a List of DOM Elements (SOAP headers).
from(routerEndpointURI).process(new Processor() { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { CxfPayload<SoapHeader> payload = exchange.getIn().getBody(CxfPayload.class); List<Element> elements = payload.getBody(); assertNotNull("We should get the elements here", elements); assertEquals("Get the wrong elements size", 1, elements.size()); assertEquals("Get the wrong namespace URI", "http://camel.apache.org/pizza/types", elements.get(0).getNamespaceURI()); List<SoapHeader> headers = payload.getHeaders(); assertNotNull("We should get the headers here", headers); assertEquals("Get the wrong headers size", headers.size(), 1); assertEquals("Get the wrong namespace URI", ((Element)(headers.get(0).getObject())).getNamespaceURI(), "http://camel.apache.org/pizza/types"); } }) .to(serviceEndpointURI);
*In 1.x" You can get/set to the CXF Message by the key "org.apache.cxf.headers.Header.list" which is a constant defined in CXF (org.apache.cxf.headers.Header.HEADER_LIST).
from(routerEndpointURI).process(new Processor() { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { Message inMessage = exchange.getIn(); CxfMessage message = (CxfMessage) inMessage; List<Element> elements = message.getMessage().get(List.class); assertNotNull("We should get the payload elements here" , elements); assertEquals("Get the wrong elements size" , elements.size(), 1); assertEquals("Get the wrong namespace URI" , elements.get(0).getNamespaceURI(), "http://camel.apache.org/pizza/types"); List<SoapHeader> headers = CastUtils.cast((List<?>)message.getMessage().get(Header.HEADER_LIST)); assertNotNull("We should get the headers here", headers); assertEquals("Get the wrong headers size", headers.size(), 1); assertEquals("Get the wrong namespace URI" , ((Element)(headers.get(0).getObject())).getNamespaceURI(), "http://camel.apache.org/pizza/types"); } }) .to(serviceEndpointURI);
SOAP headers are not available in MESSAGE mode
SOAP headers are not available in MESSAGE mode as SOAP processing is skipped.
How to throw a SOAP Fault from Camel
If you are using a camel-cxf endpoint to consume the SOAP request, you may need to throw the SOAP Fault from the camel context.
Basically, you can use the throwFault DSL to do that; it works for POJO, PAYLOAD and MESSAGE data format.
You can define the soap fault like this
SOAP_FAULT = new SoapFault(EXCEPTION_MESSAGE, SoapFault.FAULT_CODE_CLIENT);
Element detail = SOAP_FAULT.getOrCreateDetail();
Document doc = detail.getOwnerDocument();
Text tn = doc.createTextNode(DETAIL_TEXT);
detail.appendChild(tn);
Then throw it as you like
from(routerEndpointURI).setFaultBody(constant(SOAP_FAULT));
If your CXF endpoint is working in the MESSAGE data format, you could set the the SOAP Fault message in the message body and set the response code in the message header.
from(routerEndpointURI).process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { Message out = exchange.getOut(); // Set the message body with the out.setBody(this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("SoapFaultMessage.xml")); // Set the response code here out.setHeader(org.apache.cxf.message.Message.RESPONSE_CODE, new Integer(500)); } });
NOTE the response code setting only works in Camel's version >= 1.5.1
How to propagate a camel-cxf endpoint's request and response context
cxf client API provides a way to invoke the operation with request and response context. If you are using a camel-cxf endpoint producer to invoke the outside web service, you can set the request context and get response context with the following code:
CxfExchange exchange = (CxfExchange)template.send(getJaxwsEndpointUri(), new Processor() {
public void process(final Exchange exchange) {
final List<String> params = new ArrayList<String>();
params.add(TEST_MESSAGE);
// Set the request context to the inMessage
Map<String, Object> requestContext = new HashMap<String, Object>();
requestContext.put(BindingProvider.ENDPOINT_ADDRESS_PROPERTY, JAXWS_SERVER_ADDRESS);
exchange.getIn().setBody(params);
exchange.getIn().setHeader(Client.REQUEST_CONTEXT , requestContext);
exchange.getIn().setHeader(CxfConstants.OPERATION_NAME, GREET_ME_OPERATION);
}
});
org.apache.camel.Message out = exchange.getOut();
// The output is an object array, the first element of the array is the return value
Object\[\] output = out.getBody(Object\[\].class);
LOG.info("Received output text: " + output\[0\]);
// Get the response context form outMessage
Map<String, Object> responseContext = CastUtils.cast((Map)out.getHeader(Client.RESPONSE_CONTEXT));
assertNotNull(responseContext);
assertEquals("Get the wrong wsdl opertion name", "{http://apache.org/hello_world_soap_http}greetMe",
responseContext.get("javax.xml.ws.wsdl.operation").toString());
Attachment Support
POJO Mode: Both SOAP with Attachment and MTOM are supported (see example in Payload Mode for enabling MTOM). However, SOAP with Attachment is not tested. Since attachments are marshalled and unmarshalled into POJOs, users typically do not need to deal with the attachment themself. Attachments are propagated to Camel message's attachments since 2.1. So, it is possible to retreive attachments by Camel Message API
DataHandler Message.getAttachment(String id)
Payload Mode: MTOM is supported since 2.1. Attachments can be retrieve by Camel Message APIs mentioned above. SOAP with Attachment is not supported as there is no SOAP processing in this mode.
To enable MTOM, set the CXF endpoint property "mtom_enabled" to true. (I believe you can only do it with Spring.)
<cxf:cxfEndpoint id="routerEndpoint" address="http://localhost:9091/jaxws-mtom/hello" wsdlURL="mtom.wsdl" serviceName="ns:HelloService" endpointName="ns:HelloPort" xmlns:ns="http://apache.org/camel/cxf/mtom_feature"> <cxf:properties> <!-- enable mtom by setting this property to true --> <entry key="mtom-enabled" value="true"/> <!-- set the camel-cxf endpoint data fromat to PAYLOAD mode --> <entry key="dataFormat" value="PAYLOAD"/> </cxf:properties>
You can produce a Camel message with attachment to send to a CXF endpoint in Payload mode.
Exchange exchange = context.createProducerTemplate().send("direct:testEndpoint", new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.setPattern(ExchangePattern.InOut); List<Element> elements = new ArrayList<Element>(); elements.add(DOMUtils.readXml(new StringReader(MtomTestHelper.REQ_MESSAGE)).getDocumentElement()); CxfPayload<SoapHeader> body = new CxfPayload<SoapHeader>(new ArrayList<SoapHeader>(), elements); exchange.getIn().setBody(body); exchange.getIn().addAttachment(MtomTestHelper.REQ_PHOTO_CID, new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(MtomTestHelper.REQ_PHOTO_DATA, "application/octet-stream"))); exchange.getIn().addAttachment(MtomTestHelper.REQ_IMAGE_CID, new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(MtomTestHelper.requestJpeg, "image/jpeg"))); } }); // process response CxfPayload<SoapHeader> out = exchange.getOut().getBody(CxfPayload.class); Assert.assertEquals(1, out.getBody().size()); Map<String, String> ns = new HashMap<String, String>(); ns.put("ns", MtomTestHelper.SERVICE_TYPES_NS); ns.put("xop", MtomTestHelper.XOP_NS); XPathUtils xu = new XPathUtils(ns); Element ele = (Element)xu.getValue("//ns:DetailResponse/ns:photo/xop:Include", out.getBody().get(0), XPathConstants.NODE); String photoId = ele.getAttribute("href").substring(4); // skip "cid:" ele = (Element)xu.getValue("//ns:DetailResponse/ns:image/xop:Include", out.getBody().get(0), XPathConstants.NODE); String imageId = ele.getAttribute("href").substring(4); // skip "cid:" DataHandler dr = exchange.getOut().getAttachment(photoId); Assert.assertEquals("application/octet-stream", dr.getContentType()); MtomTestHelper.assertEquals(MtomTestHelper.RESP_PHOTO_DATA, IOUtils.readBytesFromStream(dr.getInputStream())); dr = exchange.getOut().getAttachment(imageId); Assert.assertEquals("image/jpeg", dr.getContentType()); BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(dr.getInputStream()); Assert.assertEquals(560, image.getWidth()); Assert.assertEquals(300, image.getHeight());
You can also consume a Camel message received from a CXF endpoint in Payload mode.
public static class MyProcessor implements Processor { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { CxfPayload<SoapHeader> in = exchange.getIn().getBody(CxfPayload.class); // verify request Assert.assertEquals(1, in.getBody().size()); Map<String, String> ns = new HashMap<String, String>(); ns.put("ns", MtomTestHelper.SERVICE_TYPES_NS); ns.put("xop", MtomTestHelper.XOP_NS); XPathUtils xu = new XPathUtils(ns); Element ele = (Element)xu.getValue("//ns:Detail/ns:photo/xop:Include", in.getBody().get(0), XPathConstants.NODE); String photoId = ele.getAttribute("href").substring(4); // skip "cid:" Assert.assertEquals(MtomTestHelper.REQ_PHOTO_CID, photoId); ele = (Element)xu.getValue("//ns:Detail/ns:image/xop:Include", in.getBody().get(0), XPathConstants.NODE); String imageId = ele.getAttribute("href").substring(4); // skip "cid:" Assert.assertEquals(MtomTestHelper.REQ_IMAGE_CID, imageId); DataHandler dr = exchange.getIn().getAttachment(photoId); Assert.assertEquals("application/octet-stream", dr.getContentType()); MtomTestHelper.assertEquals(MtomTestHelper.REQ_PHOTO_DATA, IOUtils.readBytesFromStream(dr.getInputStream())); dr = exchange.getIn().getAttachment(imageId); Assert.assertEquals("image/jpeg", dr.getContentType()); MtomTestHelper.assertEquals(MtomTestHelper.requestJpeg, IOUtils.readBytesFromStream(dr.getInputStream())); // create response List<Element> elements = new ArrayList<Element>(); elements.add(DOMUtils.readXml(new StringReader(MtomTestHelper.RESP_MESSAGE)).getDocumentElement()); CxfPayload<SoapHeader> body = new CxfPayload<SoapHeader>(new ArrayList<SoapHeader>(), elements); exchange.getOut().setBody(body); exchange.getOut().addAttachment(MtomTestHelper.RESP_PHOTO_CID, new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(MtomTestHelper.RESP_PHOTO_DATA, "application/octet-stream"))); exchange.getOut().addAttachment(MtomTestHelper.RESP_IMAGE_CID, new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(MtomTestHelper.responseJpeg, "image/jpeg"))); } }
Message Mode: Attachments are not supported as it does not process the message at all.
CXF Bean Component (2.0 or later)
The cxfbean: component allows other Camel endpoints to send exchange and invoke Web service bean objects. (Currently, it only supports JAXRS, JAXWS(new to camel2.1) annotated service bean.)
Note: CxfBeanEndpoint is a ProcessorEndpoint so it has no consumers. It works similarly to a Bean component.
URI format
cxfbean:serviceBeanRef
Where serviceBeanRef is a registry key to look up the service bean object. If serviceBeanRef references a List object, elements of the List are the service bean objects accepted by the endpoint.
Options
| Name | Description | Example | Required? | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cxfBeanBinding | CXF bean binding specified by the # notation. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.cxfbean.CxfBeanBinding. | cxfBinding=#bindingName | No | An instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.cxfbean.DefaultCxfBeanBinding |
| bus | CXF bus reference specified by the # notation. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.cxf.Bus. | bus=#busName | No | Default bus created by CXF Bus Factory |
| headerFilterStrategy | Header filter strategy specified by the # notation. The referenced object must be an instance of org.apache.camel.spi.HeaderFilterStrategy. | headerFilterStrategy=#strategyName | No | An instance of org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfHeaderFilterStrategy |
| setDefaultBus | Will set the default bus when CXF endpoint create a bus by itself. | true, false | No | false |
Headers
| Name | Description | Type | Required? | Default Value | In/Out | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CamelHttpCharacterEncoding (before 2.0-m2: CamelCxfBeanCharacterEncoding) | Character encoding | String | No | None | In | ISO-8859-1 |
| CamelContentType (before 2.0-m2: CamelCxfBeanContentType) | Content type | String | No | */* | In | text/xml |
| CamelHttpBaseUri (2.0-m3 and before: CamelCxfBeanRequestBasePath) | The value of this header will be set in the CXF message as the Message.BASE_PATH property. It is needed by CXF JAX-RS processing. Basically, it is the scheme, host and port portion of the request URI. | String | Yes | The Endpoint URI of the source endpoint in the Camel exchange | In | http://localhost:9000 |
| CamelHttpPath (before 2.0-m2: CamelCxfBeanRequestPath) | Request URI's path | String | Yes | None | In | consumer/123 |
| CamelHttpMethod (before 2.0-m2: CamelCxfBeanVerb) | RESTful request verb | String | Yes | None | In | GET, PUT, POST, DELETE |
| CamelHttpResponseCode | HTTP response code | Integer | No | None | Out | 200 |
Note: Currently, CXF Bean component has (only) been tested with Jetty HTTP component it can understand headers from Jetty HTTP component without requiring conversion.
A Working Sample
This sample shows how to create a route that starts a Jetty HTTP server. The route sends requests to a CXF Bean and invokes a JAXRS annotated service.
First, create a route as follows. The from endpoint is a Jetty HTTP endpoint that is listening on port 9000. Notice that the matchOnUriPrefix option must be set to true because RESTful request URI will not match the endpoint's URI http://localhost:9000 exactly.
<route> <from uri="jetty:http://localhost:9000?matchOnUriPrefix=true" /> <to uri="cxfbean:customerServiceBean" /> </route>
The to endpoint is a CXF Bean with bean name customerServiceBean. The name will be looked up from the registry. Next, we make sure our service bean is available in Spring registry. We create a bean definition in the Spring configuration. In this example, we create a List of service beans (of one element). We could have created just a single bean without a List.
<util:list id="customerServiceBean"> <bean class="org.apache.camel.component.cxf.jaxrs.testbean.CustomerService" /> </util:list> <bean class="org.apache.camel.wsdl_first.PersonImpl" id="jaxwsBean" />
That's it. Once the route is started, the web service is ready for business. A HTTP client can make a request and receive response.
url = new URL("http://localhost:9000/customerservice/orders/223/products/323"); in = url.openStream(); assertEquals("{\"Product\":{\"description\":\"product 323\",\"id\":323}}", CxfUtils.getStringFromInputStream(in));
See Also
CXFRS Component
The cxfrs: component provides integration with Apache CXF for connecting to JAX-RS services hosted in CXF.
Maven users will need to add the following dependency to their pom.xml for this component:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-cxf</artifactId> <version>x.x.x</version> <!-- use the same version as your Camel core version --> </dependency>
URI format
cxfrs://address?options
Where address represents the CXF endpoint's address
cxfrs:bean:rsEndpoint
Where rsEndpoint represents the spring bean's name which presents the CXFRS client or server
For either style above, you can append options to the URI as follows:
cxf:bean:cxfEndpoint?ResourceClass=org.apache.camel.rs.Example
Options
| Name | Description | Example | Required? | default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResourcesClass | The resource classes which you want to export as REST service | resourcesClass=org.apache.camel.rs.Example1,org.apache.camel.rs.Exchange2 | No | None |
| HttpClientAPI | new to Camel 2.1 If it is true, the CxfRsProducer will use the HttpClientAPI to invoke the service If it is false, the CxfRsProducer will use the ProxyClientAPI to invoke the service | httpClientAPI=true | No | true |
You can also configure the CXF REST endpoint through the spring configuration. Since there are lots of difference between the CXF REST client and CXF REST Server, we provides different configuration for them.
Please check out the schema file and CXF REST user guide for more information.
How to consumer the REST request in Camel ?
CXF JAXRS front end implements the JAXRS(JSR311) API, so we can export the resources classes as a REST service. And we leverage the CXF Invoker API to turn a REST request into a normal Java object method invocation.
Unlike the camel-restlet, you don't need to specify the URI template within your restlet endpoint, CXF take care of the REST request URI to resource class method mapping according to the JSR311 specification. All you need to do in Camel is delegate this method request to a right processor or endpoint.
Here is an example
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { errorHandler(new NoErrorHandlerBuilder()); from(CXF_RS_ENDPOINT_URI).process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { Message inMessage = exchange.getIn(); // Get the operation name from in message String operationName = inMessage.getHeader(CxfConstants.OPERATION_NAME, String.class); // The parameter of the invocation is stored in the body of in message String id = (String) inMessage.getBody(Object[].class)[0]; if ("getCustomer".equals(operationName)) { String httpMethod = inMessage.getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_METHOD, String.class); assertEquals("Get a wrong http method", "GET", httpMethod); String uri = inMessage.getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_URI, String.class); if ("/customerservice/customers/126".equals(uri)) { Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setId(Long.parseLong(id)); customer.setName("Willem"); // We just put the response Object into the out message body exchange.getOut().setBody(customer); } else { Response r = Response.status(404).entity("Can't found the customer with uri " + uri).build(); throw new WebApplicationException(r); } } } }); } }; }
How to invoke the REST service through camel-cxfrs producer ?
CXF JAXRS front end implements a proxy based client API, with this API you can invoke the remote REST service through a proxy.
camel-cxfrs producer is based on this proxy API.
So, you just need to specify the operation name in the message header and prepare the parameter in the message body, camel-cxfrs producer will generate right REST request for you.
Here is an example
Exchange exchange = template.send("direct://proxy", new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.setPattern(ExchangePattern.InOut); Message inMessage = exchange.getIn(); // set the operation name inMessage.setHeader(CxfConstants.OPERATION_NAME, "getCustomer"); // using the proxy client API inMessage.setHeader(CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_USING_HTTP_API, Boolean.FALSE); // set the parameters , if you just have one parameter // camel will put this object into an Object[] itself inMessage.setBody("123"); } }); // get the response message Customer response = (Customer) exchange.getOut().getBody(); assertNotNull("The response should not be null ", response); assertEquals("Get a wrong customer id ", String.valueOf(response.getId()), "123"); assertEquals("Get a wrong customer name", response.getName(), "John");
CXF JAXRS front end also provides a http centric client API, You can also invoke this API from camel-cxfrs producer. You need to specify the HTTP_PATH and Http method and let the the producer know to use the http centric client by using the URI option httpClientAPI or set the message header with CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_USING_HTTP_API. You can turn the response object to the type class that you specify with CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_RESPONSE_CLASS.
Exchange exchange = template.send("direct://http", new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.setPattern(ExchangePattern.InOut); Message inMessage = exchange.getIn(); // using the http central client API inMessage.setHeader(CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_USING_HTTP_API, Boolean.TRUE); // set the Http method inMessage.setHeader(Exchange.HTTP_METHOD, "GET"); // set the relative path inMessage.setHeader(Exchange.HTTP_PATH, "/customerservice/customers/123"); // Specify the response class , cxfrs will use InputStream as the response object type inMessage.setHeader(CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_RESPONSE_CLASS, Customer.class); // since we use the Get method, so we don't need to set the message body inMessage.setBody(null); } }); // get the response message Customer response = (Customer) exchange.getOut().getBody(); assertNotNull("The response should not be null ", response); assertEquals("Get a wrong customer id ", String.valueOf(response.getId()), "123"); assertEquals("Get a wrong customer name", response.getName(), "John");
From Camel 2.1, we also support to specify the query parameters from cxfrs URI for the CXFRS http centric client.
Exchange exchange = template.send("cxfrs://http://localhost:9003/testQuery?httpClientAPI=true&q1=12&q2=13"
To support the Dynamical routing, you can override the URI's query parameters by using the CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_QUERY_MAP header to set the parameter map for it.To support the Dynamical routing, you can override the URI's query parameters by using the CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_QUERY_MAP header to set the parameter map for it.
Map<String, String> queryMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); queryMap.put("q1", "new"); queryMap.put("q2", "world"); inMessage.setHeader(CxfConstants.CAMEL_CXF_RS_QUERY_MAP, queryMap);
DataSet Component
Testing of distributed and asynchronous processing is notoriously difficult. The Mock, Test and DataSet endpoints work great with the Camel Testing Framework to simplify your unit and integration testing using Enterprise Integration Patterns and Camel's large range of Components together with the powerful Bean Integration.The DataSet component (available since 1.3.0) provides a mechanism to easily perform load & soak testing of your system. It works by allowing you to create DataSet instances both as a source of messages and as a way to assert that the data set is received.
Camel will use the throughput logger when sending dataset's.
URI format
dataset:name[?options]
Where name is used to find the DataSet instance in the Registry
Camel ships with a support implementation of org.apache.camel.component.dataset.DataSet, the org.apache.camel.component.dataset.DataSetSupport class, that can be used as a base for implementing your own DataSet. Camel also ships with a default implementation, the org.apache.camel.component.dataset.SimpleDataSet that can be used for testing.
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| produceDelay | 3 | Allows a delay in ms to be specified, which causes producers to pause in order to simulate slow producers. Uses a minimum of 3 ms delay unless you set this option to -1 to force no delay at all. |
| consumeDelay | 0 | Allows a delay in ms to be specified, which causes consumers to pause in order to simulate slow consumers. |
| preloadSize | 0 | Sets how many messages should be preloaded (sent) before the route completes its initialization. |
| initialDelay | 1000 | Camel 2.1: Time period in millis to wait before starting sending messages. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Configuring DataSet
Camel will lookup in the Registry for a bean implementing the DataSet interface. So you can register your own DataSet as:
<bean id="myDataSet" class="com.mycompany.MyDataSet"> <property name="size" value="100"/> </bean>
Example
For example, to test that a set of messages are sent to a queue and then consumed from the queue without losing any messages:
// send the dataset to a queue from("dataset:foo").to("activemq:SomeQueue"); // now lets test that the messages are consumed correctly from("activemq:SomeQueue").to("dataset:foo");
The above would look in the Registry to find the foo DataSet instance which is used to create the messages.
Then you create a DataSet implementation, such as using the SimpleDataSet as described below, configuring things like how big the data set is and what the messages look like etc.
Properties on SimpleDataSet
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| defaultBody | Object | Specifies the default message body. For SimpleDataSet it is a constant payload; though if you want to create custom payloads per message, create your own derivation of DataSetSupport. |
| reportGroup | long | Specifies the number of messages to be received before reporting progress. Useful for showing progress of a large load test. |
| size | long | Specifies how many messages to send/consume. |
Load testing ActiveMQ with Camel
There is an example of load testing an ActiveMQ queue using Camel in the ActiveMQ source code repository. The code lives at this location:
You can grab the code as follows:
svn co https://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/activemq/trunk/activemq-camel-loadtest/
Then try running the test case:
cd activemq-camel-loadtest mvn clean install
To see how the test is defined, see the Spring XML file
See Also
Direct Component
The direct: component provides direct, synchronous invocation of any consumers when a producer sends a message exchange.
This endpoint can be used to connect existing routes in the same camel context.
| Asynchronous The SEDA component provides asynchronous invocation of any consumers when a producer sends a message exchange. |
| Connection to other camel contexts The VM component provides connections between Camel contexts as long they run in the same JVM. |
URI format
direct:someName[?options]
Where someName can be any string to uniquely identify the endpoint
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allowMultipleConsumers | true | @deprecated If set to false, then when a second consumer is started on the endpoint, an IllegalStateException is thrown. Will be removed in Camel 2.1: Direct endpoint does not support multiple consumers. |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Samples
In the route below we use the direct component to link the two routes together:
from("activemq:queue:order.in").to("bean:orderServer?method=validate").to("direct:processOrder"); from("direct:processOrder").to("bean:orderService?method=process").to("activemq:queue:order.out");
And the sample using spring DSL:
<route> <from uri="activemq:queue:order.in"/> <to uri="bean:orderService?method=validate"/> <to uri="direct:processOrder"/> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:processOrder"/> <to uri="bean:orderService?method=process"/> <to uri="activemq:queue:order.out"/> </route>
See also samples from the SEDA component, how they can be used together.
See Also
Esper
The Esper component supports the Esper Library for Event Stream Processing. The camel-esper library is provided by the Camel Extra project which hosts all *GPL related components for Camel.
URI format
esper:name[?options]
When consuming from an Esper endpoint you must specify a pattern or eql statement to query the event stream.
For example
from("esper://cheese?pattern=every event=MyEvent(bar=5)"). to("activemq:Foo");
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| pattern | The Esper Pattern expression as a String to filter events | |
| eql | The Esper EQL expression as a String to filter events |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Demo
There is a demo which shows how to work with ActiveMQ, Camel and Esper in the Camel Extra project
See Also
Event Component
The event: component provides access to the Spring ApplicationEvent objects. This allows you to publish ApplicationEvent objects to a Spring ApplicationContext or to consume them. You can then use Enterprise Integration Patterns to process them such as Message Filter.
URI format
spring-event://default
If you use Camel 1.x then you may need to remove the // to get it working with the Spring event notification
spring-event:default
See Also
File Component - Camel 2.0 onwards
| Using Camel 1.x This documentation is only for Camel 2.0 or newer. If you are using Camel 1.x then see this link instead. |
The File component provides access to file systems, allowing files to be processed by any other Camel Components or messages from other components to be saved to disk.
URI format
file:directoryName[?options]
or
file://directoryName[?options]
Where directoryName represents the underlying file directory.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
| Only directories Camel 2.0 only support endpoints configured with a starting directory. So the directoryName must be a directory. In Camel 1.x you could also configure a file and this caused more harm than good as it could lead to confusing situations. |
| Avoid reading files currently being written by another application Beware the JDK File IO API is a bit limited in detecting whether another application is currently writing/copying a file. And the implementation can be different depending on OS platform as well. This could lead to that Camel thinks the file is not locked by another process and start consuming it. Therefore you have to do you own investigation what suites your environment. To help with this Camel provides different readLock options that you can use. See also the section Consuming files from folders where others drop files directly. |
URI Options
Common
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| autoCreate | true | Automatically create missing directories in the file's pathname. For the file consumer, that means creating the starting directory. For the file producer, it means the directory to where the files should be written. |
| bufferSize | 128kb | Write buffer sized in bytes. |
| fileName | null | Use Expression such as File Language to dynamically set the filename. For consumers, it's used as a filename filter. For producers, it's used to evaluate the filename to write. If an expression is set, it take precedence over the CamelFileName header. (Note: The header itself can also be an Expression). The expression options support both String and Expression types. If the expression is a String type, it is always evaluated using the File Language. If the expression is an Expression type, the specified Expression type is used - this allows you, for instance, to use OGNL expressions. For the consumer, you can use it to filter filenames, so you can for instance consume today's file using the File Language syntax: mydata-${date:now:yyyyMMdd}.txt. |
| flatten | false | Flatten is used to flatten the file name path to strip any leading paths, so it's just the file name. This allows you to consume recursively into sub-directories, but when you eg write the files to another directory they will be written in a single directory. Setting this to true on the producer enforces that any file name recived in CamelFileName header will be stripped for any leading paths. |
Consumer only
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| initialDelay | 1000 | Milliseconds before polling the file/directory starts. |
| delay | 500 | Milliseconds before the next poll of the file/directory. |
| useFixedDelay | false | Set to true to use fixed delay between pools, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
| recursive | false | If a directory, will look for files in all the sub-directories as well. |
| delete | false | If true, the file will be deleted after it is processed |
| noop | false | If true, the file is not moved or deleted in any way. This option is good for readonly data, or for ETL type requirements. If noop=true, Camel will set idempotent=true as well, to avoid consuming the same files over and over again. |
| preMove | null | Use Expression such as File Language to dynamically set the filename when moving it before processing. For example to move in-progress files into the order directory set this value to order. |
| move | .camel | Use Expression such as File Language to dynamically set the filename when moving it after processing. To move files into a .done subdirectory just enter .done. |
| moveFailed | null | Use Expression such as File Language to dynamically set the filename when moving failed files after processing. To move files into a error subdirectory just enter error. Note: When moving the files to another location it can/will handle the error when you move it to another location so Camel cannot pick up the file again. |
| include | null | Is used to include files, if filename matches the regex pattern. |
| exclude | null | Is used to exclude files, if filename matches the regex pattern. |
| idempotent | false | Option to use the Idempotent Consumer EIP pattern to let Camel skip already processed files. Will by default use a memory based LRUCache that holds 1000 entries. If noop=true then idempotent will be enabled as well to avoid consuming the same files over and over again. |
| idempotentRepository | null | Pluggable repository as a org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.MessageIdRepository class. Will by default use MemoryMessageIdRepository if none is specified and idempotent is true. |
| inProgressRepository | memory | Pluggable in-progress repository as a org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.MessageIdRepository class. The in-progress repository is used to account the current in progress files being consumed. By default a memory based repository is used. |
| filter | null | Pluggable filter as a org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileFilter class. Will skip files if filter returns false in its accept() method. Camel also ships with an ANT path matcher filter in the camel-spring component. More details in section below. |
| sorter | null | Pluggable sorter as a java.util.Comparator<org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFile> class. |
| sortBy | null | Built-in sort using the File Language. Supports nested sorts, so you can have a sort by file name and as a 2nd group sort by modified date. See sorting section below for details. |
| readLock | markerFile | Used by consumer, to only poll the files if it has exclusive read-lock on the file (i.e. the file is not in-progress or being written). Camel will wait until the file lock is granted. This option provides the build in strategies:
|
| readLockTimeout | Optional timeout in milliseconds for the read-lock, if supported by the read-lock. If the read-lock could not be granted and the timeout triggered, then Camel will skip the file. At next poll Camel, will try the file again, and this time maybe the read-lock could be granted. Use a value of 0 or lower to indicate forever. In Camel 2.0 the default value is 0. In Camel 2.1 the default value is 10000. Currently fileLock, changed and rename support the timeout. | |
| exclusiveReadLockStrategy | null | Pluggable read-lock as a org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileExclusiveReadLockStrategy implementation. |
| processStrategy | null | A pluggable org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileProcessStrategy allowing you to implement your own readLock option or similar. Can also be used when special conditions must be met before a file can be consumed, such as a special ready file exists. If this option is set then the readLock option does not apply. |
| maxMessagesPerPoll | 0 | An integer that defines the maximum number of messages to gather per poll. By default, no maximum is set. Can be used to set a limit of e.g. 1000 to avoid having the server read thousands of files as it starts up. Set a value of 0 or negative to disabled it. |
Default behavior for file consumer
- By default the file is locked for the duration of the processing.
- After the route has completed, files are moved into the .camel subdirectory, so that they appear to be deleted.
- The File Consumer will always skip any file whose name starts with a dot, such as ., .camel, .m2 or .groovy.
- Only files (not directories) are matched for valid filename, if options such as: includeNamePrefix, includeNamePostfix, excludeNamePrefix, excludeNamePostfix, regexPattern are used.
Producer only
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fileExist | Override | What to do if a file already exists with the same name. The following values can be specified: Override, Append, Fail and Ignore. Override, which is the default, replaces the existing file. Append adds content to the existing file. Fail throws a GenericFileOperationException, indicating that there is already an existing file. Ignore silently ignores the problem and does not override the existing file, but assumes everything is okay. |
| tempPrefix | null | This option is used to write the file using a temporary name and then, after the write is complete, rename it to the real name. Can be used to identify files being written and also avoid consumers (not using exclusive read locks) reading in progress files. Is often used by FTP when uploading big files. |
| tempFileName | null | Camel 2.1: The same as tempPrefix option but offering a more fine grained control on the naming of the temporary filename as it uses the File Language. For example you can do tempFileName=inprogress-${file:name.noext}.tmp. |
Default behavior for file producer
- By default it will override any existing file, if one exist with the same name.

Override is now default In Camel 1.x the Append is the default for the file producer. We have changed this to Override in Camel 2.0 as this is also the default file operation using java.io.File.
And also the default for the FTP library we use in the camel-ftp component.
Move and Delete operations
Any move or delete operations is executed after (post command) the routing has completed; so during processing of the Exchange the file is still located in the inbox folder.
Lets illustrate this with an example:
from("file://inbox?move=.done").to("bean:handleOrder");
When a file is dropped in the inbox folder, the file consumer notices this and creates a new FileExchange that is routed to the handleOrder bean. The bean then processes the File object. At this point in time the file is still located in the inbox folder. After the bean completes, and thus the route is completed, the file consumer will perform the move operation and move the file to the .done sub-folder.
The move and preMove options should be a directory name, which can be either relative or absolute. If relative, the directory is created as a sub-folder from within the folder where the file was consumed.
By default, Camel will move consumed files to the .camel sub-folder relative to the directory where the file was consumed.
If you want to delete the file after processing, the route should be:
from("file://inobox?delete=true").to("bean:handleOrder");
We have introduced a pre move operation to move files before they are processed. This allows you to mark which files have been scanned as they are moved to this sub folder before being processed.
from("file://inbox?preMove=inprogress").to("bean:handleOrder");
You can combine the pre move and the regular move:
from("file://inbox?preMove=inprogress&move=.done").to("bean:handleOrder");
So in this situation, the file is in the inprogress folder when being processed and after it's processed, it's moved to the .done folder.
Fine grained control over Move and PreMove option
The move and preMove option is Expression-based, so we have the full power of the File Language to do advanced configuration of the directory and name pattern.
Camel will, in fact, internally convert the directory name you enter into a File Language expression. So when we enter move=.done Camel will convert this into: ${file:parent}/.done/${file:onlyname}. This is only done if Camel detects that you have not provided a ${ } in the option value yourself. So when you enter a ${ } Camel will not convert it and thus you have the full power.
So if we want to move the file into a backup folder with today's date as the pattern, we can do:
move=backup/${date:now:yyyyMMdd}/${file:name}
About moveFailed
The moveFailed option allows you to move files that could not be processed succesfully to another location such as a error folder of your choice. For example to move the files in an error folder with a timestamp you can use moveFailed=/error/${file:name.noext}-${date:now:yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS}.${file:name.ext}.
See more examples at File Language
Message Headers
The following headers are supported by this component:
File producer only
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| CamelFileName | Specifies the name of the file to write (relative to the endpoint directory). The name can be a String; a String with a File Language or Simple expression; or an Expression object. If it's null then Camel will auto-generate a filename based on the message unique ID. |
File consumer only
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| CamelFileName | Name of the consumed file as a relative file path with offset from the starting directory configured on the endpoint. |
| CamelFileNameOnly | Only the file name (the name with no leading paths). |
| CamelFileNameProduced | The actual absolute filepath (path + name) for the output file that was written. This header is set by Camel and its purpose is providing end-users with the name of the file that was written. |
| CamelFileAbsolute | A boolean option specifying whether the consumed file denotes an absolute path or not. Should normally be false for relative paths. Absolute paths should normally not be used but we added to the move option to allow moving files to absolute paths. But can be used elsewhere as well. |
| CamelFileAbsolutePath | The absolute path to the file. For relative files this path holds the relative path instead. |
| CamelFilePath | The file path. For relative files this is the starting directory + the relative filename. For absolute files this is the absolute path. |
| CamelFileRelativePath | The relative path. |
| CamelFileParent | The parent path. |
| CamelFileLength | A long value containing the file size. |
| CamelFileLastModified | A Date value containing the last modified timestamp of the file. |
Batch Consumer
This component implements the Batch Consumer.
Exchange Properties, file consumer only
As the file consumer is BatchConsumer it supports batching the files it polls. By batching it means that Camel will add some properties to the Exchange so you know the number of files polled the current index in that order.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| CamelBatchSize | The total number of files that was polled in this batch. |
| CamelBatchIndex | The current index of the batch. Starts from 0. |
| CamelBatchComplete | A boolean value indicating the last Exchange in the batch. Is only true for the last entry. |
This allows you for instance to know how many files exists in this batch and for instance let the Aggregator aggregate this number of files.
Common gotchas with folder and filenames
When Camel is producing files (writing files) there are a few gotchas affecting how to set a filename of your choice. By default, Camel will use the message ID as the filename, and since the message ID is normally a unique generated ID, you will end up with filenames such as: ID-MACHINENAME-2443-1211718892437-1-0. If such a filename is not desired, then you must provide a filename in the CamelFileName message header. The constant, Exchange.FILE_NAME, can also be used.
The sample code below produces files using the message ID as the filename:
from("direct:report").to("file:target/reports");
To use report.txt as the filename you have to do:
from("direct:report").setHeader(Exchange.FILE_NAME, constant("report.txt")).to( "file:target/reports");
... the same as above, but with CamelFileName:
from("direct:report").setHeader("CamelFileName", constant("report.txt")).to( "file:target/reports");
And a syntax where we set the filename on the endpoint with the fileName URI option.
from("direct:report").to("file:target/reports/?fileName=report.txt");
Filename Expression
Filename can be set either using the expression option or as a string-based File Language expression in the CamelFileName header. See the File Language for syntax and samples.
Consuming files from folders where others drop files directly
Beware if you consume files from a folder where other applications write files directly. Take a look at the different readLock options to see what suits your use cases. The best approach is however to write to another folder and after the write move the file in the drop folder. However if you write files directly to the drop folder then the option changed could better detect whether a file is currently being written/copied as it uses a file changed algorithm to see whether the file size / modification changes over a period of time. The other read lock options rely on Java File API that sadly is not always very good at detecting this.
Samples
Read from a directory and write to another directory
from("file://inputdir/?delete=true").to("file://outputdir")
Listen on a directory and create a message for each file dropped there. Copy the contents to the outputdir and delete the file in the inputdir.
Reading recursive from a directory and write the another
from("file://inputdir/?recursive=true&delete=true").to("file://outputdir")
Listen on a directory and create a message for each file dropped there. Copy the contents to the outputdir and delete the file in the inputdir. Will scan recursively into sub-directories. Will lay out the files in the same directory structure in the outputdir as the inputdir, including any sub-directories.
inputdir/foo.txt inputdir/sub/bar.txt
Will result in the following output layout:
outputdir/foo.txt outputdir/sub/bar.txt
Using flatten
If you want to store the files in the outputdir directory in the same directory, disregarding the source directory layout (e.g. to flatten out the path), you just add the flatten=true option on the file producer side:
from("file://inputdir/?recursive=true&delete=true").to("file://outputdir?flatten=true")
Will result in the following output layout:
outputdir/foo.txt outputdir/bar.txt
Reading from a directory and the default move operation
Camel will by default move any processed file into a .camel subdirectory in the directory the file was consumed from.
from("file://inputdir/?recursive=true&delete=true").to("file://outputdir")
Affects the layout as follows:
before
inputdir/foo.txt inputdir/sub/bar.txt
after
inputdir/.camel/foo.txt inputdir/sub/.camel/bar.txt outputdir/foo.txt outputdir/sub/bar.txt
Read from a directory and process the message in java
from("file://inputdir/").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { Object body = exchange.getIn().getBody(); // do some business logic with the input body } });
The body will be a File object that points to the file that was just dropped into the inputdir directory.
Read files from a directory and send the content to a jms queue
from("file://inputdir/").convertBodyTo(String.class).to("jms:test.queue")
By default the file endpoint sends a FileMessage which contains a File object as the body. If you send this directly to the JMS component the JMS message will only contain the File object but not the content. By converting the File to a String, the message will contain the file contents what is probably what you want.
The route above using Spring DSL:
<route> <from uri="file://inputdir/"/> <convertBodyTo type="java.lang.String"/> <to uri="jms:test.queue"/> </route>
Writing to files
Camel is of course also able to write files, i.e. produce files. In the sample below we receive some reports on the SEDA queue that we processes before they are written to a directory.
public void testToFile() throws Exception { MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); mock.expectedFileExists("target/test-reports/report.txt"); template.sendBody("direct:reports", "This is a great report"); assertMockEndpointsSatisfied(); } protected JndiRegistry createRegistry() throws Exception { // bind our processor in the registry with the given id JndiRegistry reg = super.createRegistry(); reg.bind("processReport", new ProcessReport()); return reg; } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { // the reports from the seda queue is processed by our processor // before they are written to files in the target/reports directory from("direct:reports").processRef("processReport").to("file://target/test-reports", "mock:result"); } }; } private class ProcessReport implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); // do some business logic here // set the output to the file exchange.getOut().setBody(body); // set the output filename using java code logic, notice that this is done by setting // a special header property of the out exchange exchange.getOut().setHeader(Exchange.FILE_NAME, "report.txt"); } }
Write to subdirectory using Exchange.FILE_NAME
Using a single route, it is possible to write a file to any number of subdirectories. If you have a route setup as such:
<route>
<from uri="bean:myBean"/>
<to uri="file:/rootDirectory"/>
</route>
You can have myBean set the header Exchange.FILE_NAME to values such as:
Exchange.FILE_NAME = hello.txt => /rootDirectory/hello.txt Exchange.FILE_NAME = foo/bye.txt => /rootDirectory/foo/bye.txt
This allows you to have a single route to write files to multiple destinations.
Using expression for filenames
In this sample we want to move consumed files to a backup folder using today's date as a sub-folder name:
from("file://inbox?move=backup/${date:now:yyyyMMdd}/${file:name}").to("...");
See File Language for more samples.
Avoiding reading the same file more than once (idempotent consumer)
Camel supports Idempotent Consumer directly within the component so it will skip already processed files. This feature can be enabled by setting the idempotent=true option.
from("file://inbox?idempotent=true").to("...");
By default Camel uses a in memory based store for keeping track of consumed files, it uses a least recently used cache storing holding up to 1000 entries. You can plugin your own implementation of this store by using the idempotentRepository option using the # sign in the value to indicate it's a referring to a bean in the Registry with the specified id.
<!-- define our store as a plain spring bean --> <bean id="myStore" class="com.mycompany.MyIdempotentStore"/> <route> <from uri="file://inbox?idempotent=true&idempotentRepository=#myStore"/> <to uri="bean:processInbox"/> </route>
Camel will log at DEBUG level if it skips a file because it has been consumed before:
DEBUG FileConsumer is idempotent and the file has been consumed before. Will skip this file: target\idempotent\report.txt
Using a file based idempotent repository
In this section we will use the file based idempotent repository org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.FileIdempotentRepository instead of the in-memory based that is used as default.
This repository uses a 1st level cache to avoid reading the file repository. It will only use the file repository to store the content of the 1st level cache. Thereby the repository can survive server restarts. It will load the content of the file into the 1st level cache upon startup. The file structure is very simple as it store the key in separate lines in the file. By default, the file store has a size limit of 1mb when the file grew larger Camel will truncate the file store be rebuilding the content by flushing the 1st level cache in a fresh empty file.
We configure our repository using Spring XML creating our file idempotent repository and define our file consumer to use our repository with the idempotentRepository using # sign to indicate Registry lookup:
<!-- this is our file based idempotent store configured to use the .filestore.dat as file --> <bean id="fileStore" class="org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.FileIdempotentRepository"> <!-- the filename for the store --> <property name="fileStore" value="target/fileidempotent/.filestore.dat"/> <!-- the max filesize in bytes for the file. Camel will trunk and flush the cache if the file gets bigger --> <property name="maxFileStoreSize" value="512000"/> <!-- the number of elements in our store --> <property name="cacheSize" value="250"/> </bean> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="file://target/fileidempotent/?idempotent=true&idempotentRepository=#fileStore&move=done/${file:name}"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext>
Using a JPA based idempotent repository
In this section we will use the JPA based idempotent repository instead of the in-memory based that is used as default.
First we need a persistence-unit in META-INF/persistence.xml where we need to use the class org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.jpa.MessageProcessed as model.
<persistence-unit name="idempotentDb" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <class>org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.jpa.MessageProcessed</class> <properties> <property name="openjpa.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:derby:target/idempotentTest;create=true"/> <property name="openjpa.ConnectionDriverName" value="org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver"/> <property name="openjpa.jdbc.SynchronizeMappings" value="buildSchema"/> <property name="openjpa.Log" value="DefaultLevel=WARN, Tool=INFO"/> </properties> </persistence-unit>
Then we need to setup a Spring jpaTemplate in the spring XML file:
<!-- this is standard spring JPA configuration --> <bean id="jpaTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTemplate"> <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"/> </bean> <bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalEntityManagerFactoryBean"> <!-- we use idempotentDB as the persitence unit name defined in the persistence.xml file --> <property name="persistenceUnitName" value="idempotentDb"/> </bean>
And finally we can create our JPA idempotent repository in the spring XML file as well:
<!-- we define our jpa based idempotent repository we want to use in the file consumer --> <bean id="jpaStore" class="org.apache.camel.processor.idempotent.jpa.JpaMessageIdRepository"> <!-- Here we refer to the spring jpaTemplate --> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="jpaTemplate"/> <!-- This 2nd parameter is the name (= a cateogry name). You can have different repositories with different names --> <constructor-arg index="1" value="FileConsumer"/> </bean>
And yes then we just need to refer to the jpaStore bean in the file consumer endpoint using the [[idempotentRepository}} using the # syntax option:
<route> <from uri="file://inbox?idempotent=true&idempotentRepository=#jpaStore"/> <to uri="bean:processInbox"/> </route>
Filter using org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileFilter
Camel supports pluggable filtering strategies. You can then configure the endpoint with such a filter to skip certain files being processed.
In the sample we have build our own filter that skips files starting with skip in the filename:
public class MyFileFilter implements GenericFileFilter { public boolean accept(GenericFile pathname) { // we dont accept any files starting with skip in the name return !pathname.getFileName().startsWith("skip"); } }
And then we can configure our route using the filter attribute to reference our filter (using # notation) that we have defines in the spring XML file:
<!-- define our sorter as a plain spring bean --> <bean id="myFilter" class="com.mycompany.MyFileSorter"/> <route> <from uri="file://inbox?filter=#myFilter"/> <to uri="bean:processInbox"/> </route>
Filtering using ANT path matcher
The ANT path matcher is shipped out-of-the-box in the camel-spring jar. So you need to depend on camel-spring if you are using Maven.
The reasons is that we leverage Spring's AntPathMatcher to do the actual matching.
The file paths is matched with the following rules:
- ? matches one character
- * matches zero or more characters
- ** matches zero or more directories in a path
The sample below demonstrates how to use it:
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <template id="camelTemplate"/> <!-- use myFilter as filter to allow setting ANT paths for which files to scan for --> <endpoint id="myFileEndpoint" uri="file://target/antpathmatcher?recursive=true&filter=#myAntFilter"/> <route> <from ref="myFileEndpoint"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext> <!-- we use the antpath file filter to use ant paths for includes and exlucde --> <bean id="myAntFilter" class="org.apache.camel.component.file.AntPathMatcherGenericFileFilter"> <!-- include and file in the subfolder that has day in the name --> <property name="includes" value="**/subfolder/**/*day*"/> <!-- exclude all files with bad in name or .xml files. Use comma to seperate multiple excludes --> <property name="excludes" value="**/*bad*,**/*.xml"/> </bean>
Sorting using Comparator
Camel supports pluggable sorting strategies. This strategy it to use the build in java.util.Comparator in Java. You can then configure the endpoint with such a comparator and have Camel sort the files before being processed.
In the sample we have built our own comparator that just sorts by file name:
public class MyFileSorter implements Comparator<GenericFile> { public int compare(GenericFile o1, GenericFile o2) { return o1.getFileName().compareToIgnoreCase(o2.getFileName()); } }
And then we can configure our route using the sorter option to reference to our sorter (mySorter) we have defined in the spring XML file:
<!-- define our sorter as a plain spring bean --> <bean id="mySorter" class="com.mycompany.MyFileSorter"/> <route> <from uri="file://inbox?sorter=#mySorter"/> <to uri="bean:processInbox"/> </route>
| URI options can reference beans using the # syntax In the Spring DSL route about notice that we can refer to beans in the Registry by prefixing the id with #. So writing sorter=#mySorter, will instruct Camel to go look in the Registry for a bean with the ID, mySorter. |
Sorting using sortBy
Camel supports pluggable sorting strategies. This strategy it to use the File Language to configure the sorting. The sortBy option is configured as follows:
sortBy=group 1;group 2;group 3;...
Where each group is separated with semi colon. In the simple situations you just use one group, so a simple example could be:
sortBy=file:name
This will sort by file name, you can reverse the order by prefixing reverse: to the group, so the sorting is now Z..A:
sortBy=reverse:file:name
As we have the full power of File Language we can use some of the other parameters, so if we want to sort by file size we do:
sortBy=file:size
You can configure to ignore the case, using ignoreCase: for string comparison, so if you want to use file name sorting but to ignore the case then we do:
sortBy=ignoreCase:file:name
You can combine ignore case and reverse, however reverse must be specified first:
sortBy=reverse:ignoreCase:file:name
In the sample below we want to sort by last modified file, so we do:
sortBy=file:modifed
And then we want to group by name as a 2nd option so files with same modifcation is sorted by name:
sortBy=file:modifed;file:name
Now there is an issue here, can you spot it? Well the modified timestamp of the file is too fine as it will be in milliseconds, but what if we want to sort by date only and then subgroup by name?
Well as we have the true power of File Language we can use the its date command that supports patterns. So this can be solved as:
sortBy=date:file:yyyyMMdd;file:name
Yeah, that is pretty powerful, oh by the way you can also use reverse per group, so we could reverse the file names:
sortBy=date:file:yyyyMMdd;reverse:file:name
Using GenericFileProcessStrategy
The option processStrategy can be used to use a custom GenericFileProcessStrategy that allows you to implement your own begin, commit and rollback logic.
For instance lets assume a system writes a file in a folder you should consume. But you should not start consuming the file before another ready file have been written as well.
So by implementing our own GenericFileProcessStrategy we can implement this as:
- In the begin() method we can test whether the special ready file exists. The begin method returns a boolean to indicate if we can consume the file or not.
- in the commit() method we can move the actual file and also delete the ready file.
Debug logging
This component has log level TRACE that can be helpful if you have problems.
See Also
Flatpack Component
The Flatpack component supports fixed width and delimited file parsing via the FlatPack library.
Notice: This component only supports consuming from flatpack files to Object model. You can not (yet) write from Object model to flatpack format.
URI format
flatpack:[delim|fixed]:flatPackConfig.pzmap.xml[?options]
Or for a delimited file handler with no configuration file just use
flatpack:someName[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
URI Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| delimiter | , | The default character delimiter for delimited files. |
| textQualifier | " | The text qualifier for delimited files. |
| ignoreFirstRecord | true | Whether the first line is ignored for delimited files (for the column headers). |
| splitRows | true | As of Camel 1.5, the component can either process each row one by one or the entire content at once. |
Examples
- flatpack:fixed:foo.pzmap.xml creates a fixed-width endpoint using the foo.pzmap.xml file configuration.
- flatpack:delim:bar.pzmap.xml creates a delimited endpoint using the bar.pzmap.xml file configuration.
- flatpack:foo creates a delimited endpoint called foo with no file configuration.
Message Headers
Camel will store the following headers on the IN message:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| camelFlatpackCounter | The current row index. For splitRows=false the counter is the total number of rows. |
Message Body
The component delivers the data in the IN message as a org.apache.camel.component.flatpack.DataSetList object that has converters for java.util.Map or java.util.List.
Usually you want the Map if you process one row at a time (splitRows=true). Use List for the entire content (splitRows=false), where each element in the list is a Map.
Each Map contains the key for the column name and its corresponding value.
For example to get the firstname from the sample below:
Map row = exchange.getIn().getBody(Map.class); String firstName = row.get("FIRSTNAME");
However, you can also always get it as a List (even for splitRows=true). The same example:
List data = exchange.getIn().getBody(List.class); Map row = (Map)data.get(0); String firstName = row.get("FIRSTNAME");
Header and Trailer records
In Camel 1.5 onwards the header and trailer notions in Flatpack are supported. However, you must use fixed record IDs:
- header for the header record (must be lowercase)
- trailer for the trailer record (must be lowercase)
The example below illustrates this fact that we have a header and a trailer. You can omit one or both of them if not needed.
<RECORD id="header" startPosition="1" endPosition="3" indicator="HBT">
<COLUMN name="INDICATOR" length="3"/>
<COLUMN name="DATE" length="8"/>
</RECORD>
<COLUMN name="FIRSTNAME" length="35" />
<COLUMN name="LASTNAME" length="35" />
<COLUMN name="ADDRESS" length="100" />
<COLUMN name="CITY" length="100" />
<COLUMN name="STATE" length="2" />
<COLUMN name="ZIP" length="5" />
<RECORD id="trailer" startPosition="1" endPosition="3" indicator="FBT">
<COLUMN name="INDICATOR" length="3"/>
<COLUMN name="STATUS" length="7"/>
</RECORD>
Using the endpoint
A common use case is sending a file to this endpoint for further processing in a separate route. For example:
<camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="file://someDirectory"/> <to uri="flatpack:foo"/> </route> <route> <from uri="flatpack:foo"/> ... </route> </camelContext>
You can also convert the payload of each message created to a Map for easy Bean Integration
Flatpack DataFormat
The Flatpack component ships with the Flatpack data format that can be used to format between fixed width or delimited text messages to a List of rows as Map.
- marshal = from List<Map<String, Object>> to OutputStream (can be converted to String)
- unmarshal = from java.io.InputStream (such as a File or String) to a java.util.List as an org.apache.camel.component.flatpack.DataSetList instance.
The result of the operation will contain all the data. If you need to process each row one by one you can split the exchange, using Splitter.
Notice: The Flatpack library does currently not support header and trailers for the marshal operation.
Options
The data format has the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| definition | null | The flatpack pzmap configuration file. Can be omitted in simpler situations, but its preferred to use the pzmap. |
| fixed | false | Delimited or fixed. |
| ignoreFirstRecord | true | Whether the first line is ignored for delimited files (for the column headers). |
| textQualifier | " | If the text is qualified with a char such as ". |
| delimiter | , | The delimiter char (could be ; , or similar) |
| parserFactory | null | Uses the default Flatpack parser factory. |
Usage
To use the data format, simply instantiate an instance and invoke the marhsal or unmarshal operation in the route builder:
FlatpackDataFormat fp = new FlatpackDataFormat(); fp.setDefinition(new ClassPathResource("INVENTORY-Delimited.pzmap.xml")); ... from("file:order/in").unmarshal(df).to("seda:queue:neworder");
The sample above will read files from the order/in folder and unmarshal the input using the Flatpack configuration file INVENTORY-Delimited.pzmap.xml that configures the structure of the files. The result is a DataSetList object we store on the SEDA queue.
FlatpackDataFormat df = new FlatpackDataFormat(); df.setDefinition(new ClassPathResource("PEOPLE-FixedLength.pzmap.xml")); df.setFixed(true); df.setIgnoreFirstRecord(false); from("seda:people").marshal(df).convertBodyTo(String.class).to("jms:queue:people");
In the code above we marshal the data from a Object representation as a List of rows as Maps. The rows as Map contains the column name as the key, and the the corresponding value. This structure can be created in Java code from e.g. a processor. We marshal the data according to the Flatpack format and convert the result as a String object and store it on a JMS queue.
Dependencies
To use Flatpack in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-flatpack which implements this data format.
If you use maven you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-flatpack</artifactId> <version>1.5.0</version> </dependency>
See Also
Freemarker
Available as of Camel 1.6
The freemarker: component allows you to process a message using a Freemarker template. This can be ideal when using Templating to generate responses for requests.
URI format
freemarker:templateName[?options]
Where templateName is the classpath-local URI of the template to invoke; or the complete URL of the remote template (eg: file://folder/myfile.ftl).
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| contentCache | true | Cache for the resource content when its loaded. |
| encoding | null | Character encoding of the resource content. |
Headers
Camel will store a reference to the resource in the message header in the key org.apache.camel.freemarker.resource. The Resource is an org.springframework.core.io.Resource object. And the key org.apache.camel.freemarker.resourceUri holds the templateName as a String object.
Note From Camel 2.1 and Camel 1.6.2, freemarker endpoint will not store these headers into to message, as these header will cause some side effect on the dynamic templates feature.
Headers set during the Freemarker evaluation are returned to the message and added as headers. Then its kinda possible to return values from Freemarker to the Message.
An example: Set the header value of fruit in the Freemarker template:
${request.setHeader('fruit', 'Apple')}
The header, fruit, is now accessible from the message.out.headers.
Freemarker Context
Camel will provide exchange information in the Freemarker context (just a Map). The Exchange is transfered as:
| key | value |
|---|---|
| exchange | The Exchange itself. |
| headers | The headers of the In message. |
| camelContext | The Camel Context. |
| request | The In message. |
| body | The In message body. |
| response | The Out message (only for InOut message exchange pattern). |
Hot reloading
The Freemarker template resource is by default not hot reloadable for both file and classpath resources (expanded jar). If you set contentCache=false, then Camel will not cache the resource and hot reloading is thus enabled. This scenario can be used in development.
Dynamic templates
Available as of Camel 2.1
Camel provides two headers by which you can define a different resource location for a template or the template content itself. If any of these headers is set then Camel uses this over the endpoint configured resource. This allows you to provide a dynamic template at runtime.
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CamelFreemarkerResourceUri | String | Camel 2.1: A URI for the template resource to use instead of the endpoint configured. |
| CamelFreemarkerTemplate | String | Camel 2.1: The template to use instead of the endpoint configured. |
Samples
For example you could use something like:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("freemarker:com/acme/MyResponse.ftl");
To use a Freemarker template to formulate a response for a message for InOut message exchanges (where there is a JMSReplyTo header).
If you want to use InOnly and consume the message and send it to another destination you could use:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("freemarker:com/acme/MyResponse.ftl"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
And to disable the content cache, e.g. for development usage where the .ftl template should be hot reloaded:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("freemarker:com/acme/MyResponse.ftl?contentCache=false"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
And a file-based resource:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("freemarker:file://myfolder/MyResponse.ftl?contentCache=false"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
In Camel 2.1 it's possible to specify what template the component should use dynamically via a header, so for example:
from("direct:in"). setHeader("CamelFreemarkerResourceUri").constant("path/to/my/template.ftl"). to("freemarker:dummy");
The Email Sample
In this sample we want to use Freemarker templating for an order confirmation email. The email template is laid out in Freemarker as:
Dear ${headers.lastName}, ${headers.firstName}
Thanks for the order of ${headers.item}.
Regards Camel Riders Bookstore
${body}
And the java code:
private Exchange createLetter() { Exchange exchange = context.getEndpoint("direct:a").createExchange(); Message msg = exchange.getIn(); msg.setHeader("firstName", "Claus"); msg.setHeader("lastName", "Ibsen"); msg.setHeader("item", "Camel in Action"); msg.setBody("PS: Next beer is on me, James"); return exchange; } @Test public void testFreemarkerLetter() throws Exception { MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Dear Ibsen, Claus\n\nThanks for the order of Camel in Action.\n\nRegards Camel Riders Bookstore\nPS: Next beer is on me, James"); template.send("direct:a", createLetter()); mock.assertIsSatisfied(); } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:a").to("freemarker:org/apache/camel/component/freemarker/letter.ftl").to("mock:result"); } }; }
See Also
FTP/SFTP Component - Camel 2.0 onwards
This component provides access to remote file systems over the FTP and SFTP protocols.
| Using Camel 1.x If you are using Camel 1.x then see this link for documentation. |
URI format
ftp://[username@]hostname[:port]/directoryname[?options] sftp://[username@]hostname[:port]/directoryname[?options]
Where directoryname represents the underlying directory. Can contain nested folders.
The username is currently only possible to provide in the hostname parameter.
If no username is provided, then anonymous login is attempted using no password.
If no port number is provided, Camel will provide default values according to the protocol (ftp = 21, sftp = 22).
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
URI Options
The options below are exclusive for the FTP2 component.
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| password | null | Specifies the password to use to log in to the remote file system. |
| binary | false | Specifies the file transfer mode, BINARY or ASCII. Default is ASCII (false). |
| localWorkDirectory | null | When consuming, a local work directory can be used to store the remote file content directly in local files, to avoid loading the content into memory. This is beneficial, if you consume a very big remote file and thus can conserve memory. See below for more details. |
| passiveMode | false | FTP only: Specifies whether to use passive mode connections. Default is active mode {false). |
| ftpClientConfig | null | FTP only: Reference to a bean in the registry as a org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClientConfig class. Use this option if you need to configure the client according to the FTP Server date format, locale, timezone, platform etc. See the javadoc FTPClientConfig for more documentation. |
| knownHostsFile | null | SFTP only: Sets the known_hosts file, so that the SFTP endpoint can do host key verification. |
| privateKeyFile | null | SFTP only: Set the private key file to that the SFTP endpoint can do private key verification. |
| privateKeyFilePassphrase | null | SFTP only: Set the private key file passphrase to that the SFTP endpoint can do private key verification. |
| maximumReconnectAttempts | 3 | Specifies the maximum reconnect attempts Camel performs when it tries to connect to the remote FTP server. Use 0 to disable this behavior. |
| reconnectDelay | 1000 | Delay in millis Camel will wait before performing a reconnect attempt. |
| ftpClient | null | FTP Only: Camel 2.1: Allows you to use a custom org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClient instance. |
| ftpClientConfig | null | FTP Only: Camel 2.1: Allows you to use a custom org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClientConfig instance. |
You can configure additional options on the ftpClient and ftpClientConfig from the URI directly by using the ftpClient. or ftpClientConfig. prefix.
For example to set the setDataTimeout on the FTPClient to 30 seconds you can do:
from("ftp://foo@myserver?password=secret&ftpClient.dataTimeout=30000").to("bean:foo");
You can mix and match and have use both prefixes, for example to configure date format or timezones.
from("ftp://foo@myserver?password=secret&ftpClient.dataTimeout=30000&ftpClientConfig.serverLanguageCode=fr").to("bean:foo");
You can have as many of these options as you like.
See the documentation of the Apache Commons FTP FTPClientConfig for possible options and more details.
And as well for Apache Commons FTP FTPClient.
If you do not like having many and long configuration in the url you can refer to the ftpClient or ftpClientConfig to use by letting Camel lookup in the Registry for it.
For example:
<bean id="myConfig" class="org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClientConfig"> <property name="lenientFutureDates" value="true"/> <property name="serverLanguageCode" value="fr"/> </bean>
And then let Camel lookup this bean when you use the # notation in the url.
from("ftp://foo@myserver?password=secret&ftpClientConfig=#myConfig").to("bean:foo");
More URI options
See File2 as all the options there also applies for this component. |
Examples
ftp://someone@someftpserver.com/public/upload/images/holiday2008?password=secret&binary=true
ftp://someoneelse@someotherftpserver.co.uk:12049/reports/2008/password=secret&binary=false
ftp://publicftpserver.com/download
| FTP Consumer does not support concurrency The FTP consumer (with the same endpoint) does not support concurrency (the backing FTP client is not thread safe). The FTP producer does not have this issue, it supports concurrency. In the future we will add consumer pooling to Camel to allow this consumer to support concurrency as well. |
| More information This component is an extension of the File2 component. So there are more samples and details on the File2 component page. |
Default when consuming files
The FTP consumer will by default leave the consumed files untouched on the remote FTP server. You have to configure it explicit if you want it to delete the files or move them to another location. For example you can use delete=true to delete the files, or use move=.done to move the files into a hidden done sub directory.
The regular File consumer is different as it will by default move files to a .camel sub directory. The reason Camel does not do this by default for the FTP consumer is that it may lack permissions by default to be able to move or delete files.
limitations
The option readLock can be used to force Camel not to consume files that is currently in the progress of being written. However, this option is turned off by default, as it requires that the user has write access. There are other solutions to avoid consuming files that are currently being written over FTP; for instance, you can write to a temporary destination and move the file after it has been written.
Message Headers
The following message headers can be used to affect the behavior of the component
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| CamelFileName | Specifies the output file name (relative to the endpoint directory) to be used for the output message when sending to the endpoint. If this is not present and no expression either, then a generated message ID is used as the filename instead. |
| CamelFileNameProduced | The actual absolute filepath (path + name) for the output file that was written. This header is set by Camel and its purpose is providing end-users the name of the file that was written. |
| CamelFileBatchIndex | Current index out of total number of files being consumed in this batch. |
| CamelFileBatchSize | Total number of files being consumed in this batch. |
| CamelFileHost | The remote hostname. |
| CamelFileLocalWorkPath | Path to the local work file, if local work directory is used. |
Using Local Work Directory
Camel supports consuming from remote FTP servers and downloading the files directly into a local work directory. This avoids reading the entire remote file content into memory as it is streamed directly into the local file using FileOutputStream.
Camel will store to a local file with the same name as the remote file, though with .inprogress as extension while the file is being downloaded. Afterwards, the file is renamed to remove the .inprogress suffix. And finally, when the Exchange is complete the local file is deleted.
So if you want to download files from a remote FTP server and store it as files then you need to route to a file endpoint such as:
from("ftp://someone@someserver.com?password=secret&localWorkDirectory=/tmp").to("file://inbox");
| Optimization by renaming work file The route above is ultra efficient as it avoids reading the entire file content into memory. It will download the remote file directly to a local file stream. The java.io.File handle is then used as the Exchange body. The file producer leverages this fact and can work directly on the work file java.io.File handle and perform a java.io.File.rename to the target filename. As Camel knows it's a local work file, it can optimize and use a rename instead of a file copy, as the work file is meant to be deleted anyway. |
Samples
In the sample below we set up Camel to download all the reports from the FTP server once every hour (60 min) as BINARY content and store it as files on the local file system.
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { // we use a delay of 60 minutes (eg. once pr. hour we poll the FTP server long delay = 60 * 60 * 1000L; // from the given FTP server we poll (= download) all the files // from the public/reports folder as BINARY types and store this as files // in a local directory. Camel will use the filenames from the FTPServer // notice that the FTPConsumer properties must be prefixed with "consumer." in the URL // the delay parameter is from the FileConsumer component so we should use consumer.delay as // the URI parameter name. The FTP Component is an extension of the File Component. from("ftp://scott@localhost/public/reports?password=tiger&binary=true&consumer.delay=" + delay). to("file://target/test-reports"); } }; }
And the route using Spring DSL:
<route> <from uri="ftp://scott@localhost/public/reports?password=tiger&binary=true&delay=60000"/> <to uri="file://target/test-reports"/> </route>
Consuming a remote FTP server triggered by a route
The FTP consumer is built as a scheduled consumer to be used in the from route. However, if you want to start consuming from an FTP server triggered within a route.
Notice we use the Content Enricher EIP with the pollEnrich DSL to consume the FTP file:
from("seda:start") // set the filename in FILE_NAME header so Camel know the name of the remote file to poll .setHeader(Exchange.FILE_NAME, header("myfile")) .pollEnrich("ftp://admin@localhost:21/getme?password=admin&binary=false") .to("mock:result");
Filter using org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileFilter
Camel supports pluggable filtering strategies. This strategy it to use the build in org.apache.camel.component.file.GenericFileFilter in Java. You can then configure the endpoint with such a filter to skip certain filters before being processed.
In the sample we have build our own filter that only accepts files starting with report in the filename.
public class MyFileFilter implements GenericFileFilter { public boolean accept(GenericFile file) { // we only want report files return file.getFileName().startsWith("report"); } }
And then we can configure our route using the filter attribute to reference our filter (using # notation) that we have defines in the spring XML file:
<!-- define our sorter as a plain spring bean --> <bean id="myFilter" class="com.mycompany.MyFileFilter"/> <route> <from uri="ftp://someuser@someftpserver.com?password=secret&filter=#myFilter"/> <to uri="bean:processInbox"/> </route>
Filtering using ANT path matcher
The ANT path matcher is a filter that is shipped out-of-the-box in the camel-spring jar. So you need to depend on camel-spring if you are using Maven.
The reason is that we leverage Spring's AntPathMatcher to do the actual matching.
The file paths are matched with the following rules:
- ? matches one character
- * matches zero or more characters
- ** matches zero or more directories in a path
The sample below demonstrates how to use it:
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <template id="camelTemplate"/> <!-- use myFilter as filter to allow setting ANT paths for which files to scan for --> <endpoint id="myFTPEndpoint" uri="ftp://admin@localhost:20123/antpath?password=admin&recursive=true&delay=10000&initialDelay=2000&filter=#myAntFilter"/> <route> <from ref="myFTPEndpoint"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext> <!-- we use the AntPathMatcherRemoteFileFilter to use ant paths for includes and exlucde --> <bean id="myAntFilter" class="org.apache.camel.component.file.AntPathMatcherGenericFileFilter"> <!-- include and file in the subfolder that has day in the name --> <property name="includes" value="**/subfolder/**/*day*"/> <!-- exclude all files with bad in name or .xml files. Use comma to seperate multiple excludes --> <property name="excludes" value="**/*bad*,**/*.xml"/> </bean>
Debug logging
This component has log level TRACE that can be helpful if you have problems.
See Also
Hibernate Component
The hibernate: component allows you to work with databases using Hibernate as the object relational mapping technology to map POJOs to database tables. The camel-hibernate library is provided by the Camel Extra project which hosts all *GPL related components for Camel.
Sending to the endpoint
Sending POJOs to the hibernate endpoint inserts entities into the database. The body of the message is assumed to be an entity bean that you have mapped to a relational table using the hibernate .hbm.xml files.
If the body does not contain an entity bean, use a Message Translator in front of the endpoint to perform the necessary conversion first.
Consuming from the endpoint
Consuming messages removes (or updates) entities in the database. This allows you to use a database table as a logical queue; consumers take messages from the queue and then delete/update them to logically remove them from the queue.
If you do not wish to delete the entity when it has been processed, you can specify consumeDelete=false on the URI. This will result in the entity being processed each poll.
If you would rather perform some update on the entity to mark it as processed (such as to exclude it from a future query) then you can annotate a method with @Consumed which will be invoked on your entity bean when the entity bean is consumed.
URI format
hibernate:[entityClassName][?options]
For sending to the endpoint, the entityClassName is optional. If specified it is used to help use the [Type Conversion] to ensure the body is of the correct type.
For consuming the entityClassName is mandatory.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| entityType | entityClassName | Is the provided entityClassName from the URI. |
| consumeDelete | true | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Specifies whether or not the entity is deleted after it is consumed. |
| consumeLockEntity | true | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Specifies whether or not to use exclusive locking of each entity while processing the results from the pooling. |
| flushOnSend | true | Option for HibernateProducer only. Flushes the EntityManager after the entity bean has been persisted. |
| maximumResults | -1 | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Set the maximum number of results to retrieve on the Query. |
| consumer.delay | 500 | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Delay in millis between each poll. |
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Millis before polling starts. |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | false | Option for HibernateConsumer only. Set to true to use fixed delay between polls, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
See Also
HL7 Component
The hl7 component is used for working with the HL7 MLLP protocol and the HL7 model using the HAPI library.
This component supports the following:
- HL7 MLLP codec for Mina
- Agnostic data format using either plain String objects or HAPI HL7 model objects.
- Type Converter from/to HAPI and String
- HL7 DataFormat using HAPI library
- Even more easy-of-use as its integrated well with the camel-mina component.
HL7 MLLP protocol
HL7 is often used with the HL7 MLLP protocol that is a text based TCP socket based protocol. This component ships with a Mina Codec that conforms to the MLLP protocol so you can easily expose a HL7 listener that accepts HL7 requests over the TCP transport.
To expose a HL7 listener service we reuse the existing camel-mina component where we just use the HL7MLLPCodec as codec.
The HL7 MLLP codec has the following options:
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| startByte | 0x0b | The start byte spanning the HL7 payload. Is the HL7 default value of 0x0b (11 decimal). |
| endByte1 | 0x1c | The first end byte spanning the HL7 payload. Is the HL7 default value of 0x1c (28 decimal). |
| endByte2 | 0x0d | The 2nd end byte spanning the HL7 payload. Is the HL7 default value of 0x0d (13 decimal). |
| charset | JVM Default | The encoding (is a charset name) to use for the codec. If not provided, Camel will use the JVM default Charset. |
| convertLFtoCR | true | Will convert \n to \r (0x0d, 13 decimal) as HL7 usually uses \r as segment terminators. The HAPI library requires the use of \r. |
| validate | true | Camel 2.0: Whether HAPI Parser should validate or not. |
Exposing a HL7 listener
In our Spring XML file, we configure an endpoint to listen for HL7 requests using TCP:
<endpoint id="hl7listener" uri="mina:tcp://localhost:8888?sync=true&codec=hl7codec"/>
Notice we configure it to use camel-mina with TCP on the localhost on port 8888. We use sync=true to indicate that this listener is synchronous and therefore will return a HL7 response to the caller. Then we setup mina to use our HL7 codec with codec=hl7codec. Notice that hl7codec is just a Spring bean ID, so we could have named it mygreatcodecforhl7 or whatever. The codec is also set up in the Spring XML file:
<bean id="hl7codec" class="org.apache.camel.component.hl7.HL7MLLPCodec">
<property name="charset" value="iso-8859-1"/>
</bean>
And here we configure the charset encoding to use, and iso-8859-1 is commonly used.
The endpoint hl7listener can then be used in a route as a consumer, as this java DSL example illustrates:
from("hl7socket").to("patientLookupService");
This is a very simple route that will listen for HL7 and route it to a service named patientLookupService that is also a Spring bean ID we have configured in the Spring XML as:
<bean id="patientLookupService" class="com.mycompany.healtcare.service.PatientLookupService"/>
And another powerful feature of Camel is that we can have our busines logic in POJO classes that is not at all tied to Camel as shown here:
public class PatientLookupService { public Message lookupPatient(Message input) throws HL7Exception { QRD qrd = (QRD)input.get("QRD"); String patientId = qrd.getWhoSubjectFilter(0).getIDNumber().getValue(); // find patient data based on the patient id and create a HL7 model object with the response Message response = ... create and set response data return response }
Notice that this class is just using imports from the HAPI library and none from Camel.
HL7 Model using java.lang.String
The HL7MLLP codec uses plain String as data format. And Camel uses Type Converter to convert from/to strings to the HAPI HL7 model objects. However, you can use the plain String objects if you prefer, for instance if you need to parse the data yourself.
See samples for such an example.
HL7 Model using HAPI
The HL7 model is Java objects from the HAPI library. Using this library, we can encode and decode from the EDI format (ER7) that is mostly used with HL7.
With this model you can code with Java objects instead of the EDI based HL7 format that can be hard for humans to read and understand.
The ER7 sample below is a request to lookup a patient with the patient ID, 0101701234.
MSH|^~\\&|MYSENDER|MYRECEIVER|MYAPPLICATION||200612211200||QRY^A19|1234|P|2.4 QRD|200612211200|R|I|GetPatient|||1^RD|0101701234|DEM||
Using the HL7 model we can work with the data as a ca.uhn.hl7v2.model.Message.Message object.
To retrieve the patient ID for the patient in the ER7 above, you can do this in java code:
Message msg = exchange.getIn().getBody(Message.class); QRD qrd = (QRD)msg.get("QRD"); String patientId = qrd.getWhoSubjectFilter(0).getIDNumber().getValue();
Camel has built-in type converters, so when this operation is invoked:
Message msg = exchange.getIn().getBody(Message.class);
Camel will convert the received HL7 data from String to Message. This is powerful when combined with the HL7 listener, then you as the end-user don't have to work with byte[], String or any other simple object formats. You can just use the HAPI HL7 model objects.
HL7 DataFormat
The HL7 component ships with a HL7 data format that can be used to format between String and HL7 model objects.
- marshal = from Message to byte stream (can be used when returning as response using the HL7 MLLP codec)
- unmarshal = from byte stream to Message (can be used when receiving streamed data from the HL7 MLLP
To use the data format, simply instantiate an instance and invoke the marhsal or unmarshl operation in the route builder:
DataFormat hl7 = new HL7DataFormat(); ... from("direct:hl7in").marshal(hl7).to("jms:queue:hl7out");
In the sample above, the HL7 is marshalled from a HAPI Message object to a byte stream and put on a JMS queue.
The next example is the opposite:
DataFormat hl7 = new HL7DataFormat(); ... from("jms:queue:hl7out").unmarshal(hl7).to("patientLookupService");
Here we unmarshal the byte stream into a HAPI Message object that is passed to our patient lookup service.
Notice there is a shorthand syntax in Camel for well-known data formats that is commonly used.
Then you don't need to create an instance of the HL7DataFormat object:
from("direct:hl7in").marshal().hl7().to("jms:queue:hl7out"); from("jms:queue:hl7out").unmarshal().hl7().to("patientLookupService");
Message Headers
The unmarshal operation adds these MSH fields as headers on the Camel message:
Camel 1.x
| Key | MSH field | Example |
|---|---|---|
| hl7.msh.sendingApplication | MSH-3 | MYSERVER |
| hl7.msh.sendingFacility | MSH-4 | MYSERVERAPP |
| hl7.msh.receivingApplication | MSH-5 | MYCLIENT |
| hl7.msh.receivingFacility | MSH-6 | MYCLIENTAPP |
| hl7.msh.timestamp | MSH-7 | 20071231235900 |
| hl7.msh.security | MSH-8 | null |
| hl7.msh.messageType | MSH-9-1 | ADT |
| hl7.msh.triggerEvent | MSH-9-2 | A01 |
| hl7.msh.messageControl | MSH-10 | 1234 |
| hl7.msh.processingId | MSH-11 | P |
| hl7.msh.versionId | MSH-12 | 2.4 |
Camel 2.0
| Key | MSH field | Example |
|---|---|---|
| CamelHL7SendingApplication | MSH-3 | MYSERVER |
| CamelHL7SendingFacility | MSH-4 | MYSERVERAPP |
| CamelHL7ReceivingApplication | MSH-5 | MYCLIENT |
| CamelHL7ReceivingFacility | MSH-6 | MYCLIENTAPP |
| CamelHL7Timestamp | MSH-7 | 20071231235900 |
| CamelHL7Security | MSH-8 | null |
| CamelHL7MessageType | MSH-9-1 | ADT |
| CamelHL7TriggerEvent | MSH-9-2 | A01 |
| CamelHL7MessageControl | MSH-10 | 1234 |
| CamelHL7ProcessingId | MSH-11 | P |
| CamelHL7VersionId | MSH-12 | 2.4 |
All headers are String types. If a header value is missing, its value is null.
Options
The HL7 Data Format supports the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| validate | true | Camel 2.0: Whether the HAPI Parser should validate. |
Dependencies
To use HL7 in your camel routes you need to add a dependency on camel-hl7, which implements this data format.
If you use Maven, you could just add the following to your pom.xml, substituting the version number for the latest & greatest release (see the download page for the latest versions).
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId> <artifactId>camel-hl7</artifactId> <version>1.6.0</version> </dependency>
Samples
In the following example we send a HL7 request to a HL7 listener and retrieves a response. We use plain String types in this example:
String line1 = "MSH|^~\\&|MYSENDER|MYRECEIVER|MYAPPLICATION||200612211200||QRY^A19|1234|P|2.4"; String line2 = "QRD|200612211200|R|I|GetPatient|||1^RD|0101701234|DEM||"; StringBuffer in = new StringBuffer(); in.append(line1); in.append("\n"); in.append(line2); String out = (String)template.requestBody("mina:tcp://127.0.0.1:8888?sync=true&codec=#hl7codec", in.toString());
In the next sample, we want to route HL7 requests from our HL7 listener to our business logic. We have our business logic in a plain POJO that we have registered in the registry as hl7service = for instance using Spring and letting the bean id = hl7service.
Our business logic is a plain POJO only using the HAPI library so we have these operations defined:
public class MyHL7BusinessLogic { // This is a plain POJO that has NO imports whatsoever on Apache Camel. // its a plain POJO only importing the HAPI library so we can much easier work with the HL7 format. public Message handleA19(Message msg) throws Exception { // here you can have your business logic for A19 messages assertTrue(msg instanceof QRY_A19); // just return the same dummy response return createADR19Message(); } public Message handleA01(Message msg) throws Exception { // here you can have your business logic for A01 messages assertTrue(msg instanceof ADT_A01); // just return the same dummy response return createADT01Message(); } }
Then we set up the Camel routes using the RouteBuilder as follows:
DataFormat hl7 = new HL7DataFormat(); // we setup or HL7 listener on port 8888 (using the hl7codec) and in sync mode so we can return a response from("mina:tcp://127.0.0.1:8888?sync=true&codec=#hl7codec") // we use the HL7 data format to unmarshal from HL7 stream to the HAPI Message model // this ensures that the camel message has been enriched with hl7 specific headers to // make the routing much easier (see below) .unmarshal(hl7) // using choice as the content base router .choice() // where we choose that A19 queries invoke the handleA19 method on our hl7service bean .when(header("CamelHL7TriggerEvent").isEqualTo("A19")) .beanRef("hl7service", "handleA19") .to("mock:a19") // and A01 should invoke the handleA01 method on our hl7service bean .when(header("CamelHL7TriggerEvent").isEqualTo("A01")).to("mock:a01") .beanRef("hl7service", "handleA01") .to("mock:a19") // other types should go to mock:unknown .otherwise() .to("mock:unknown") // end choice block .end() // marhsal response back .marshal(hl7);
Notice that we use the HL7 DataFormat to enrich our Camel Message with the MSH fields preconfigued on the Camel Message. This lets us much more easily define our routes using the fluent builders.
If we do not use the HL7 DataFormat, then we do not gains these headers and we must resort to a different technique for computing the MSH trigger event (= what kind of HL7 message it is). This is a big advantage of the HL7 DataFormat over the plain HL7 type converters.
Sample using plain String objects
In this sample we use plain String objects as the data format, that we send, process and receive. As the sample is part of a unit test, there is some code for assertions, but you should be able to understand what happens. First we send the plain string, Hello World, to the HL7MLLPCodec and receive the response as a plain string, Bye World.
MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Bye World"); // send plain hello world as String Object out = template.requestBody("mina:tcp://127.0.0.1:8888?sync=true&codec=#hl7codec", "Hello World"); assertMockEndpointsSatisfied(); // and the response is also just plain String assertEquals("Bye World", out);
Here we process the incoming data as plain String and send the response also as plain String:
from("mina:tcp://127.0.0.1:8888?sync=true&codec=#hl7codec") .process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { // use plain String as message format String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); assertEquals("Hello World", body); // return the response as plain string exchange.getOut().setBody("Bye World"); } }) .to("mock:result");
See Also
HTTP Component
The http: component provides HTTP based endpoints for consuming external HTTP resources (as a client to call external servers using HTTP).
URI format
http:hostname[:port][/resourceUri][?options]
Will by default use port 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
| camel-http vs camel-jetty You can only produce to endpoints generated by the HTTP component. Therefore it should never be used as input into your camel Routes. To bind/expose an HTTP endpoint via a HTTP server as input to a camel route, you can use the Jetty Component |
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| throwExceptionOnFailure | true | Camel 2.0: Option to disable throwing the HttpOperationFailedException in case of failed responses from the remote server. This allows you to get all responses regardles of the HTTP status code. |
| bridgeEndpoint | false | Camel 2.1: If the option is true , HttpProducer will ignore the Exchange.HTTP_URI header, and use the endpoint's URI for request. You may also set the throwExcpetionOnFailure to be false to let the HttpProducer send all the fault response back. |
| httpBindingRef | null | Reference to a org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpBinding in the Registry. |
| username | null | Username for Basic HTTP/NTML Authentication. |
| password | null | Password for Basic HTTP/NTML Authentication. |
| domain | null | Camel 2.1: Domain for NTML Authentication. This option must be used to force NTML authentication. |
| proxyHost | null | The proxy host name * only for >= Camel 1.6.2 *. |
| proxyPort | null | The proxy port number * only for >= Camel 1.6.2 *. |
| proxyUsername | null | Username for proxy authentication * only for >= Camel 1.6.2 *. |
| proxyPassword | null | Password for proxy authentication * only for >= Camel 1.6.2 *. |
| httpClientConfigurerRef | null | Reference to a org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpClientConfigurer in the Registry. |
| httpClient.XXX | null | Setting options on the HttpClientParams. For instance httpClient.soTimeout=5000 will set the SO_TIMEOUT to 5 seconds. |
Message Headers
Camel 1.x
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HttpProducer.HTTP_URI | String | Camel 1.5.1: URI to call. Will override existing URI set directly on the endpoint. Is set on the In message. |
| HttpProducer.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE | int | The HTTP response code from the external server. Is 200 for OK. Is set on the Out message. |
| HttpProducer.QUERY | String | URI parameters. Will override existing URI parameters set directly on the endpoint. Is set on the In message. |
Camel 2.0
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Exchange.HTTP_URI | String | URI to call. Will override existing URI set directly on the endpoint. |
| Exchange.HTTP_PATH | String | Request URI's path. |
| Exchange.HTTP_QUERY | String | URI parameters. Will override existing URI parameters set directly on the endpoint. |
| Exchange.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE | int | The HTTP response code from the external server. Is 200 for OK. |
| Exchange.HTTP_CHARACTER_ENCODING | String | Character encoding. |
| Exchange.CONTENT_TYPE | String | The HTTP content type. Is set on both the IN and OUT message to provide a content type, such as text/html. |
| Exchange.CONTENT_ENCODING | String | The HTTP content encoding. Is set on both the IN and OUT message to provide a content encoding, such as gzip. |
Message Body
Camel will store the HTTP response from the external server on the OUT body. All headers from the IN message will be copied to the OUT message, so headers are preserved during routing. Additionally Camel will add the HTTP response headers as well to the OUT message headers.
Response code
Camel will handle according to the HTTP response code:
- Response code is in the range 100..299, Camel regards it as a success response.
- Response code is in the range 300..399, Camel regards it as a redirection response and will throw a HttpOperationFailedException with the information.
- Response code is 400+, Camel regards it as an external server failure and will throw a HttpOperationFailedException with the information.

throwExceptionOnFailure The option, throwExceptionOnFailure, can be set to false to prevent the HttpOperationFailedException from being thrown for failed response codes. This allows you to get any response from the remote server.
There is a sample below demonstrating this.
HttpOperationFailedException
This exception contains the following information:
- The HTTP status code
- The HTTP status line (text of the status code)
- Redirect location, if server returned a redirect
- Response body as a java.io.InputStream, if server provided a body as response
Calling using GET or POST
In Camel 1.5 the following algorithm is used to determine if either GET or POST HTTP method should be used:
1. Use method provided in header.
2. GET if query string is provided in header.
3. GET if endpoint is configured with a query string.
4. POST if there is data to send (body is not null).
5. GET otherwise.
How to get access to HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse
Available as of Camel 2.0
You can get access to these two using the Camel type converter system using
HttpServletRequest request = exchange.getIn().getBody(HttpServletRequest.class); HttpServletRequest response = exchange.getIn().getBody(HttpServletResponse.class);
Or you can get access to them from HttpMessage directly using a type cast:
HttpMessage msg = (HttpMessage) exchange.getIn(); HttpServletRequest request = msg.getRequest(); HttpServletRequest response = msg.getResponse();
Configuring URI to call
You can set the HTTP producer's URI directly form the endpoint URI. In the route below, Camel will call out to the external server, oldhost, using HTTP.
from("direct:start") .to("http://oldhost");
And the equivalent Spring sample:
<camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <to uri="http://oldhost"/> </route> </camelContext>
In Camel 1.5.1 you can override the HTTP endpoint URI by adding a header with the key, HttpProducer.HTTP_URI, on the message.
from("direct:start") .setHeader(org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpProducer.HTTP_URI, constant("http://newhost")) .to("http://oldhost");
In the sample above Camel will call the http://newhost despite the endpoint is configured with http://oldhost.
And the same code in Camel 2.0:
from("direct:start") .setHeader(HttpConstants.HTTP_URI, constant("http://newhost")) .to("http://oldhost");
Where Constants is the class, org.apache.camel.component.http.Constants.
Configuring URI Parameters
The http producer supports URI parameters to be sent to the HTTP server. The URI parameters can either be set directly on the endpoint URI or as a header with the key HttpProducer.QUERY on the message.
from("direct:start") .to("http://oldhost?order=123&detail=short");
Or options provided in a header:
from("direct:start") .setHeader(HttpConstants.HTTP_QUERY, constant("order=123&detail=short")) .to("http://oldhost");
How to set the http method (GET/POST/PUT/DELETE/HEAD/OPTIONS/TRACE) to the HTTP producer
The HTTP component provides a way to set the HTTP request method by setting the message header. Here is an example;
Camel 1.x
from("direct:start") .setHeader(HttpConstants.HTTP_METHOD, constant(org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpMethods.POST)) .to("http://www.google.com") .to("mock:results");
Camel 2.x
from("direct:start") .setHeader(Exchange.HTTP_METHOD, constant(org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpMethods.POST)) .to("http://www.google.com") .to("mock:results");
The method can be written a bit shorter using the string constants:
.setHeader("CamelHttpMethod", constant("POST"))
And the equivalent Spring sample:
<camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <setHeader headerName="CamelHttpMethod"> <constant>POST</constant> </setHeader> <to uri="http://www.google.com"/> <to uri="mock:results"/> </route> </camelContext>
Using client tineout - SO_TIMEOUT
See the unit test in this link
Configuring a Proxy
Only for >= Camel 1.6.2
The HTTP component provides a way to configure a proxy.
from("direct:start") .to("http://oldhost?proxyHost=www.myproxy.com&proxyPort=80");
There is also support for proxy authentication via the proxyUsername and proxyPassword options.
Using proxy settings from Java System Properties
Only for >= Camel 1.6.2
The HTTP component will detect Java System Properties for http.proxyHost and http.proxyPort and use them if provided.
See more at SUN http proxy documentation.
Camel will first set the settings from Java System Properties and then the endpoint proxy options if provided.
So you can override the system properties with the endpoint options.
Configuring charset
If you are using POST to send data you can configure the charset using the Exchange property:
exchange.setProperty(Exchange.CHARSET_NAME, "iso-8859-1");
Or the httpClient options: httpClient.contentCharset=iso-8859-1
Sample with scheduled poll
The sample polls the Google homepage every 10 seconds and write the page to the file message.html:
from("timer://foo?fixedRate=true&delay=0&period=10000") .to("http://www.google.com") .setHeader(FileComponent.HEADER_FILE_NAME, "message.html").to("file:target/google");
URI Parameters from the endpoint URI
In this sample we have the complete URI endpoint that is just what you would have typed in a web browser. Multiple URI parameters can of course be set using the & character as separator, just as you would in the web browser. Camel does no tricks here.
// we query for Camel at the Google page template.sendBody("http://www.google.com/search?q=Camel", null);
URI Parameters from the Message
Map headers = new HashMap(); headers.put(HttpProducer.QUERY, "q=Camel&lr=lang_en"); // we query for Camel and English language at Google template.sendBody("http://www.google.com/search", null, headers);
In the header value above notice that it should not be prefixed with ? and you can separate parameters as usual with the & char.
Getting the Response Code
You can get the HTTP response code from the HTTP component by getting the value from the Out message header with HttpProducer.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE.
Exchange exchange = template.send("http://www.google.com/search", new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.getIn().setHeader(HttpProducer.QUERY, constant("hl=en&q=activemq")); } }); Message out = exchange.getOut(); int responseCode = out.getHeader(HttpProducer.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE, Integer.class);
Using throwExceptionOnFailure=false to get any response back
Available as of Camel 2.0
In the route below we want to route a message that we enrich with data returned from a remote HTTP call. As we want any response from the remote server, we set the throwExceptionOnFailure option to false so we get any response in the AggregationStrategy. As the code is based on a unit test that simulates a HTTP status code 404, there is some assertion code etc.
// We set throwExceptionOnFailure to false to let Camel return any response from the remove HTTP server without thrown // HttpOperationFailedException in case of failures. // This allows us to handle all responses in the aggregation strategy where we can check the HTTP response code // and decide what to do. As this is based on an unit test we assert the code is 404 from("direct:start").enrich("http://localhost:8222/myserver?throwExceptionOnFailure=false&user=Camel", new AggregationStrategy() { public Exchange aggregate(Exchange original, Exchange resource) { // get the response code Integer code = resource.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE, Integer.class); assertEquals(404, code.intValue()); return resource; } }).to("mock:result"); // this is our jetty server where we simulate the 404 from("jetty://http://localhost:8222/myserver") .process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.getOut().setBody("Page not found"); exchange.getOut().setHeader(Exchange.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE, 404); } });
Disabling Cookies
To disable cookies you can set the HTTP Client to ignore cookies by adding this URI option:
httpClient.cookiePolicy=ignoreCookies
Advanced Usage
If you need more control over the HTTP producer you should use the HttpComponent where you can set various classes to give you custom behavior.
Setting MaxConnectionsPerHost
The HTTP Component has a org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpConnectionManager where you can configure various global configuration for the given component.
By global, we mean that any endpoint the component creates has the same shared HttpConnectionManager. So, if we want to set a different value for the max connection per host, we need to define it on the HTTP component and not on the endpoint URI that we usually use. So here comes:
First, we define the http component in Spring XML. Yes, we use the same scheme name, http, because otherwise Camel will auto-discover and create the component with default settings. What we need is to overrule this so we can set our options. In the sample below we set the max connection to 5 instead of the default of 2.
<bean id="http" class="org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpComponent"> <property name="camelContext" ref="camel"/> <property name="httpConnectionManager" ref="myHttpConnectionManager"/> </bean> <bean id="myHttpConnectionManager" class="org.apache.commons.httpclient.MultiThreadedHttpConnectionManager"> <property name="params" ref="myHttpConnectionManagerParams"/> </bean> <bean id="myHttpConnectionManagerParams" class="org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpConnectionManagerParams"> <property name="defaultMaxConnectionsPerHost" value="5"/> </bean>
And then we can just use it as we normally do in our routes:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring" trace="true"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <to uri="http://www.google.com"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext>
Using HTTPS to authenticate gotchas
An end user reported that he had problem with authenticating with HTTPS. The problem was eventually resolved when he discovered the HTTPS server did not return a HTTP code 401 Authorization Required. The solution was to set the following URI option: httpClient.authenticationPreemptive=true
Accepting self signed certifications from remote server
See this link from a mailing list discussion with some code to outline how to do this with the Apache Commons HTTP API.
Setting up SSL for HTTP Client
Basically camel-http component is built on the top of Apache HTTP client, and you can implement a custom org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpClientConfigurer to do some configuration on the http client if you need full control of it.
However if you just want to specify the keystore and truststore you can do this with Apache HTTP HttpClientConfigurer, for example:
Protocol authhttps = new Protocol("https", new AuthSSLProtocolSocketFactory( new URL("file:my.keystore"), "mypassword", new URL("file:my.truststore"), "mypassword"), 443); Protocol.registerProtocol("https", authhttps);
And then you need to create a class that implements HttpClientConfigurer, and registers https protocol providing a keystore or truststore per example above. Then, from your camel route builder class you can hook it up like so:
HttpComponent httpComponent = getContext().getComponent("http", HttpComponent.class); httpComponent.setHttpClientConfigurer(new MyHttpClientConfigurer());
See Also
iBATIS
The ibatis: component allows you to query, poll, insert, update and delete data in a relational database using Apache iBATIS.
URI format
ibatis:statementName[?options]
Where statementName is the name in the iBATIS XML configuration file which maps to the query, insert, update or delete operation you wish to evaluate.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| consumer.onConsume | String | null | Statements to run after consuming. Can be used, for example, to update rows after they have been consumed and processed in Camel. See sample later. Multiple statements can be separated with comma. |
| consumer.useIterator | boolean | true | If true each row returned when polling will be processed individually. If false the entire List of data is set as the IN body. |
| consumer.routeEmptyResultSet | boolean | false | Camel 2.0: Sets whether empty result set should be routed or not. By default, empty result sets are not routed. |
| statementType | StatementType | null | Camel 1.6.1/2.0: Mandatory to specify for IbatisProducer to control which iBatis SqlMapClient method to invoke. The enum values are: QueryForObject, QueryForList, Insert, Update, Delete. |
| maxMessagesPerPoll | int | 0 | Camel 2.0: An integer to define a maximum messages to gather per poll. By default, no maximum is set. Can be used to set a limit of e.g. 1000 to avoid when starting up the server that there are thousands of files. Set a value of 0 or negative to disabled it. |
Message Headers
Camel will populate the result message, either IN or OUT with a header with the operationName used:
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.ibatis.queryName | String | Camel 1.x: The statementName used (for example: insertAccount). |
| CamelIBatisStatementName | String | Camel 2.0: The statementName used (for example: insertAccount). |
| CamelIBatisResult | Object | Camel 1.6.2/2.0: The response returned from iBatis in any of the operations. For instance an INSERT could return the auto-generated key, or number of rows etc. |
Message Body
Camel 1.6.1: The response from iBatis will be set as OUT body
Camel 1.6.2/2.0: The response from iBatis will only be set as body if it's a SELECT statement. That means, for example, for INSERT statements Camel will not replace the body. This allows you to continue routing and keep the original body. The response from iBatis is always stored in the header with the key CamelIBatisResult.
Samples
For example if you wish to consume beans from a JMS queue and insert them into a database you could do the following:
from("activemq:queue:newAccount"). to("ibatis:insertAccount?statementType=Insert");
Notice we have to specify the statementType, as we need to instruct Camel which SqlMapClient operation to invoke.
Where insertAccount is the iBatis ID in the SQL map file:
<!-- Insert example, using the Account parameter class --> <insert id="insertAccount" parameterClass="Account"> insert into ACCOUNT ( ACC_ID, ACC_FIRST_NAME, ACC_LAST_NAME, ACC_EMAIL ) values ( #id#, #firstName#, #lastName#, #emailAddress# ) </insert>
Using StatementType for better control of IBatis
Available as of Camel 1.6.1/2.0
When routing to an iBatis endpoint you want more fine grained control so you can control whether the SQL statement to be executed is a SELEECT, UPDATE, DELETE or INSERT etc. This is now possible in Camel 1.6.1/2.0. So for instance if we want to route to an iBatis endpoint in which the IN body contains parameters to a SELECT statement we can do:
from("direct:start") .to("ibatis:selectAccountById?statementType=QueryForObject") .to("mock:result");
In the code above we can invoke the iBatis statement selectAccountById and the IN body should contain the account id we want to retrieve, such as an Integer type.
We can do the same for some of the other operations, such as QueryForList:
from("direct:start") .to("ibatis:selectAllAccounts?statementType=QueryForList") .to("mock:result");
And the same for UPDATE, where we can send an Account object as IN body to iBatis:
from("direct:start") .to("ibatis:updateAccount?statementType=Update") .to("mock:result");
Scheduled polling example
Since this component does not support scheduled polling, you need to use another mechanism for triggering the scheduled polls, such as the Timer or Quartz components.
In the sample below we poll the database, every 30 seconds using the Timer component and send the data to the JMS queue:
from("timer://pollTheDatabase?delay=30000").to("ibatis:selectAllAccounts?statementType=QueryForList").to("activemq:queue:allAccounts");
And the iBatis SQL map file used:
<!-- Select with no parameters using the result map for Account class. --> <select id="selectAllAccounts" resultMap="AccountResult"> select * from ACCOUNT </select>
Using onConsume
This component supports executing statements after data have been consumed and processed by Camel. This allows you to do post updates in the database. Notice all statements must be UPDATE statements. Camel supports executing multiple statements whose name should be separated by comma.
The route below illustrates we execute the consumeAccount statement data is processed. This allows us to change the status of the row in the database to processed, so we avoid consuming it twice or more.
from("ibatis:selectUnprocessedAccounts?consumer.onConsume=consumeAccount").to("mock:results");
And the statements in the sqlmap file:
<select id="selectUnprocessedAccounts" resultMap="AccountResult"> select * from ACCOUNT where PROCESSED = false </select>
<update id="consumeAccount" parameterClass="Account"> update ACCOUNT set PROCESSED = true where ACC_ID = #id# </update>
See Also
IRC Component
The irc component implements an IRC (Internet Relay Chat) transport.
URI format
irc:nick@host[:port]/#room[?options]
In Camel 2.0, you can also use the following format:
irc:nick@host[:port]?channels=#channel1,#channel2,#channel3[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Description | Example | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| channels | New in 2.0, comma separated list of IRC channels to join. | channels=#channel1,#channel2 | null |
| nickname | The nickname used in chat. | irc:MyNick@irc.server.org#channel or irc:irc.server.org#channel?nickname=MyUser | null |
| username | The IRC server user name. | irc:MyUser@irc.server.org#channel or irc:irc.server.org#channel?username=MyUser | Same as nickname. |
| password | The IRC server password. | password=somepass | None |
| realname | The IRC user's actual name. | realname=MyName | None |
| colors | Whether or not the server supports color codes. | true, false | true |
| onReply | Whether or not to handle general responses to commands or informational messages. | true, false | false |
| onNick | Handle nickname change events. | true, false | true |
| onQuit | Handle user quit events. | true, false | true |
| onJoin | Handle user join events. | true, false | true |
| onKick | Handle kick events. | true, false | true |
| onMode | Handle mode change events. | true, false | true |
| onPart | Handle user part events. | true, false | true |
| onTopic | Handle topic change events. | true, false | true |
| onPrivmsg | Handle message events. | true, false | true |
| trustManager | New in 2.0, the trust manager used to verify the SSL server's certificate. | trustManager=#referenceToTrustManagerBean | The default trust manager, which accepts all certificates, will be used. |
SSL Support
As of Camel 2.0, you can also connect to an SSL enabled IRC server, as follows:
ircs:host[:port]/#room?username=user&password=pass
By default, the IRC transport uses SSLDefaultTrustManager. If you need to provide your own custom trust manager, use the trustManager parameter as follows:
ircs:host[:port]/#room?username=user&password=pass&trustManager=#referenceToMyTrustManagerBean
See Also
JBI Component
The jbi component is implemented by the ServiceMix Camel module and provides integration with a JBI Normalized Message Router, such as the one provided by Apache ServiceMix.
See below for information about how to use StreamSource types from ServiceMix in Camel. |
The following code:
from("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint")
Automatically exposes a new endpoint to the bus, where the service QName is {http://foo.bar.org}MyService and the endpoint name is MyEndpoint (see URI-format).
When a JBI endpoint appears at the end of a route, for example:
to("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint")
The messages sent by this producer endpoint are sent to the already deployed JBI endpoint.
URI format
jbi:service:serviceNamespace[sep]serviceName[?options] jbi:endpoint:serviceNamespace[sep]serviceName[sep]endpointName[?options] jbi:name:endpointName[?options]
The separator that should be used in the endpoint URL is:
- / (forward slash), if serviceNamespace starts with http://, or
- : (colon), if serviceNamespace starts with urn:foo:bar.
For more details of valid JBI URIs see the ServiceMix URI Guide.
Using the jbi:service: or jbi:endpoint: URI formats sets the service QName on the JBI endpoint to the one specified. Otherwise, the default Camel JBI Service QName is used, which is:
{http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/jbi}endpoint
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Examples
jbi:service:http://foo.bar.org/MyService jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint jbi:name:cheese
URI options
| Name | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mep | MEP of the Camel Exchange | Allows users to override the MEP set on the Exchange object. Valid values for this option are in-only, in-out, robust-in-out and in-optional-out. |
| operation | Value of the jbi.operation header property | Specifies the JBI operation for the MessageExchange. If no value is supplied, the JBI binding will use the value of the jbi.operation header property. |
| serialization | basic | Default value (basic) will check if headers are serializable by looking at the type, setting this option to strict will detect objects that can not be serialized although they implement the Serializable interface |
| convertException | false | false: send any exceptions thrown from the Camel route back unmodified true: convert all exceptions to a JBI FaultException (can be used to avoid non-serializable exceptions or to implement generic error handling |
Examples
jbi:service:http://foo.bar.org/MyService?mep=in-out (override the MEP, use InOut JBI MessageExchanges) jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint?mep=in (override the MEP, use InOnly JBI MessageExchanges) jbi:endpoint:urn:foo:bar:MyService:MyEndpoint?operation={http://www.mycompany.org}AddNumbers (overide the operation for the JBI Exchange to {http://www.mycompany.org}AddNumbers)
Using Stream bodies
If you are using a stream type as the message body, you should be aware that a stream is only capable of being read once. So if you enable DEBUG logging, the body is usually logged and thus read. To deal with this, Camel has a streamCaching option that can cache the stream, enabling you to read it multiple times.
from("jbi:endpoint:http://foo.bar.org/MyService/MyEndpoint").streamCaching().to("xslt:transform.xsl", "bean:doSomething");
From Camel 1.5 onwards, the stream caching is default enabled, so it is not necessary to set the streamCaching() option.
In Camel 2.0 we store big input streams (by default, over 64K) in a temp file using CachedOutputStream. When you close the input stream, the temp file will be deleted.
Creating a JBI Service Unit
If you have some Camel routes that you want to deploy inside JBI as a Service Unit, you can use the JBI Service Unit Archetype to create a new Maven project for the Service Unit.
If you have an existing Maven project that you need to convert into a JBI Service Unit, you may want to consult ServiceMix Maven JBI Plugins for further help. The key steps are as follows:
- Create a Spring XML file at src/main/resources/camel-context.xml to bootstrap your routes inside the JBI Service Unit.
- Change the POM file's packaging to jbi-service-unit.
Your pom.xml should look something like this to enable the jbi-service-unit packaging:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>myGroupId</groupId> <artifactId>myArtifactId</artifactId> <packaging>jbi-service-unit</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>A Camel based JBI Service Unit</name> <url>http://www.myorganization.org</url> <properties> <camel-version>1.0.0</camel-version> <servicemix-version>3.3</servicemix-version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.servicemix</groupId> <artifactId>servicemix-camel</artifactId> <version>${servicemix-version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.servicemix</groupId> <artifactId>servicemix-core</artifactId> <version>${servicemix-version}</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <defaultGoal>install</defaultGoal> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.5</source> <target>1.5</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- creates the JBI deployment unit --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.servicemix.tooling</groupId> <artifactId>jbi-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${servicemix-version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
See Also
JCR Component
The jcr component allows you to add nodes to a JCR (JSR-170) compliant content repository (for example, Apache Jackrabbit ).
URI format
jcr://user:password@repository/path/to/node
Usage
The repository element of the URI is used to look up the JCR Repository object in the Camel context registry.
If a message is sent to a JCR producer endpoint:
- A new node is created in the content repository,
- All the message properties of the IN message are transformed to JCR Value instances and added to the new node,
- The node's UUID is returned in the OUT message.
Message properties
All message properties are converted to node properties, except for the CamelJcrNodeName property (you can refer to JcrConstants.NODE_NAME in your code), which is used to determine the node name.
Example
The snippet below creates a node named node under the /home/test node in the content repository. One additional attribute is added to the node as well: my.contents.property which will contain the body of the message being sent.
from("direct:a").setProperty(JcrConstants.JCR_NODE_NAME, constant("node")) .setProperty("my.contents.property", body()).to("jcr://user:pass@repository/home/test");
See Also
JDBC Component
The jdbc component enables you to access databases through JDBC, where SQL queries and operations are sent in the message body. This component uses the standard JDBC API, unlike the SQL Component component, which uses spring-jdbc.
This component can only be used to define producer endpoints, which means that you cannot use the JDBC component in a from() statement. |
URI format
jdbc:dataSourceName[?options]
This component only supports producer endpoints.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| readSize | 0 / 2000 | The default maximum number of rows that can be read by a polling query. The default value is 2000 for Camel 1.5.0 or older. In newer releases the default value is 0. |
Result
The result is returned in the OUT body as an ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>. The List object contains the list of rows and the Map objects contain each row with the String key as the column name.
Note: This component fetches ResultSetMetaData to be able to return the column name as the key in the Map.
Message Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| CamelJdbcRowCount | If the query is a SELECT, query the row count is returned in this OUT header. |
| CamelJdbcUpdateCount | If the query is an UPDATE, query the update count is returned in this OUT header. |
Samples
In the following example, we fetch the rows from the customer table.
First we register our datasource in the Camel registry as testdb:
JndiRegistry reg = super.createRegistry(); reg.bind("testdb", ds); return reg;
Then we configure a route that routes to the JDBC component, so the SQL will be executed. Note how we refer to the testdb datasource that was bound in the previous step:
// lets add simple route public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:hello").to("jdbc:testdb?readSize=100"); }
Or you can create a DataSource in Spring like this:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="timer://kickoff?period=10000"/> <setBody> <constant>select * from customer</constant> </setBody> <to uri="jdbc:testdb"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext> <!-- Just add a demo to show how to bind a date source for camel in Spring--> <bean id="testdb" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:camel_jdbc" /> <property name="username" value="sa" /> <property name="password" value="" /> </bean>
We create an endpoint, add the SQL query to the body of the IN message, and then send the exchange. The result of the query is returned in the OUT body:
// first we create our exchange using the endpoint Endpoint endpoint = context.getEndpoint("direct:hello"); Exchange exchange = endpoint.createExchange(); // then we set the SQL on the in body exchange.getIn().setBody("select * from customer order by ID"); // now we send the exchange to the endpoint, and receives the response from Camel Exchange out = template.send(endpoint, exchange); // assertions of the response assertNotNull(out); assertNotNull(out.getOut()); ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> data = out.getOut().getBody(ArrayList.class); assertNotNull("out body could not be converted to an ArrayList - was: " + out.getOut().getBody(), data); assertEquals(2, data.size()); HashMap<String, Object> row = data.get(0); assertEquals("cust1", row.get("ID")); assertEquals("jstrachan", row.get("NAME")); row = data.get(1); assertEquals("cust2", row.get("ID")); assertEquals("nsandhu", row.get("NAME"));
If you want to work on the rows one by one instead of the entire ResultSet at once you need to use the Splitter EIP such as:
from("direct:hello") // here we split the data from the testdb into new messages one by one // so the mock endpoint will receive a message per row in the table .to("jdbc:testdb").split(body()).to("mock:result");
Sample - Polling the database every minute
If we want to poll a database using the JDBC component, we need to combine it with a polling scheduler such as the Timer or Quartz etc. In the following example, we retrieve data from the database every 60 seconds:
from("timer://foo?period=60000").setBody(constant("select * from customer")).to("jdbc:testdb").to("activemq:queue:customers");
See Also
Jetty Component
Supports non blocking Request Reply producer in Camel 2.1 onwards
The jetty component provides HTTP-based endpoints for consuming HTTP requests. That is, the Jetty component behaves as a simple Web server.
In Camel 2.1 the jetty component also provides non blocking Request Reply for producing HTTP requests. That is it can also acts as HTTP client sending to a remote HTTP server and use non blocking in this process. See more at ToAsync and the HTTP Async Example.
URI format
jetty:http://hostname[:port][/resourceUri][?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sessionSupport | false | Specifies whether to enable the session manager on the server side of Jetty. |
| httpClient.XXX | null | Camel 1.5.1/2.0: Configuration of Jetty's HttpClient. For example, setting httpClient.idleTimeout=30000 sets the idle timeout to 30 seconds. |
| httpBindingRef | null | Camel 1.5.1/2.0: Reference to an org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpBinding in the Registry. HttpBinding can be used to customize how a response should be written. |
| matchOnUriPrefix | false | Camel 2.0: Whether or not the CamelServlet should try to find a target consumer by matching the URI prefix if no exact match is found. |
| handlers | null | Camel 1.6.1/2.0: Specifies a comma-delimited set of org.mortbay.jetty.Handler instances in your Registry (such as your Spring ApplicationContext). These handlers are added to the Jetty servlet context (for example, to add security). |
Message Headers
Camel uses the same message headers as the HTTP component.
Camel also populates all request.parameter and request.headers. For example, given a client request with the URL, http://myserver/myserver?orderid=123, the exchange will contain a header named orderid with the value 123. This feature was introduced in Camel 1.5.
Usage
The Jetty component only supports consumer endpoints. Therefore a Jetty endpoint URI should be used only as the input for a Camel route (in a from() DSL call). To issue HTTP requests against other HTTP endpoints, use the HTTP Component
Sample
In this sample we define a route that exposes a HTTP service at http://localhost:8080/myapp/myservice:
from("jetty:http://localhost:9080/myapp/myservice").process(new MyBookService());
| Usage of localhost When you specify localhost in a URL, Camel exposes the endpoint only on the local TCP/IP network interface, so it cannot be accessed from outside the machine it operates on. If you need to expose a Jetty endpoint on a specific network interface, the numerical IP address of this interface should be used as the host. If you need to expose a Jetty endpoint on all network interfaces, the 0.0.0.0 address should be used. |
Our business logic is implemented in the MyBookService class, which accesses the HTTP request contents and then returns a response.
Note: The assert call appears in this example, because the code is part of an unit test.
public class MyBookService implements Processor { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { // just get the body as a string String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); // we have access to the HttpServletRequest here and we can grab it if we need it HttpServletRequest req = exchange.getIn().getBody(HttpServletRequest.class); assertNotNull(req); // for unit testing assertEquals("bookid=123", body); // send a html response exchange.getOut().setBody("<html><body>Book 123 is Camel in Action</body></html>"); } }
The following sample shows a content-based route that routes all requests containing the URI parameter, one, to the endpoint, mock:one, and all others to mock:other.
from("jetty:" + serverUri) .choice() .when().simple("in.header.one").to("mock:one") .otherwise() .to("mock:other");
So if a client sends the HTTP request, http://serverUri?one=hello, the Jetty component will copy the HTTP request parameter, one to the exchange's in.header. We can then use the simple language to route exchanges that contain this header to a specific endpoint and all others to another. If we used a language more powerful than Simple—such as EL or OGNL—we could also test for the parameter value and do routing based on the header value as well.
Session Support
The session support option, sessionSupport, can be used to enable a HttpSession object and access the session object while processing the exchange. For example, the following route enables sessions:
<route> <from uri="jetty:http://0.0.0.0/myapp/myservice/?sessionSupport=true"/> <processRef ref="myCode"/> <route>
The myCode Processor can be instantiated by a Spring bean element:
<bean id="myCode" class="com.mycompany.MyCodeProcessor"/>
Where the processor implementation can access the HttpSession as follows:
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { HttpSession session = ((HttpExchange)exchange).getRequest().getSession(); ... }
SSL Support (HTTPS)
Jetty provides SSL support out of the box. To enable Jetty to run in SSL mode, simply format the URI with the https:// prefix—for example:
<from uri="jetty:https://0.0.0.0/myapp/myservice/"/>
Jetty also needs to know where to load your keystore from and what passwords to use in order to load the correct SSL certificate. Set the following JVM System Properties:
- jetty.ssl.keystore specifies the location of the Java keystore file, which contains the Jetty server's own X.509 certificate in a key entry. A key entry stores the X.509 certificate (effectively, the public key) and also its associated private key.
- jetty.ssl.password the store password, which is required to access the keystore file (this is the same password that is supplied to the keystore command's -storepass option).
- jetty.ssl.keypassword the key password, which is used to access the certificate's key entry in the keystore (this is the same password that is supplied to the keystore command's -keypass option).
For details of how to configure SSL on a Jetty endpoint, read the following documentation at the Jetty Site: http://docs.codehaus.org/display/JETTY/How+to+configure+SSL
Default behavior for returning HTTP status codes
The default behavior of HTTP status codes is defined by the org.apache.camel.component.http.DefaultHttpBinding class, which handles how a response is written and also sets the HTTP status code.
If the exchange was processed successfully, the 200 HTTP status code is returned.
If the exchange failed with an exception, the 500 HTTP status code is returned, and the stacktrace is returned in the body. If you want to specify which HTTP status code to return, set the code in the HttpProducer.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE header of the OUT message.
Customizing HttpBinding
Available as of Camel 1.5.1/2.0
By default, Camel uses the org.apache.camel.component.http.DefaultHttpBinding to handle how a response is written. If you like, you can customize this behavior either by implementing your own HttpBinding class or by extending DefaultHttpBinding and overriding the appropriate methods.
The following example shows how to customize the DefaultHttpBinding in order to change how exceptions are returned:
public class MyHttpBinding extends DefaultHttpBinding { @Override public void doWriteExceptionResponse(Throwable exception, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { // we override the doWriteExceptionResponse as we only want to alter the binding how exceptions is // written back to the client. // we just return HTTP 200 so the client thinks its okay response.setStatus(200); // and we return this fixed text response.getWriter().write("Something went wrong but we dont care"); } }
We can then create an instance of our binding and register it in the Spring registry as follows:
<bean id="mybinding" class="com.mycompany.MyHttpBinding"/>
And then we can reference this binding when we define the route:
<route> <from uri="jetty:http://0.0.0.0:8080/myapp/myservice?httpBindingRef=mybinding"/> <to uri="bean:doSomething"/> </route>
Jetty handlers and security configuration
Available as of Camel 1.6.1/2.0: You can configure a list of Jetty handlers on the endpoint, which can be useful for enabling advanced Jetty security features. These handlers are configured in Spring XML as follows:
<-- Jetty Security handling -->
<bean id="userRealm" class="org.mortbay.jetty.plus.jaas.JAASUserRealm">
<property name="name" value="tracker-users" />
<property name="loginModuleName" value="ldaploginmodule" />
</bean>
<bean id="constraint" class="org.mortbay.jetty.security.Constraint">
<property name="name" value="BASIC" />
<property name="roles" value="tracker-users" />
<property name="authenticate" value="true" />
</bean>
<bean id="constraintMapping" class="org.mortbay.jetty.security.ConstraintMapping">
<property name="constraint" ref="constraint" />
<property name="pathSpec" value="/*" />
</bean>
<bean id="securityHandler" class="org.mortbay.jetty.security.SecurityHandler">
<property name="userRealm" ref="userRealm" />
<property name="constraintMappings" ref="constraintMapping" />
</bean>
You can then define the endpoint as:
from("jetty:http://0.0.0.0:9080/myservice?handlers=securityHandler")
If you need more handlers, set the handlers option equal to a comma-separated list of bean IDs.
See Also
Jing Component
The Jing component uses the Jing Library to perform XML validation of the message body using either
Note that the MSV component can also support RelaxNG XML syntax.
URI format
rng:someLocalOrRemoteResource rnc:someLocalOrRemoteResource
Where rng means use the RelaxNG XML Syntax whereas rnc means use RelaxNG Compact Syntax. The following examples show possible URI values
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| rng:foo/bar.rng | References the XML file foo/bar.rng on the classpath |
| rnc:http://foo.com/bar.rnc | References the RelaxNG Compact Syntax file from the URL, http://foo.com/bar.rnc |
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| useDom | false | Camel 2.0: Specifies whether DOMSource/DOMResult or SaxSource/SaxResult should be used by the validator. |
Example
The following example shows how to configure a route from the endpoint direct:start which then goes to one of two endpoints, either mock:valid or mock:invalid based on whether or not the XML matches the given RelaxNG Compact Syntax schema (which is supplied on the classpath).
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <doTry> <to uri="rnc:org/apache/camel/component/validator/jing/schema.rnc"/> <to uri="mock:valid"/> <doCatch> <exception>org.apache.camel.ValidationException</exception> <to uri="mock:invalid"/> </doCatch> <doFinally> <to uri="mock:finally"/> </doFinally> </doTry> </route> </camelContext>
See Also
JMS Component
The JMS component allows messages to be sent to (or consumed from) a JMS Queue or Topic. The implementation of the JMS Component uses Spring's JMS support for declarative transactions, using Spring's JmsTemplate for sending and a MessageListenerContainer for consuming.
| For users with Camel 1.6.1 or older JMS consumers have a bad default in Camel 1.6.1 or older. The maxMessagesPerTask is set to 1, whereas it really should be -1. To remedy this, change a route such as:
<from uri="jms:queue:foo"/>
By adding the maxMessagesPerTask option and setting its value to -1, as follows:
<from uri="jms:queue:foo&maxMessagesPerTask=-1"/>
This has been fixed in Camel 1.6.2/2.0. |
| Using ActiveMQ If you are using Apache ActiveMQ, you should prefer the ActiveMQ component as it has been particularly optimized for ActiveMQ. |
| Using JMS API 1.0.2 The old JMS API 1.0.2 has been @deprecated in Camel 2.1 and will be removed in Camel 2.2 release. |
URI format
jms:[temp:][queue:|topic:]destinationName[?options]
Where destinationName is a JMS queue or topic name. By default, the
destinationName is interpreted as a queue name. For example, to connect
to the queue, FOO.BAR, use:
jms:FOO.BAR
You can include the optional queue: prefix, if you prefer:
jms:queue:FOO.BAR
To connect to a topic, you must include the topic: prefix. For example, to
connect to the topic, Stocks.Prices, use:
jms:topic:Stocks.Prices
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Using Temporary Destinations
As of Camel 1.4.0, you can access temporary queues using the following URL format:
jms:temp:queue:foo
Or temporary topics using the following URL format:
jms:temp:topic:bar
This URL format enables multiple routes or processors or beans to refer to the same temporary destination. For example, you can create three temporary destinations and use them in routes as inputs or outputs by referring to them by name.
Notes
| If you are using ActiveMQ Note that the JMS component reuses Spring 2's JmsTemplate for sending messages. This is not ideal for use in a non-J2EE container and typically requires some caching in the JMS provider to avoid performance being lousy. So if you intend to use Apache ActiveMQ as your Message Broker - which is a good choice as ActiveMQ rocks
|
If you wish to use durable topic subscriptions, you need to specify both clientId and durableSubscriptionName. Note that the value of the clientId must be unique and can only be used by a single JMS connection instance in your entire network. You may prefer to use Virtual Topics instead to avoid this limitation. More background on durable messaging here.
When using message headers, the JMS specification states that header names must be valid Java identifiers. So, by default, Camel ignores any headers that do not match this rule. So try to name your headers as if they are valid Java identifiers. One benefit of doing this is that you can then use your headers inside a JMS Selector (whose SQL92 syntax mandates Java identifier syntax for headers).
From Camel 1.4 onwards, a simple strategy for mapping header names is used by default. The strategy is to replace any dots in the header name with the underscore character and to reverse the replacement when the header name is restored from a JMS message sent over the wire. What does this mean? No more losing method names to invoke on a bean component, no more losing the filename header for the File Component, and so on.
The current header name strategy for accepting header names in Camel is as follows:
- Replace all dots with underscores (for example, org.apache.camel.MethodName becomes org_apache_camel_MethodName).
- Test if the name is a valid java identifier using the JDK core classes.
- If the test success, the header is added and sent over the wire; otherwise it is dropped (and logged at DEBUG level).
In Camel 2.0 this strategy has been change a bit to use the following replacement strategy:
- Dots are replaced by _DOT_ and the replacement is reversed when Camel consume the message
- Hyphen is replaced by _HYPHEN_ and the replacement is reversed when Camel consumes the message
| For Consuming Messages cacheLevelName settings are vital! If you are using Spring before 2.5.1 and Camel before 1.3.0, you might want to set the cacheLevelName to be CACHE_CONSUMER for maximum performance. Due to a bug in earlier Spring versions causing a lack of transactional integrity, previous versions of Camel and Camel versions from 1.3.0 onwwards when used with Spring versions earlier than 2.5.1 will default to using CACHE_CONNECTION. See the JIRAs CAMEL-163 and CAMEL-294. Also, if you are using XA resources or running in a J2EE container, you may want to set the cacheLevelName to be CACHE_NONE as we have found that when using JBoss with TibCo EMS and JTA/XA you must disable caching. Another user reports problems using WebSphere MQ 6.0.2.5, Camel 1.6.0 and Spring 2.5.6. The application does not use XA and is not running inside a J2EE Container, but the cacheLevelName=CACHE_NONE setting seems to solve the problem with WebSphere MQ. See also more about JmsTemplate gotchas. |
Options
You can configure many different properties on the JMS endpoint which map to properties on the JMSConfiguration POJO. Note: Many of these properties map to properties on Spring JMS, which Camel uses for sending and receiving messages. So you can get more information about these properties by consulting the relevant Spring documentation.
The options is divided into two tables, the first one with the most common options used. The latter contains the rest.
Most commonly used options
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| autoStartup | true | Specifies whether the consumer container should auto-startup. |
| clientId | null | Sets the JMS client ID to use. Note that this value, if specified, must be unique and can only be used by a single JMS connection instance. It is typically only required for durable topic subscriptions. You may prefer to use Virtual Topics instead. |
| concurrentConsumers | 1 | Specifies the default number of concurrent consumers. |
| disableReplyTo | false | If true, ignore the JMSReplyTo header and so treat messages as InOnly by default and do not send a reply back. |
| durableSubscriptionName | null | The durable subscriber name for specifying durable topic subscriptions. |
| maxConcurrentConsumers | 1 | Specifies the maximum number of concurrent consumers. |
| replyTo | null | Provides an explicit ReployTo destination, which overrides any incoming value of Message.getJMSReplyTo(). |
| requestTimeout | 20000 | The timeout for sending messages (in milliseconds). The default is 20 seconds. |
| selector | null | Sets the JMS Selector, which is an SQL 92 predicate that is used to filter messages within the broker. You may have to encode special characters such as = as %3D |
| timeToLive | null | When sending messages, specifies the time-to-live of the message (in milliseconds). The explicitQosEnabled option must also be enabled in order for this option to have any effect. |
| transacted | false | Specifies whether to use transacted mode for sending/receiving messages using the InOnly Exchange Pattern. |
| testConnectionOnStartup | false | Camel 2.1: Specifies whether to test the connection on startup. This ensures that when Camel starts that all the JMS consumers have a valid connection to the JMS broker. If a connection cannot be granted then Camel throws an exception on startup. This ensure that Camel is not started with failed connections. |
All the other options
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| acceptMessagesWhileStopping | false | Specifies whether the consumer accept messages while it is stopping. |
| acknowledgementModeName | AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE | The JMS acknowledgement name, which is one of: TRANSACTED, CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE, AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE, DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE |
| acknowledgementMode | -1 | The JMS acknowledgement mode defined as an Integer. Allows you to set vendor-specific extensions to the acknowledgment mode. For the regular modes, it is preferable to use the acknowledgementModeName instead. |
| alwaysCopyMessage | false | If true, Camel will always make a JMS message copy of the message when it is passed to the producer for sending. Copying the message is needed in some situations, such as when a replyToDestinationSelectorName is set (incidentally, Camel will set the alwaysCopyMessage option to true, if a replyToDestinationSelectorName is set) |
| cacheLevelName | CACHE_CONSUMER | Sets the cache level by name for the underlying JMS resources. Possible values are: CACHE_AUTO, CACHE_CONNECTION, CACHE_CONSUMER, CACHE_NONE, and CACHE_SESSION. See the Spring documentation and see the warning above. |
| cacheLevel | -1 | Sets the cache level by ID for the underlying JMS resources. |
| consumerType | Default | The consumer type to use, which can be one of: Simple, Default or ServerSessionPool. The consumer type determines which Spring JMS listener to use. Default will use org.springframework.jms.listener.DefaultMessageListenerContainer, Simple will use org.springframework.jms.listener.SimpleMessageListenerContainer, and ServerSessionPool will use org.springframework.jms.listener.serversession.ServerSessionMessageListenerContainer. If the option, useVersion102=true, Camel will use the JMS 1.0.2 Spring classes instead. ServerSessionPool is @deprecated and will be removed in Camel 2.0. |
| connectionFactory | null | The default JMS connection factory to use for the listenerConnectionFactory and templateConnectionFactory, if neither is specified. |
| deliveryMode | 2 | Specifies the delivery mode when sending, where 1 = non-persistent, and 2 = persistent. |
| deliveryPersistent | true | Specifies whether persistent delivery is used by default. |
| destination | null | Camel 2.0: Specifies the JMS Destination object to use on this endpoint. |
| destinationName | null | Camel 2.0: Specifies the JMS destination name to use on this endpoint. |
| destinationResolver | null | A pluggable org.springframework.jms.support.destination.DestinationResolver that allows you to use your own resolver (for example, to lookup the real destination in a JNDI registry). |
| eagerLoadingOfProperties | false | Enables eager loading of JMS properties as soon as a message is received, which is generally inefficient, because the JMS properties might not be required. But this feature can sometimes catch early any issues with the underlying JMS provider and the use of JMS properties. This feature can also be used for testing purposes, to ensure JMS properties can be understood and handled correctly. |
| exceptionListener | null | Specifies the JMS Exception Listener that is to be notified of any underlying JMS exceptions. |
| explicitQosEnabled | false | Set if the deliveryMode, priority or timeToLive qualities of service should be used when sending messages. This option is based on Spring's JmsTemplate. The deliveryMode, priority and timeToLive options are applied to the current endpoint. This contrasts with the preserveMessageQos option, which operates at message granularity, reading QoS properties exclusively from the Camel In message headers. |
| exposeListenerSession | true | Specifies whether the listener session should be exposed when consuming messages. |
| idleTaskExecutionLimit | 1 | Specifies the limit for idle executions of a receive task, not having received any message within its execution. If this limit is reached, the task will shut down and leave receiving to other executing tasks (in the case of dynamic scheduling; see the maxConcurrentConsumers setting). |
| jmsMessageType | null | Camel 2.0: Allows you to force the use of a specific javax.jms.Message implementation for sending JMS messages. Possible values are: Bytes, Map, Object, Stream, Text. By default, Camel would determine which JMS message type to use from the In body type. This option allows you to specify it. |
| jmsKeyFormatStrategy | default | Camel 2.0: Pluggable strategy for encoding and decoding JMS keys so they can be compliant with the JMS specification. Camel provides two implementations out of the box: default and passthrough. The default strategy will safely marshal dots and hyphens (. and -). The passthrough strategy leaves the key as is. Can be used for JMS brokers which do not care whether JMS header keys contain illegal characters. You can provide your own implementation of the org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsKeyFormatStrategy and refer to it using the # notation. |
| jmsOperations | null | Allows you to use your own implementation of the org.springframework.jms.core.JmsOperations interface. Camel uses JmsTemplate as default. Can be used for testing purpose, but not used much as stated in the spring API docs. |
| lazyCreateTransactionManager | true | Camel 2.0: If true, Camel will create a JmsTransactionManager, if there is no transactionManager injected when option transacted=true. |
| listenerConnectionFactory | null | The JMS connection factory used for consuming messages. |
| mapJmsMessage | true | Camel 1.6.2/2.0: Specifies whether Camel should auto map the received JMS message to an appropiate payload type, such as javax.jms.TextMessage to a String etc. See section about how mapping works below for more details. |
| maxMessagesPerTask | -1 | The number of messages per task. -1 is unlimited. |
| messageConverter | null | Camel 1.6.2/2.0: To use a custom Spring org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConverter so you can be 100% in control how to map to/from a javax.jms.Message. |
| messageIdEnabled | true | When sending, specifies whether message IDs should be added. |
| messageTimestampEnabled | true | Specifies whether timestamps should be enabled by default on sending messages. |
| password | null | The password for the connector factory. |
| priority | 4 | Values greater than 1 specify the message priority when sending (where 0 is the lowest priority and 9 is the highest). The explicitQosEnabled option must also be enabled in order for this option to have any effect. |
| preserveMessageQos | false | Camel 2.0: Set to true, if you want to send message using the QoS settings specified on the message, instead of the QoS settings on the JMS endpoint. The following three headers are considered JMSPriority, JMSDeliveryMode, and JMSExpiration. You can provide all or only some of them. If not provided, Camel will fall back to use the values from the endpoint instead. So, when using this option, the headers override the values from the endpoint. The explicitQosEnabled option, by contrast, will only use options set on the endpoint, and not values from the message header. |
| pubSubNoLocal | false | Specifies whether to inhibit the delivery of messages published by its own connection. |
| receiveTimeout | None | The timeout for receiving messages (in milliseconds). |
| recoveryInterval | 5000 | Specifies the interval between recovery attempts, i.e. when a connection is being refreshed, in milliseconds. The default is 5000 ms, that is, 5 seconds. |
| replyToTempDestinationAffinity | endpoint | Defines the component-created temporary replyTo destination sharing strategy. Possible values are: component, endpoint or producer. component = a single temp queue is shared among all producers for a given component instance; endpoint = a single temp queue is shared among all producers for a given endpoint instance; producer = a single temp queue is created for each producer. |
| replyToDestinationSelectorName | null | Sets the JMS Selector using the fixed name to be used so you can filter out your own replies from the others when using a shared queue (that is, if you are not using a temporary reply queue). |
| replyToDeliveryPersistent | true | Specifies whether to use persistent delivery by default for replies. |
| serverSessionFactory | null | @deprecated - will be removed in Camel 2.0. The JMS ServerSessionFactory, if you wish to use ServerSessionFactory for consumption |
| subscriptionDurable | false | Enabled by default, if you specify a durableSubscriberName and a clientId. |
| taskExecutor | null | Allows you to specify a custom task executor for consuming messages. |
| templateConnectionFactory | null | The JMS connection factory used for sending messages. |
| transactedInOut | false | @deprecated: Specifies whether to use transacted mode for sending messages using the InOut Exchange Pattern. Applies only to producer endpoints. See section Enabling Transacted Consumption for more details. |
| transactionManager | null | The Spring transaction manager to use. |
| transactionName | null | The name of the transaction to use. |
| transactionTimeout | null | The timeout value of the transaction, if using transacted mode. |
| transferException | false | Camel 2.0: If enabled and you are using Request Reply messaging (InOut) and an Exchange failed on the consumer side, then the caused Exception will be send back in response as a javax.jms.ObjectMessage. If the client is Camel, the returned Exception is rethrown. This allows you to use Camel JMS as a bridge in your routing - for example, using persistent queues to enable robust routing. Notice that if you also have transferExchange enabled, this option takes precedence. The caught exception is required to be serializable. The original Exception on the consumer side can be wrapped in an outer exception such as org.apache.camel.RuntimeCamelException when returned to the producer. |
| transferExchange | false | Camel 2.0: You can transfer the exchange over the wire instead of just the body and headers. The following fields are transferred: In body, Out body, Fault body, In headers, Out headers, Fault headers, exchange properties, exchange exception. This requires that the objects are serializable. Camel will exclude any non-serializable objects and log it at WARN level. |
| username | null | The username for the connector factory. |
| useMessageIDAsCorrelationID | false | Specifies whether JMSMessageID should be used as JMSCorrelationID for InOut messages. Camel will by default use a GUID. |
| useVersion102 | false | @deprecated: Specifies whether the old JMS API should be used. Will be removed in Camel 2.2, as JMS API 1.0.2 is no longer provided in Spring 3.0. |
Message Mapping between JMS and Camel
Camel automatically maps messages between javax.jms.Message and org.apache.camel.Message.
When sending a JMS message, Camel converts the message body to the following JMS message types:
| Body Type | JMS Message | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| String | javax.jms.TextMessage | |
| org.w3c.dom.Node | javax.jms.TextMessage | The DOM will be converted to String. |
| Map | javax.jms.MapMessage | |
| java.io.Serializable | javax.jms.ObjectMessage | |
| byte[] | javax.jms.BytesMessage | |
| java.io.File | javax.jms.BytesMessage | |
| java.io.Reader | javax.jms.BytesMessage | |
| java.io.InputStream | javax.jms.BytesMessage | |
| java.nio.ByteBuffer | javax.jms.BytesMessage |
When receiving a JMS message, Camel converts the JMS message to the following body type:
| JMS Message | Body Type |
|---|---|
| javax.jms.TextMessage | String |
| javax.jms.BytesMessage | byte[] |
| javax.jms.MapMessage | Map<String, Object> |
| javax.jms.ObjectMessage | Object |
Disabling auto-mapping of JMS messages
Available as of Camel 1.6.2/2.0
You can use the mapJmsMessage option to disable the auto-mapping above. If disabled, Camel will not try to map the received JMS message, but instead uses it directly as the payload. This allows you to avoid the overhead of mapping and let Camel just pass through the JMS message. For instance, it even allows you to route javax.jms.ObjectMessage JMS messages with classes you do not have on the classpath.
Using a custom MessageConverter
Available as of Camel 1.6.2/2.0
You can use the messageConverter option to do the mapping yourself in a Spring org.springframework.jms.support.converter.MessageConverter class.
For example, in the route below we use a custom message converter when sending a message to the JMS order queue:
from("file://inbox/order").to("jms:queue:order?messageConcter=#myMessageConverter");
You can also use a custom message converter when consuming from a JMS destination.
Controlling the mapping strategy selected
Available as of Camel 2.0
You can use the jmsMessageType option on the endpoint URL to force a specific message type for all messages.
In the route below, we poll files from a folder and send them as javax.jms.TextMessage as we have forced the JMS producer endpoint to use text messages:
from("file://inbox/order").to("jms:queue:order?jmsMessageType=Text");
You can also specify the message type to use for each messabe by setting the header with the key CamelJmsMessageType. For example:
from("file://inbox/order").setHeader("CamelJmsMessageType", JmsMessageType.Text).to("jms:queue:order");
The possible values are defined in the enum class, org.apache.camel.jms.JmsMessageType.
Message format when sending
The exchange that is sent over the JMS wire must conform to the JMS Message spec.
For the exchange.in.header the following rules apply for the header keys:
- Keys starting with JMS or JMSX are reserved.
- exchange.in.headers keys must be literals and all be valid Java identifiers (do not use dots in the key name).
- From Camel 1.4 until Camel 1.6.x, Camel automatically replaces all dots with underscores in key names. This replacement is reversed when Camel consumes JMS messages.
- From Camel 2.0 onwards, Camel replaces dots & hyphens and the reverse when when consuming JMS messages:
. is replaced by _DOT_ and the reverse replacement when Camel consumes the message.
- is replaced by _HYPHEN_ and the reverse replacement when Camel consumes the message. - See also the option jmsKeyFormatStrategy introduced in Camel 2.0, which allows you to use your own custom strategy for formatting keys.
For the exchange.in.header, the following rules apply for the header values:
- The values must be primitives or their counter objects (such as Integer, Long, Character). The types, String, CharSequence, Date, BigDecimal and BigInteger are all converted to their toString() representation. All other types are dropped.
Camel will log with category org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsBinding at DEBUG level if it drops a given header value. For example:
2008-07-09 06:43:04,046 [main ] DEBUG JmsBinding
- Ignoring non primitive header: order of class: org.apache.camel.component.jms.issues.DummyOrder with value: DummyOrder{orderId=333, itemId=4444, quantity=2}
Message format when receiving
Camel adds the following properties to the Exchange when it receives a message:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.jms.replyDestination | javax.jms.Destination | The reply destination. |
Camel adds the following JMS properties to the In message headers when it receives a JMS message:
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JMSCorrelationID | String | The JMS correlation ID. |
| JMSDeliveryMode | int | The JMS delivery mode. |
| JMSDestination | javax.jms.Destination | The JMS destination. |
| JMSExpiration | long | The JMS expiration. |
| JMSMessageID | String | The JMS unique message ID. |
| JMSPriority | int | The JMS priority (with 0 as the lowest priority and 9 as the highest). |
| JMSRedelivered | boolean | Is the JMS message redelivered. |
| JMSReplyTo | javax.jms.Destination | The JMS reply-to destination. |
| JMSTimestamp | long | The JMS timestamp. |
| JMSType | String | The JMS type. |
| JMSXGroupID | String | The JMS group ID. |
As all the above information is standard JMS you can check the JMS documentation for further details.
About using Camel to send and receive messages and JMSReplyTo
The JMS component is complex and you have to pay close attention to how it works in some cases. So this is a short summary of some of the areas/pitfalls to look for.
When Camel sends a message using its JMSProducer, it checks the following conditions:
- The message exchange pattern,
- Whether a JMSReplyTo was set in the endpoint or in the message headers,
- Whether any of the following options have been set on the JMS endpoint: disableReplyTo, preserveMessageQos, explicitQosEnabled.
All this can be a tad complex to understand and configure to support your use case.
JmsProducer
The JmsProducer behaves as follows, depending on configuration:
| Exchange Pattern | Other options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| InOut | - | Camel will expect a reply, set a temporary JMSReplyTo, and after sending the message, it will start to listen for the reply message on the temporary queue. |
| InOut | JMSReplyTo is set | Camel will expect a reply and, after sending the message, it will start to listen for the reply message on the specified JMSReplyTo queue. |
| InOnly | - | Camel will send the message and not expect a reply. |
| InOnly | JMSReplyTo is set | Camel sees this as a contradiction and will suppress the JMSReplyTo. In fact, Camel will disable it by clearing it before sending. Camel will send the message and not expect a reply. Camel logs this in the log at WARN level and you should see: WARN JmsProducer - Disabling JMSReplyTo as this Exchange is not OUT capable with JMSReplyTo: myReplyQueue to destination: myQueue. Note: You can use the preserveMessageQos=true setting or the explicitQosEnabled=true setting to force Camel to send the JMSReplyTo anyway, and the WARN log will disappear. |
JmsConsumer
The JmsConsumer behaves as follows, depending on configuration:
| Exchange Pattern | Other options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| InOut | - | Camel will send the reply back to the JMSReplyTo queue. |
| InOnly | - | Camel will not send a reply back, as the pattern is InOnly. |
| - | disableReplyTo=true | This option suppresses replies. |
So pay attention to the message exchange pattern set on your exchanges.
If you send a message to a JMS destination in the middle of your route you can specify the exchange pattern to use, see more at Request Reply.
This is useful if you want to send an InOnly message to a JMS topic:
from("activemq:queue:in") .to("bean:validateOrder") .to(ExchangePattern.InOnly, "activemq:topic:order") .to("bean:handleOrder");
Reuse endpoint and send to different destinations computed at runtime
Available as of Camel 1.6.2/2.0
If you need to send messages to a lot of different JMS destinations, it makes sense to reuse a JMS endpoint and specify the real destination in a message header. This allows Camel to reuse the same endpoint, but send to different destinations. This greatly reduces the number of endpoints created and economizes on memory and thread resources.
You can specify the destination in the following headers:
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CamelJmsDestination | javax.jms.Destination | Camel 2.0: A destination object. |
| CamelJmsDestinationName | String | Camel 1.6.2/2.0: The destination name. |
For example, the following route shows how you can compute a destination at run time and use it to override the destination appearing in the JMS URL:
from("file://inbox") .to("bean:computeDestination") .to("activemq:queue:dummy");
The queue name, dummy, is just a placeholder. It must be provided as part of the JMS endpoint URL, but it will be ignored in this example.
In the computeDestination bean, specify the real destination by setting the CamelJmsDestinationName header as follows:
public void setJmsHeader(Exchange exchange) { String id = .... exchange.getIn().setHeader("CamelJmsDestinationName", "order:" + id"); }
Then Camel will read this header and use it as the destination instead of the one configured on the endpoint. So, in this example Camel sends the message to activemq:queue:order:2, assuming the id value was 2.
If both the CamelJmsDestination and the CamelJmsDestinationName headers are set, CamelJmsDestination takes priority.
Configuring different JMS providers
You can configure your JMS provider in Spring XML as follows:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> </camelContext> <bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsComponent"> <property name="connectionFactory"> <bean class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory"> <property name="brokerURL" value="vm://localhost?broker.persistent=false"/> </bean> </property> </bean>
Basically, you can configure as many JMS component instances as you wish and give them a unique name using the id attribute. The preceding example configures an activemq component. You could do the same to configure MQSeries, TibCo, BEA, Sonic and so on.
Once you have a named JMS component, you can then refer to endpoints within that component using URIs. For example for the component name, activemq, you can then refer to destinations using the URI format, activemq:[queue:|topic:]destinationName. You can use the same approach for all other JMS providers.
This works by the SpringCamelContext lazily fetching components from the spring context for the scheme name you use for Endpoint URIs and having the Component resolve the endpoint URIs.
Using JNDI to find the ConnectionFactory
If you are using a J2EE container, you might need to look up JNDI to find the JMS ConnectionFactory rather than use the usual <bean> mechanism in Spring. You can do this using Spring's factory bean or the new Spring XML namespace. For example:
<bean id="weblogic" class="org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsComponent"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="myConnectionFactory"/> </bean> <jee:jndi-lookup id="myConnectionFactory" jndi-name="jms/connectionFactory"/>
See The jee schema in the Spring reference documentation for more details about JNDI lookup.
Using JNDI to lookup the physical queues
You need to use the destinationResolver option to use the Spring JNDI resolver that can lookup in the JNDI, or use your own custom implementation.
See this nabble post for more details: http://www.nabble.com/JMS-queue---JNDI-instead-of-physical-name-td24484994.html
Using WebSphere MQ
See this link at nabble for details of how a Camel user configured JMS to connect to remote WebSphere MQ brokers.
Concurrent Consuming
A common requirement with JMS is to consume messages concurrently in multiple threads in order to make an application more responsive. You can set the concurrentConsumers option to specify the number of threads servicing the JMS endpoint, as follows:
from("jms:SomeQueue?concurrentConsumers=20").
bean(MyClass.class);
You can configure this option in one of the following ways:
- On the JmsComponent,
- On the endpoint URI or,
- By invoking setConcurrentConsumers() directly on the JmsEndpoint.
Enabling Transacted Consumption
A common requirement is to consume from a queue in a transaction and then process the message using the Camel route. To do this, just ensure that you set the following properties on the component/endpoint:
- transacted = true
- transactionManager = a Transsaction Manager - typically the JmsTransactionManager
See also the Transactional Client EIP pattern for further details.
| Transaction and Request Reply over JMS Note that when using Request Reply over JMS you cannot use a single transaction; as JMS will not send any messages until a commit is performed, the server side won't receive anything at all until the transaction commits. So, with request/response you must commit a transaction after sending the first request and then use a separate transaction for receiving the response. This is why the transacted property applies only to the InOnly message Exchange Pattern (MEP). If you want to use transactions for the InOut MEP as well, you must set transactedInOut=true. To recap: if you have transacted=true, transactedInOut=false and are sending an InOut, the Exchange will not use transactions. |
Using JMSReplyTo for late replies
Avaiable as of Camel 2.0
When using Camel as a JMS listener, it sets an Exchange property with the value of the ReplyTo javax.jms.Destination object, having the key ReplyTo. You can obtain this Destination as follows:
Destination replyDestination = exchange.getIn().getHeader(JmsConstants.JMS_REPLY_DESTINATION, Destination.class);
And then later use it to send a reply using regular JMS or Camel.
// we need to pass in the JMS component, and in this sample we use ActiveMQ
JmsEndpoint endpoint = JmsEndpoint.newInstance(replyDestination, activeMQComponent);
// now we have the endpoint we can use regular Camel API to send a message to it
template.sendBody(endpoint, "Here is the late reply.");
A different solution to sending a reply is to provide the replyDestination object in the same Exchange property when sending. Camel will then pick up this property and use it for the real destination. The endpoint URI must include a dummy destination, however. For example:
// we pretend to send it to some non existing dummy queue
template.send("activemq:queue:dummy, new Processor() {
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
// and here we override the destination with the ReplyTo destination object so the message is sent to there instead of dummy
exchange.getIn().setHeader(JmsConstants.JMS_DESTINATION, replyDestination);
exchange.getIn().setBody("Here is the late reply.");
}
}
Using a request timeout
In the sample below we send a Request Reply style message Exchange (we use the requestBody method = InOut) to the slow queue for further processing in Camel and we wait for a return reply:
// send a in-out with a timeout for 5 sec Object out = template.requestBody("activemq:queue:slow?requestTimeout=5000", "Hello World");
Samples
JMS is used in many examples for other components as well. But we provide a few samples below to get started.
Receiving from JMS
In the following sample we configure a route that receives JMS messages and routes the message to a POJO:
from("jms:queue:foo"). to("bean:myBusinessLogic");
You can of course use any of the EIP patterns so the route can be context based. For example, here's how to filter an order topic for the big spenders:
from("jms:topic:OrdersTopic"). filter().method("myBean", "isGoldCustomer"). to("jms:queue:BigSpendersQueue");
Sending to a JMS
In the sample below we poll a file folder and send the file content to a JMS topic. As we want the content of the file as a TextMessage instead of a BytesMessage, we need to convert the body to a String:
from("file://orders"). convertBodyTo(String.class). to("jms:topic:OrdersTopic");
Using Annotations
Camel also has annotations so you can use POJO Consuming and POJO Producing.
Spring DSL sample
The preceding examples use the Java DSL. Camel also supports Spring XML DSL. Here is the big spender sample using Spring DSL:
<route> <from uri="jms:topic:OrdersTopic"/> <filter> <method bean="myBean" method="isGoldCustomer"/> <to uri="jms:queue:BigSpendersQueue"/> </filter> </route>
Other samples
JMS appears in many of the examples for other components and EIP patterns, as well in this Camel documentation. So feel free to browse the documentation. If you have time, check out the this tutorial that uses JMS but focuses on how well Spring Remoting and Camel works together Tutorial-JmsRemoting.
Using JMS as a Dead Letter Queue storing Exchange
Available as of Camel 2.0
Normally, when using JMS as the transport, it only transfers the body and headers as the payload. If you want to use JMS with a Dead Letter Channel, using a JMS queue as the Dead Letter Queue, then normally the caused Exception is not stored in the JMS message. You can, however, use the transferExchange option on the JMS dead letter queue to instruct Camel to store the entire Exchange in the queue as a javax.jms.ObjectMessage that holds a org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultExchangeHolder. This allows you to consume from the Dead Letter Queue and retrieve the caused exception from the Exchange property with the key Exchange.EXCEPTION_CAUGHT. The demo below illustrates this:
// setup error handler to use JMS as queue and store the entire Exchange errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("jms:queue:dead?transferExchange=true"));
Then you can consume from the JMS queue and analyze the problem:
from("jms:queue:dead").to("bean:myErrorAnalyzer"); // and in our bean String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(); Exception cause = exchange.getProperty(Exchange.EXCEPTION_CAUGHT, Exception.class); // the cause message is String problem = cause.getMessage();
Using JMS as a Dead Letter Channel storing error only
You can use JMS to store the cause error message or to store a custom body, which you can initialize yourself. The following example uses the Message Translator EIP to do a transformation on the failed exchange before it is moved to the JMS dead letter queue:
// we sent it to a seda dead queue first errorHandler(deadLetterChannel("seda:dead")); // and on the seda dead queue we can do the custom transformation before its sent to the JMS queue from("seda:dead").transform(exceptionMessage()).to("jms:queue:dead");
Here we only store the original cause error message in the transform. You can, however, use any Expression to send whatever you like. For example, you can invoke a method on a Bean or use a custom processor.
See Also
JPA Component
The jpa component enables you to store and retrieve Java objects from persistent storage using EJB 3's Java Persistence Architecture (JPA), which is a standard interface layer that wraps Object/Relational Mapping (ORM) products such as OpenJPA, Hibernate, TopLink, and so on.
Sending to the endpoint
You can store a Java entity bean in a database by sending it to a JPA producer endpoint. The body of the In message is assumed to be an entity bean (that is, a POJO with an @Entity annotation on it).
If the body does not contain an entity bean, put a Message Translator in front of the endpoint to perform the necessary conversion first.
Consuming from the endpoint
Consuming messages from a JPA consumer endpoint removes (or updates) entity beans in the database. This allows you to use a database table as a logical queue: consumers take messages from the queue and then delete/update them to logically remove them from the queue.
If you do not wish to delete the entity bean when it has been processed, you can specify consumeDelete=false on the URI. This will result in the entity being processed each poll.
If you would rather perform some update on the entity to mark it as processed (such as to exclude it from a future query) then you can annotate a method with @Consumed which will be invoked on your entity bean when the entity bean is consumed.
URI format
jpa:[entityClassName][?options]
For sending to the endpoint, the entityClassName is optional. If specified, it helps the Type Converter to ensure the body is of the correct type.
For consuming, the entityClassName is mandatory.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| entityType | entityClassName | Overrides the entityClassName from the URI. |
| persistenceUnit | camel | The JPA persistence unit used by default. |
| consumeDelete | true | JPA consumer only: If true, the entity is deleted after it is consumed; if false, the entity is not deleted. |
| consumeLockEntity | true | JPA consumer only: Specifies whether or not to set an exclusive lock on each entity bean while processing the results from polling. |
| flushOnSend | true | JPA producer only: Flushes the EntityManager after the entity bean has been persisted. |
| maximumResults | -1 | JPA consumer only: Set the maximum number of results to retrieve on the Query. |
| transactionManager | null | Camel 1.6.1/2.0: Specifies the transaction manager to use. If none provided, Camel will use a JpaTransactionManager by default. Can be used to set a JTA transaction manager (for integration with an EJB container). |
| consumer.delay | 500 | JPA consumer only: Delay in milliseconds between each poll. |
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | JPA consumer only: Milliseconds before polling starts. |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | false | JPA consumer only: Set to true to use fixed delay between polls, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
| maxMessagesPerPoll | 0 | Camel 2.0: JPA consumer only: An integer value to define the maximum number of messages to gather per poll. By default, no maximum is set. Can be used to avoid polling many thousands of messages when starting up the server. Set a value of 0 or negative to disable. |
| consumer.query | JPA consumer only: To use a custom query when consuming data. | |
| consumer.namedQuery | JPA consumer only: To use a named query when consuming data. | |
| consumer.nativeQuery | JPA consumer only: To use a custom native query when consuming data. |
Message Headers
Camel adds the following message headers to the exchange:
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CamelJpaTemplate | JpaTemplate | Camel 2.0: The JpaTemplate object that is used to access the entity bean. You need this object in some situations, for instance in a type converter or when you are doing some custom processing. |
Configuring EntityManagerFactory
You can configure the JPA component to use a specific EntityManagerFactory instance. For example, you can instantiate a JPA component that references the myEMFactory entity manager factory, as follows:
<bean id="jpa" class="org.apache.camel.component.jpa.JpaComponent"> <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="myEMFactory"/> </bean>
Configuring TransactionManager
You can specify the TransactionManager instance used by the JPA component. For example, you can instantiate a JPA component that references the myTransactionManager transaction manager, as follows:
<bean id="jpa" class="org.apache.camel.component.jpa.JpaComponent"> <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="myEMFactory"/> <property name="transactionManager" ref="myTransactionManager"/> </bean>
Example
See Tracer Example for an example using JPA to store traced messages into a database.
See Also
JT/400 Component
The jt400 component allows you to exchanges messages with an AS/400 system using data queues. This components is only available in Camel 1.5 and above.
URI format
jt400://user:password@system/QSYS.LIB/LIBRARY.LIB/QUEUE.DTAQ[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
URI options
| Name | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ccsid | default system CCSID | Specifies the CCSID to use for the connection with the AS/400 system. |
| format | text | Specifies the data format for sending messages valid options are: text (represented by String) and binary (represented by byte[]) |
| consumer.delay | 500 | Delay in milliseconds between each poll. |
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | Milliseconds before polling starts. |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | false | true to use fixed delay between polls, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
Usage
When configured as a consumer endpoint, the endpoint will poll a data queue on a remote system. For every entry on the data queue, a new Exchange is sent with the entry's data in the In message's body, formatted either as a String or a byte[], depending on the format. For a provider endpoint, the In message body contents will be put on the data queue as either raw bytes or text.
Example
In the snippet below, the data for an exchange sent to the direct:george endpoint will be put in the data queue PENNYLANE in library BEATLES on a system named LIVERPOOL.
Another user connects to the same data queue to receive the information from the data queue and forward it to the mock:ringo endpoint.
public class Jt400RouteBuilder extends RouteBuilder { @Override public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:george").to("jt400://GEORGE:EGROEG@LIVERPOOL/QSYS.LIB/BEATLES.LIB/PENNYLANE.DTAQ"); from("jt400://RINGO:OGNIR@LIVERPOOL/QSYS.LIB/BEATLES.LIB/PENNYLANE.DTAQ").to("mock:ringo"); } }
See Also
LDAP Component
The ldap component allows you to perform searches in LDAP servers using filters as the message payload.
This component uses standard JNDI (javax.naming package) to access the server.
URI format
ldap:ldapServerBean[?options]
The ldapServerBean portion of the URI refers to a DirContext bean in the registry. The LDAP component only supports producer endpoints, which means that an ldap URI cannot appear in the from at the start of a route.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| base | ou=system | The base DN for searches. |
| scope | subtree | Specifies how deeply to search the tree of entries, starting at the base DN. Value can be object, onelevel, or subtree. |
Result
The result is returned in the Out body as a ArrayList<javax.naming.directory.SearchResult> object.
DirContext
The URI, ldap:ldapserver, references a Spring bean with the ID, ldapserver. The ldapserver bean may be defined as follows:
<bean id="ldapserver" class="javax.naming.directory.InitialDirContext" scope="prototype"> <constructor-arg> <props> <prop key="java.naming.factory.initial">com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory</prop> <prop key="java.naming.provider.url">ldap://localhost:10389</prop> <prop key="java.naming.security.authentication">none</prop> </props> </constructor-arg> </bean>
The preceding example declares a regular Sun based LDAP DirContext that connects anonymously to a locally hosted LDAP server.
DirContext objects are not required to support concurrency by contract. It is therefore important that the directory context is declared with the setting, scope="prototype", in the bean definition or that the context supports concurrency. In the Spring framework, prototype scoped objects are instantiated each time they are looked up. |
Camel 1.6.1 and Camel 2.0 include a fix to support concurrency for LDAP producers. ldapServerBean contexts are now looked up each time a request is sent to the LDAP server. In addition, the contexts are released as soon as the producer completes. |
Samples
Following on from the Spring configuration above, the code sample below sends an LDAP request to filter search a group for a member. The Common Name is then extracted from the response.
ProducerTemplate<Exchange> template = exchange
.getContext().createProducerTemplate();
Collection<?> results = (Collection<?>) (template
.sendBody(
"ldap:ldapserver?base=ou=mygroup,ou=groups,ou=system",
"(member=uid=huntc,ou=users,ou=system)"));
if (results.size() > 0) {
// Extract what we need from the device's profile
Iterator<?> resultIter = results.iterator();
SearchResult searchResult = (SearchResult) resultIter
.next();
Attributes attributes = searchResult
.getAttributes();
Attribute deviceCNAttr = attributes.get("cn");
String deviceCN = (String) deviceCNAttr.get();
...
If no specific filter is required - for example, you just need to look up a single entry - specify a wildcard filter expression. For example, if the LDAP entry has a Common Name, use a filter expression like:
(cn=*)
See Also
Log Component
The log: component logs message exchanges to the underlying logging mechanism.
Camel uses commons-logging which allows you to configure logging via
- Log4j
- JDK 1.4 logging
- Avalon
- SimpleLog - a simple provider in commons-logging
Refer to the commons-logging user guide for a more complete overview of how to use and configure commons-logging.
URI format
log:loggingCategory[?options]
Where loggingCategory is the name of the logging category to use. You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
For example, a log endpoint typically specifies the logging level using the level option, as follows:
log:org.apache.camel.example?level=DEBUG
The default logger logs every exchange (regular logging). But Camel also ships with the Throughput logger, which is used whenever the groupSize option is specified.
Options
| Option | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| level | INFO | String | Logging level to use. Possible values: FATAL, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE, OFF |
| groupSize | null | Integer | An integer that specifies a group size for throughput logging. By default, regular logging is used. |
Formatting
The log formats the execution of exchanges to log lines.
By default, the log uses LogFormatter to format the log output, where LogFormatter has the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| showAll | false | Quick option for turning all options on. |
| showExchangeId | false | Show the unique exchange ID. |
| showProperties | false | Show the exchange properties. |
| showHeaders | false | Show the In message headers. |
| showBodyType | true | Show the In body Java type. |
| showBody | true | Show the In body. |
| showOut | false | If the exchange has an Out message, show the Out message. |
| showException | false | Camel 2.0: If the exchange has an exception, show the exception message (no stack trace). |
| showCaughtException | false | Camel 2.0: If the exchange has a caught exception, show the exception message (no stack trace). A caught exception is stored as a property on the exchange and for instance a doCatch can catch exceptions. See Try Catch Finally. |
| showStackTrace | false | Camel 2.0: Show the stack trace, if an exchange has an exception. |
| showFuture | false | Camel 2.1: Whether Camel should show java.util.concurrent.Future bodies or not. If enabled Camel could potentially wait until the Future task is done. Will by default not wait. |
| multiline | false | If true, each piece of information is logged on a new line. |
| maxChars | Camel 2.0: Limits the number of characters logged per line. |
Regular logger sample
In the route below we log the incoming orders at DEBUG level before the order is processed:
from("activemq:orders").to("log:com.mycompany.order?level=DEBUG").to("bean:processOrder");
Or using Spring XML to define the route:
<route> <from uri="activemq:orders"/> <to uri="log:com.mycompany.order?level=DEBUG"/> <to uri="bean:processOrder"/> </route>
Regular logger with formatter sample
In the route below we log the incoming orders at INFO level before the order is processed.
from("activemq:orders"). to("log:com.mycompany.order?showAll=true&multiline=true").to("bean:processOrder");
Throughput logger sample
In the route below we log the throughput of the incoming orders at DEBUG level grouped by 10 messages.
from("activemq:orders"). to("log:com.mycompany.order?level=DEBUG?groupSize=10").to("bean:processOrder");
See Also
Mail Component
The mail component provides access to Email via Spring's Mail support and the underlying JavaMail system.
| Classpath issue If you have trouble with sending mails that, for instance, don't contain any subject, have wrong recipients, or manifest other unforeseen errors, it could be due to having geronimo-javamail_1.4_spec-1.3.jar in your classpath. This was the culprit in a long bug hunt reported in CAMEL-869. |
| Geronimo mail .jar We have discovered that the geronimo mail .jar (v1.6) has a bug when polling mails with attachments. It cannot correctly identify the Content-Type. So, if you attach a .jpeg file to a mail and you poll it, the Content-Type is resolved as text/plain and not as image/jpeg. For that reason, we have added an org.apache.camel.component.ContentTypeResolver SPI interface which enables you to provide your own implementation and fix this bug by returning the correct Mime type based on the file name. So if the file name ends with jpeg/jpg, you can return image/jpeg. You can set your custom resolver on the MailComponent instance or on the MailEndpoint instance. This feature is added in Camel 1.6.2/2.0. |
| POP3 or IMAP POP3 has some limitations and end users are encouraged to use IMAP if possible. |
URI format
Mail endpoints can have one of the following URI formats (for the protocols, SMTP, POP3, or IMAP, respectively):
smtp://[username@]host[:port][?options] pop3://[username@]host[:port][?options] imap://[username@]host[:port][?options]
The mail component also supports secure variants of these protocols (layered over SSL). You can enable the secure protocols by adding s to the scheme:
smtps://[username@]host[:port][?options] pop3s://[username@]host[:port][?options] imaps://[username@]host[:port][?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Sample endpoints
Typically, you specify a URI with login credentials as follows (taking SMTP as an example):
smtp://[username@]host[:port][?password=somepwd]
Alternatively, it is possible to specify both the user name and the password as query options:
smtp://host[:port]?password=somepwd&username=someuser
For example:
smtp://mycompany.mailserver:30?password=tiger&username=scott
Default ports
As of Camel 1.4, default port numbers are supported. If the port number is omitted, Camel determines the port number to use based on the protocol.
| Protocol | Default Port Number |
|---|---|
| SMPT | 25 |
| SMPTS | 465 |
| POP3 | 110 |
| POP3S | 995 |
| IMAP | 143 |
| IMAPS | 993 |
Options
| Property | Default | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| host | The host name or IP address to connect to. | |||
| port | See DefaultPorts | The TCP port number to connect on. | ||
| username | The user name on the email server. | |||
| password | null | The password on the email server. | ||
| ignoreUriScheme | false | If false, Camel uses the scheme to determine the transport protocol (POP, IMAP, SMTP etc.) | ||
| defaultEncoding | null | The default encoding to use for Mime Messages. | ||
| contentType | text/plain | New option in Camel 1.5. The mail message content type. Use text/html for HTML mails. | ||
| folderName | INBOX | The folder to poll. | ||
| destination | username@host | @deprecated Use the to option instead. The TO recipients (receivers of the email). | ||
| to | username@host | As of Camel 1.4, the TO recipients (the receivers of the mail). Separate multiple email addresses with a comma. | ||
| CC | null | As of Camel 1.4, the CC recipients (the receivers of the mail). Separate multiple email addresses with a comma. | ||
| BCC | null | As of Camel 1.4, the BCC recipients (the receivers of the mail). Separate multiple email addresses with a comma. | ||
| from | camel@localhost | The FROM email address. | ||
| deleteProcessedMessages | true/false | Deletes the messages after they have been processed. This is done by setting the DELETED flag on the mail message. If false, the SEEN flag is set instead. As of Camel 1.5, the default setting is false. | ||
| delete | false | Camel 2.0: Deletes the messages after they have been processed. This is done by setting the DELETED flag on the mail message. If false, the SEEN flag is set instead. | ||
| processOnlyUnseenMessages | false/true | As of Camel 1.4, it is possible to configure a consumer endpoint so that it processes only unseen messages (that is, new messages) or all messages. Note that Camel always skips deleted messages. Setting this option to true will filter to only unseen messages. As of Camel 1.5, the default setting is true. POP3 does not support the SEEN flag, so this option is not supported in POP3; use IMAP instead. | ||
| unseen | true | Camel 2.0: Is used to fetch only unseen messages (that is, new messages). Note that POP3 does not support the SEEN flag; use IMAP instead. | ||
| fetchSize | -1 | As of Camel 1.4, this option sets the maximum number of messages to consume during a poll. This can be used to avoid overloading a mail server, if a mailbox folder contains a lot of messages. Default value of -1 means no fetch size and all messages will be consumed. Setting the value to 0 is a special corner case, where Camel will not consume any messages at all. | ||
| alternateBodyHeader | mail_alternateBody | Camel 1.6.1: Specifies the key to an IN message header that contains an alternative email body. For example, if you send emails in text/html format and want to provide an alternative mail body for non-HTML email clients, set the alternative mail body with this key as a header. In Camel 2.0, this option has been renamed to alternativeBodyHeader. | ||
| alternativeBodyHeader | CamelMailAlternativeBody | Camel 2.0: Specifies the key to an IN message header that contains an alternative email body. For example, if you send emails in text/html format and want to provide an alternative mail body for non-HTML email clients, set the alternative mail body with this key as a header. | ||
| debugMode | false | As of Camel 1.4, it is possible to enable debug mode on the underlying mail framework. The SUN Mail framework logs the debug messages to System.out by default. | ||
| connectionTimeout | 30000 | As of Camel 1.4, the connection timeout can be configured in milliseconds. Default is 30 seconds. | ||
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | Milliseconds before the polling starts. | ||
| consumer.delay | 60000 | As of Camel 1.4, the default consumer delay is now 60 seconds. Camel will therefore only poll the mailbox once a minute to avoid overloading the mail server. The default value in Camel 1.3 is 500 milliseconds. | ||
| consumer.useFixedDelay | false | Set to true to use a fixed delay between polls, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. | ||
| mail.XXX | null | As of Camel 2.0, you can set any additional java mail properties. For instance if you want to set a special property when using POP3 you can now provide the option directly in the URI such as: mail.pop3.forgettopheaders=true. You can set multiple such options, for example: mail.pop3.forgettopheaders=true&mail.mime.encodefilename=true. | ||
| maxMessagesPerPoll | 0 | Camel 2.0: Specifies the maximum number of messages to gather per poll. By default, no maximum is set. Can be used to set a limit of e.g. 1000 to avoid downloading thousands of files when the server starts up. Set a value of 0 or negative to disable this option. | ||
| javaMailSender | null | Camel 2.0: Specifies a pluggable org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender instance in order to use a custom email implementation. If none provided, Camel uses the default, org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl. | ||
| dummyTrustManager | false | As of Camel 1.4, when testing SSL connections, you can enable the dummy trust manager by setting this option to true. When the dummy trust manager is enabled, the mail client skips the server certificate check.
| ||
| ignoreUnsupportedCharset | false | Camel 2.0: Option to let Camel ignore unsupported charset in the local JVM when sending mails. If the charset is unsupported then charset=XXX (where XXX represents the unsupported charset) is removed from the content-type and it relies on the platform default instead. |
SSL support
The underlying mail framework is responsible for providing SSL support. Camel uses SUN JavaMail, which only trusts certificates issued by well known Certificate Authorities. So if you issue your own certificate, you have to import it into the local Java keystore file (see SSLNOTES.txt in JavaMail for details).
Defaults changed in Camel 1.4
As of Camel 1.4 the default consumer delay is now 60 seconds. Camel will therefore only poll the mailbox once a minute to avoid overloading the mail server. The default value in Camel 1.3 is 500 milliseconds.
Defaults changed in Camel 1.5
In Camel 1.5 the following default options have changed:
- deleteProcessedMessages is now false, as we felt Camel should not delete mails on the mail server by default.
- processOnlyUnseenMessages is now true, as we felt Camel should only poll new mails by default.
Mail Message Content
Camel uses the message exchange's IN body as the MimeMessage text content. The body is converted to String.class.
Camel copies all of the exchange's IN headers to the MimeMessage headers.
The subject of the MimeMessage can be configured using a header property on the IN message. The code below demonstrates this:
from("direct:a").setHeader("subject", constant(subject)).to("smtp://james2@localhost");
The same applies for other MimeMessage headers such as recipients, so you can use a header property as To:
Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("To", "davsclaus@apache.org"); map.put("From", "jstrachan@apache.org"); map.put("Subject", "Camel rocks"); String body = "Hello Claus.\nYes it does.\n\nRegards James."; template.sendBodyAndHeaders("smtp://davsclaus@apache.org", body, map);
Headers take precedence over pre-configured recipients
From Camel 1.5 onwards, the recipients specified in the message headers always take precedence over recipients pre-configured in the endpoint URI. The idea is that if you provide any recipients in the message headers, that is what you get. The recipients pre-configured in the endpoint URI are treated as a fallback.
In the sample code below, the email message is sent to davsclaus@apache.org, because it takes precedence over the pre-configured recipient, info@mycompany.com. Any CC and BCC settings in the endpoint URI are also ignored and those recipients will not receive any mail. The choice between headers and pre-configured settings is all or nothing: the mail component either takes the recipients exclusively from the headers or exclusively from the pre-configured settings. It is not possible to mix and match headers and pre-configured settings.
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<String, Object>();
headers.put("to", "davsclaus@apache.org");
template.sendBodyAndHeaders("smtp://admin@localhost?to=info@mycompany.com", "Hello World", headers);
Multiple recipients for easier configuration
As of Camel 1.5, it is possible to set multiple recipients using a comma-separated or a semicolon-separated list. This applies both to header settings and to settings in an endpoint URI. For example:
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<String, Object>();
headers.put("to", "davsclaus@apache.org ; jstrachan@apache.org ; ningjiang@apache.org");
The preceding example uses a semicolon, ;, as the separator character.
Setting sender name and email
You can specify recipients in the format, name <email>, to include both the name and the email address of the recipient.
For example, you define the following headers on the a Message:
Map headers = new HashMap(); map.put("To", "Claus Ibsen <davsclaus@apache.org>"); map.put("From", "James Strachan <jstrachan@apache.org>"); map.put("Subject", "Camel is cool");
SUN JavaMail
SUN JavaMail is used under the hood for consuming and producing mails.
We encourage end-users to consult these references when using either POP3 or IMAP protocol. Note particularly that POP3 has a much more limited set of features than IMAP.
- SUN POP3 API
- SUN IMAP API
- And generally about the MAIL Flags
Samples
We start with a simple route that sends the messages received from a JMS queue as emails. The email account is the admin account on mymailserver.com.
from("jms://queue:subscription").to("smtp://admin@mymailserver.com?password=secret");
In the next sample, we poll a mailbox for new emails once every minute. Notice that we use the special consumer option for setting the poll interval, consumer.delay, as 60000 milliseconds = 60 seconds.
from("imap://admin@mymailserver.com?password=secret&processOnlyUnseenMessages=true&consumer.delay=60000").to("seda://mails");
In this sample we want to send a mail to multiple recipients. This feature was introduced in camel 1.4:
// all the recipients of this mail are: // To: camel@riders.org , easy@riders.org // CC: me@you.org // BCC: someone@somewhere.org String recipients = "&To=camel@riders.org,easy@riders.org&CC=me@you.org&BCC=someone@somewhere.org"; from("direct:a").to("smtp://you@mymailserver.com?password=secret&From=you@apache.org" + recipients);
Sending mail with attachment sample
| Attachments are not support by all Camel components The Attachments API is based on the Java Activation Framework and is generally only used by the Mail API. Since many of the other Camel components do not support attachments, the attachments could potentially be lost as they propagate along the route. The rule of thumb, therefore, is to add attachments just before sending a message to the mail endpoint. |
The mail component supports attachments, which is a feature that was introduced in Camel 1.4. In the sample below, we send a mail message containing a plain text message with a logo file attachment.
// create an exchange with a normal body and attachment to be produced as email Endpoint endpoint = context.getEndpoint("smtp://james@mymailserver.com?password=secret"); // create the exchange with the mail message that is multipart with a file and a Hello World text/plain message. Exchange exchange = endpoint.createExchange(); Message in = exchange.getIn(); in.setBody("Hello World"); in.addAttachment("logo.jpeg", new DataHandler(new FileDataSource("src/test/data/logo.jpeg"))); // create a producer that can produce the exchange (= send the mail) Producer producer = endpoint.createProducer(); // start the producer producer.start(); // and let it go (processes the exchange by sending the email) producer.process(exchange);
SSL sample
In this sample, we want to poll our Google mail inbox for mails. To download mail onto a local mail client, Google mail requires you to enable and configure SSL. This is done by logging into your Google mail account and changing your settings to allow IMAP access. Google have extensive documentation on how to do this.
from("imaps://imap.gmail.com?username=YOUR_USERNAME@gmail.com&password=YOUR_PASSWORD" + "&deleteProcessedMessages=false&processOnlyUnseenMessages=true&consumer.delay=60000").to("log:newmail");
The preceding route polls the Google mail inbox for new mails once every minute and logs the received messages to the newmail logger category.
Running the sample with DEBUG logging enabled, we can monitor the progress in the logs:
2008-05-08 06:32:09,640 DEBUG MailConsumer - Connecting to MailStore imaps//imap.gmail.com:993 (SSL enabled), folder=INBOX 2008-05-08 06:32:11,203 DEBUG MailConsumer - Polling mailfolder: imaps//imap.gmail.com:993 (SSL enabled), folder=INBOX 2008-05-08 06:32:11,640 DEBUG MailConsumer - Fetching 1 messages. Total 1 messages. 2008-05-08 06:32:12,171 DEBUG MailConsumer - Processing message: messageNumber=[332], from=[James Bond <007@mi5.co.uk>], to=YOUR_USERNAME@gmail.com], subject=[... 2008-05-08 06:32:12,187 INFO newmail - Exchange[MailMessage: messageNumber=[332], from=[James Bond <007@mi5.co.uk>], to=YOUR_USERNAME@gmail.com], subject=[...
Consuming mails with attachment sample
In this sample we poll a mailbox and store all attachments from the mails as files. First, we define a route to poll the mailbox. As this sample is based on google mail, it uses the same route as shown in the SSL sample:
from("imaps://imap.gmail.com?username=YOUR_USERNAME@gmail.com&password=YOUR_PASSWORD" + "&deleteProcessedMessages=false&processOnlyUnseenMessages=true&consumer.delay=60000").process(new MyMailProcessor());
Instead of logging the mail we use a processor where we can process the mail from java code:
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
// the API is a bit clunky so we need to loop
Map<String, DataHandler> attachments = exchange.getIn().getAttachments();
if (attacments.size() > 0) {
for (String name : attachments.keySet()) {
DataHandler dh = attachments.get(name);
// get the file name
String filename = dh.getName();
// get the content and convert it to byte[]
byte[] data = exchange.getContext().getTypeConverter().convertTo(byte[].class, dh.getInputStream());
// write the data to a file
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filename);
out.write(data);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
}
As you can see the API to handle attachments is a bit clunky but it's there so you can get the javax.activation.DataHandler so you can handle the attachments using standard API.
See Also
MINA Component
The mina: component is a transport for working with Apache MINA
URI format
mina:tcp://hostname[:port][?options] mina:udp://hostname[:port][?options] mina:multicast://hostname[:port][?options] mina:vm://hostname[:port][?options]
From Camel 1.3 onwards you can specify a codec in the Registry using the codec option. If you are using TCP and no codec is specified then the textline flag is used to determine if text line based codec or object serialization should be used instead. By default the object serialization is used.
For UDP/Multicast if no codec is specified the default uses a basic ByteBuffer based codec.
Multicast also has a shorthand notation mcast.
The VM protocol is used as a direct forwarding mechanism in the same JVM. See the MINA VM-Pipe API documentation for details.
A Mina producer has a default timeout value of 30 seconds, while it waits for a response from the remote server.
In normal use, camel-mina only supports marshalling the body content—message headers and exchange properties are not sent.
However, the option, transferExchange, does allow you to transfer the exchange itself over the wire. See options below.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| codec | null | As of 1.3, you can refer to a named ProtocolCodecFactory instance in your Registry such as your Spring ApplicationContext, which is then used for the marshalling. |
| codec | null | Camel 2.0: You must use the # notation to look up your codec in the Registry. For example, use #myCodec to look up a bean with the id value, myCodec. |
| textline | false | Only used for TCP. If no codec is specified, you can use this flag in 1.3 or later to indicate a text line based codec; if not specified or the value is false, then Object Serialization is assumed over TCP. |
| textlineDelimiter | DEFAULT | Camel 1.5.1/2.0 Only used for TCP and if textline=true. Sets the text line delimiter to use. Possible values are: DEFAULT, AUTO, WINDOWS, UNIX or MAC. If none provided, Camel will use DEFAULT. This delimiter is used to mark the end of text. |
| sync | false/true | As of 1.3, you can configure the exchange pattern to be either InOnly (default) or InOut. Setting sync=true means a synchronous exchange (InOut), where the client can read the response from MINA (the exchange Out message). The default value has changed in Camel 1.5 to true. In older releases, the default value is false. |
| lazySessionCreation | See description | As of 1.3, sessions can be lazily created to avoid exceptions, if the remote server is not up and running when the Camel producer is started. From Camel 2.0 onwards, the default is true. In Camel 1.x, the default is false. |
| timeout | 30000 | As of 1.3, you can configure the timeout that specifies how long to wait for a response from a remote server. The timeout unit is in milliseconds, so 60000 is 60 seconds. The timeout is only used for Mina producer. |
| encoding | JVM Default | As of 1.3, you can configure the encoding (a charset name) to use for the TCP textline codec and the UDP protocol. If not provided, Camel will use the JVM default Charset. |
| transferExchange | false | Only used for TCP. As of 1.3, you can transfer the exchange over the wire instead of just the body. The following fields are transferred: In body, Out body, fault body, In headers, Out headers, fault headers, exchange properties, exchange exception. This requires that the objects are serializable. Camel will exclude any non-serializable objects and log it at WARN level. |
| minaLogger | false | As of 1.3, you can enable the Apache MINA logging filter. Apache MINA uses slf4j logging at INFO level to log all input and output. |
| filters | null | As of 2.0, you can set a list of Mina IoFilters to register. The type must be List<org.apache.mina.common.IoFilter>. |
| encoderMaxLineLength | -1 | As of 2.1, you can set the textline protocol encoder max line length. By default the default value of Mina itself is used which are Integer.MAX_VALUE. |
| decorderMaxLineLength | -1 | As of 2.1, you can set the textline protocol decoder max line length. By default the default value of Mina itself is used which are 1024. |
| producerPoolSize | 16 | 1.6.2 (only in 1.6.x): The TCP producer is now thread safe and supports concurrency much better. This option allows you to configure the number of threads in its thread pool for concurrent producers. Note: Camel 2.0 have a pooled service which ensured it was already thread safe and supported concurrency already. So this is a special patch for 1.6.x. |
Default behavior changed
In Camel 2.0 the codec option must use # notation for lookup of the codec bean in the Registry.
In Camel 2.0 the lazySessionCreation option now defaults to true.
In Camel 1.5 the sync option has changed its default value from false to true, as we felt it was confusing for end-users when they used MINA to call remote servers and Camel wouldn't wait for the response.
In Camel 1.4 or later codec=textline is no longer supported. Use the textline=true option instead.
Using a custom codec
See the Mina documentation how to write your own codec. To use your custom codec with camel-mina, you should register your codec in the Registry; for example, by creating a bean in the Spring XML file. Then use the codec option to specify the bean ID of your codec. See HL7 that has a custom codec.
Sample with sync=false
In this sample, Camel exposes a service that listens for TCP connections on port 6200. We use the textline codec. In our route, we create a Mina consumer endpoint that listens on port 6200:
from("mina:tcp://localhost:6200?textline=true&sync=false").to("mock:result");
As the sample is part of a unit test, we test it by sending some data to it on port 6200.
MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Hello World"); template.sendBody("mina:tcp://localhost:6200?textline=true&sync=false", "Hello World"); assertMockEndpointsSatisfied();
Sample with sync=true
In the next sample, we have a more common use case where we expose a TCP service on port 6201 also use the textline codec. However, this time we want to return a response, so we set the sync option to true on the consumer.
from("mina:tcp://localhost:6201?textline=true&sync=true").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class); exchange.getOut().setBody("Bye " + body); } });
Then we test the sample by sending some data and retrieving the response using the template.requestBody() method. As we know the response is a String, we cast it to String and can assert that the response is, in fact, something we have dynamically set in our processor code logic.
String response = (String)template.requestBody("mina:tcp://localhost:6201?textline=true&sync=true", "World"); assertEquals("Bye World", response);
Sample with Spring DSL
Spring DSL can, of course, also be used for MINA. In the sample below we expose a TCP server on port 5555:
<route> <from uri="mina:tcp://localhost:5555?textline=true"/> <to uri="bean:myTCPOrderHandler"/> </route>
In the route above, we expose a TCP server on port 5555 using the textline codec. We let the Spring bean with ID, myTCPOrderHandler, handle the request and return a reply. For instance, the handler bean could be implemented as follows:
public String handleOrder(String payload) {
...
return "Order: OK"
}
Configuring Mina endpoints using Spring bean style
Available as of Camel 2.0
Configuration of Mina endpoints is now possible using regular Spring bean style configuration in the Spring DSL.
However, in the underlying Apache Mina toolkit, it is relatively difficult to set up the acceptor and the connector, because you can not use simple setters. To resolve this difficulty, we leverage the MinaComponent as a Spring factory bean to configure this for us. If you really need to configure this yourself, there are setters on the MinaEndpoint to set these when needed.
The sample below shows the factory approach:
<!-- Creating mina endpoints is a bit complex so we reuse MinaComponnet
as a factory bean to create our endpoint, this is the easiest to do -->
<bean id="myMinaFactory" class="org.apache.camel.component.mina.MinaComponent">
<!-- we must provide a camel context so we refer to it by its id -->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="myCamel"/>
</bean>
<!-- This is our mina endpoint configured with spring, we will use the factory above
to create it for us. The goal is to invoke the createEndpoint method with the
mina configuration parameter we defined using the constructor-arg option -->
<bean id="myMinaEndpoint"
factory-bean="myMinaFactory"
factory-method="createEndpoint">
<!-- and here we can pass it our configuration -->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="myMinaConfig"/>
</bean>
<!-- this is our mina configuration with plain properties -->
<bean id="myMinaConfig" class="org.apache.camel.component.mina.MinaConfiguration">
<property name="protocol" value="tcp"/>
<property name="host" value="localhost"/>
<property name="port" value="1234"/>
<property name="sync" value="false"/>
</bean>
And then we can refer to our endpoint directly in the route, as follows:
<route> <!-- here we route from or mina endpoint we have defined above --> <from ref="myMinaEndpoint"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route>
Closing Session When Complete
Available as of Camel 1.6.1
When acting as a server you sometimes want to close the session when, for example, a client conversion is finished. To instruct Camel to close the session, you should add a header with the key CamelMinaCloseSessionWhenComplete set to a boolean true value.
For instance, the example below will close the session after it has written the bye message back to the client:
from("mina:tcp://localhost:8080?sync=true&textline=true").process(new Processor() {
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
String body = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class);
exchange.getOut().setBody("Bye " + body);
exchange.getOut().setHeader(MinaConsumer.HEADER_CLOSE_SESSION_WHEN_COMPLETE, true);
}
});
Get the IoSession for message
Available since Camel 2.1
You can get the IoSession from the message header with this key MinaEndpoint.HEADER_MINA_IOSESSION, and also get the local host address with the key MinaEndpoint.HEADER_LOCAL_ADDRESS and remote host address with the key MinaEndpoint.HEADER_REMOTE_ADDRESS.
Configuring Mina filters
Available since Camel 2.0
Filters permit you to use some Mina Filters, such as SslFilter. You can also implement some customized filters. Please note that codec and logger are also implemented as Mina filters of type, IoFilter. Any filters you may define are appended to the end of the filter chain; that is, after codec and logger.
For instance, the example below will send a keep-alive message after 10 seconds of inactivity:
public class KeepAliveFilter extends IoFilterAdapter { @Override public void sessionCreated(NextFilter nextFilter, IoSession session) throws Exception { session.setIdleTime(IdleStatus.BOTH_IDLE, 10); nextFilter.sessionCreated(session); } @Override public void sessionIdle(NextFilter nextFilter, IoSession session, IdleStatus status) throws Exception { session.write("NOOP"); // NOOP is a FTP command for keep alive nextFilter.sessionIdle(session, status); } }
As Camel Mina may use a request-reply scheme, the endpoint as a client would like to drop some message, such as greeting when the connection is established. For example, when you connect to an FTP server, you will get a 220 message with a greeting (220 Welcome to Pure-FTPd). If you don't drop the message, your request-reply scheme will be broken.
public class DropGreetingFilter extends IoFilterAdapter { @Override public void messageReceived(NextFilter nextFilter, IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception { if (message instanceof String) { String ftpMessage = (String) message; // "220" is given as greeting. "200 Zzz" is given as a response to "NOOP" (keep alive) if (ftpMessage.startsWith("220") || or ftpMessage.startsWith("200 Zzz")) { // Dropping greeting return; } } nextFilter.messageReceived(session, message); } }
Then, you can configure your endpoint using Spring DSL:
<bean id="myMinaFactory" class="org.apache.camel.component.mina.MinaComponent"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="camelContext" /> </bean> <bean id="myMinaEndpoint" factory-bean="myMinaFactory" factory-method="createEndpoint"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="myMinaConfig"/> </bean> <bean id="myMinaConfig" class="org.apache.camel.component.mina.MinaConfiguration"> <property name="protocol" value="tcp" /> <property name="host" value="localhost" /> <property name="port" value="2121" /> <property name="sync" value="true" /> <property name="minaLogger" value="true" /> <property name="filters" ref="listFilters"/> </bean> <bean id="listFilters" class="java.util.ArrayList" > <constructor-arg> <list value-type="org.apache.mina.common.IoFilter"> <bean class="com.example.KeepAliveFilter"/> <bean class="com.example.DropGreetingFilter"/> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean>
See Also
Mock Component
Testing of distributed and asynchronous processing is notoriously difficult. The Mock, Test and DataSet endpoints work great with the Camel Testing Framework to simplify your unit and integration testing using Enterprise Integration Patterns and Camel's large range of Components together with the powerful Bean Integration.The Mock component provides a powerful declarative testing mechanism, which is similar to jMock in that it allows declarative expectations to be created on any Mock endpoint before a test begins. Then the test is run, which typically fires messages to one or more endpoints, and finally the expectations can be asserted in a test case to ensure the system worked as expected.
This allows you to test various things like:
- The correct number of messages are received on each endpoint,
- The correct payloads are received, in the right order,
- Messages arrive on an endpoint in order, using some Expression to create an order testing function,
- Messages arrive match some kind of Predicate such as that specific headers have certain values, or that parts of the messages match some predicate, such as by evaluating an XPath or XQuery Expression.
Note that there is also the Test endpoint which is a Mock endpoint, but which uses a second endpoint to provide the list of expected message bodies and automatically sets up the Mock endpoint assertions. In other words, it's a Mock endpoint that automatically sets up its assertions from some sample messages in a File or database, for example.
URI format
mock:someName[?options]
Where someName can be any string that uniquely identifies the endpoint.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reportGroup | null | A size to use a throughput logger for reporting |
Simple Example
Here's a simple example of Mock endpoint in use. First, the endpoint is resolved on the context. Then we set an expectation, and then, after the test has run, we assert that our expectations have been met.
MockEndpoint resultEndpoint = context.resolveEndpoint("mock:foo", MockEndpoint.class); resultEndpoint.expectedMessageCount(2); // send some messages ... // now lets assert that the mock:foo endpoint received 2 messages resultEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied();
You typically always call the assertIsSatisfied() method to test that the expectations were met after running a test.
Camel will by default wait 20 seconds when the assertIsSatisfied() is invoked. This can be configured by setting the setResultWaitTime(millis) method.
Setting expectations
You can see from the javadoc of MockEndpoint the various helper methods you can use to set expectations. The main methods are as follows:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| expectedMessageCount(int) | To define the expected message count on the endpoint. |
| expectedMinimumMessageCount(int) | To define the minimum number of expected messages on the endpoint. |
| expectedBodiesReceived(...) | To define the expected bodies that should be received (in order). |
| expectedHeaderReceived(...) | To define the expected header that should be received |
| expectsAscending(Expression) | To add an expectation that messages are received in order, using the given Expression to compare messages. |
| expectsDescending(Expression) | To add an expectation that messages are received in order, using the given Expression to compare messages. |
| expectsNoDuplicates(Expression) | To add an expectation that no duplicate messages are received; using an Expression to calculate a unique identifier for each message. This could be something like the JMSMessageID if using JMS, or some unique reference number within the message. |
Here's another example:
resultEndpoint.expectedBodiesReceived("firstMessageBody", "secondMessageBody", "thirdMessageBody");
Adding expectations to specific messages
In addition, you can use the message(int messageIndex) method to add assertions about a specific message that is received.
For example, to add expectations of the headers or body of the first message (using zero-based indexing like java.util.List), you can use the following code:
resultEndpoint.message(0).header("foo").isEqualTo("bar");
There are some examples of the Mock endpoint in use in the camel-core processor tests.
A Spring Example
First, here's the spring.xml file
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="file:src/test/data?noop=true"/> <filter> <xpath>/person/city = 'London'</xpath> <to uri="mock:matched"/> </filter> </route> </camelContext> <bean id="myBean" class="org.apache.camel.spring.mock.MyAssertions" scope="singleton"/>
As you can see, it defines a simple routing rule which consumes messages from the local src/test/data directory. The noop flag just means not to delete or move the file after its been processed.
Also note we instantiate a bean called myBean, here is the source of the MyAssertions bean.
public class MyAssertions implements InitializingBean { @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:matched") private MockEndpoint matched; @EndpointInject(uri = "mock:notMatched") private MockEndpoint notMatched; public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // lets add some expectations matched.expectedMessageCount(1); notMatched.expectedMessageCount(0); } public void assertEndpointsValid() throws Exception { // now lets perform some assertions that the test worked as we expect Assert.assertNotNull("Should have a matched endpoint", matched); Assert.assertNotNull("Should have a notMatched endpoint", notMatched); MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(matched, notMatched); } }
The bean is injected with a bunch of Mock endpoints using the @EndpointInject annotation, it then sets a bunch of expectations on startup (using Spring's InitializingBean interface and afterPropertiesSet() method) before the CamelContext starts up.
Then in our test case (which could be JUnit or TesNG) we lookup myBean in Spring (or have it injected into our test) and then invoke the assertEndpointsValid() method on it to verify that the mock endpoints have their assertions met. You could then inspect the message exchanges that were delivered to any of the endpoints using the getReceivedExchanges() method on the Mock endpoint and perform further assertions or debug logging.
Here is the actual JUnit test case we use.
See Also
MSV Component
The MSV component performs XML validation of the message body using the MSV Library and any of the supported XML schema languages, such as XML Schema or RelaxNG XML Syntax.
Note that the Jing component also supports RelaxNG Compact Syntax
URI format
msv:someLocalOrRemoteResource[?options]
Where someLocalOrRemoteResource is some URL to a local resource on the classpath or a full URL to a remote resource or resource on the file system. For example
msv:org/foo/bar.rng
msv:file:../foo/bar.rng
msv:http://acme.com/cheese.rng
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| useDom | true | Camel 2.0: Whether DOMSource/DOMResult or SaxSource/SaxResult should be used by the validator. Note: DOM must be used by the MSV component. |
Example
The following example shows how to configure a route from endpoint direct:start which then goes to one of two endpoints, either mock:valid or mock:invalid based on whether or not the XML matches the given RelaxNG XML Schema (which is supplied on the classpath).
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <doTry> <to uri="msv:org/apache/camel/component/validator/msv/schema.rng"/> <to uri="mock:valid"/> <doCatch> <exception>org.apache.camel.ValidationException</exception> <to uri="mock:invalid"/> </doCatch> <doFinally> <to uri="mock:finally"/> </doFinally> </doTry> </route> </camelContext>
See Also
Quartz Component
The quartz: component provides a scheduled delivery of messages using the Quartz scheduler.
Each endpoint represents a different timer (in Quartz terms, a Trigger and JobDetail).
| Using cron expressions Configuring the cron expression in Camel 1.x is based on path separators. We changed this to an URI option in Camel 2.0, allowing a more elegant configuration. |
URI format
quartz://timerName?options quartz://groupName/timerName?options quartz://groupName/timerName/cronExpression (@deprecated) quartz://groupName/timerName/?cron=expression (Camel 2.0) quartz://timerName?cron=expression (Camel 2.0)
The component uses either a CronTrigger or a SimpleTrigger. If no cron expression is provided, the component uses a simple trigger. If no groupName is provided, the quartz component uses the Camel group name.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cron | None | Specifies a cron expression (not compatible with the trigger.* or job.* options). |
| trigger.repeatCount | 0 | SimpleTrigger: How many times should the timer repeat? |
| trigger.repeatInterval | 0 | SimpleTrigger: The amount of time in milliseconds between repeated triggers. |
| job.name | null | Sets the job name. |
| job.XXX | null | Sets the job option with the XXX setter name. |
| trigger.XXX | null | Sets the trigger option with the XXX setter name. |
| stateful | false | Uses a Quartz StatefulJob instead of the default job. |
For example, the following routing rule will fire two timer events to the mock:results endpoint:
from("quartz://myGroup/myTimerName?trigger.repeatInterval=2&trigger.repeatCount=1").to("mock:result");
When using a StatefulJob, the JobDataMap is re-persisted after every execution of the job, thus preserving state for the next execution.
Message Headers
Camel adds the getters from the Quartz Execution Context as header values. The following headers are added:
calendar, fireTime, jobDetail, jobInstance, jobRuntTime, mergedJobDataMap, nextFireTime, previousFireTime, refireCount, result, scheduledFireTime, scheduler, trigger, triggerName, triggerGroup.
The fireTime header contains the java.util.Date of when the exchange was fired.
Using Cron Triggers
Avaiable as of Camel 2.0
Quartz supports Cron-like expressions for specifying timers in a handy format. You can use these expressions in the cron URI parameter; though to preserve valid URI encoding we allow + to be used instead of spaces. Quartz provides a little tutorial on how to use cron expressions.
For example the following will fire a message at 12pm (noon) every day
from("quartz://myGroup/myTimerName?cron=0+0/5+12-18+?+*+MON-FRI").to("activemq:Totally.Rocks");
which is equivalent to using the cron expression
0 0/5 12-18 ? * MON-FRI
The following table shows the URI character encodings we use to preserve valid URI syntax:
| URI Character | Cron character |
|---|---|
| + | Space |
Using Cron Triggers in Camel 1.x
@deprecated
Quartz supports Cron-like expressions for specifying timers in a handy format. You can use these expressions in the URI; though to preserve valid URI encoding we allow / to be used instead of spaces and $ to be used instead of ?.
For example, the following endpoint URI will fire a message at 12pm (noon) every day
from("quartz://myGroup/myTimerName/0/0/12/*/*/$").to("activemq:Totally.Rocks");
which is equivalent to using the cron expression
0 0 12 * * ?
The following table shows the URI character encodings we use to preserve valid URI syntax:
| URI Character | Cron character |
|---|---|
| / | Space |
| $ | ? |
See Also
Printer Component
Available as of Camel 2.1
The printer component provides a way to direct payloads on a route to a printer. Obviously the payload has to be a formatted piece of payload in order for the component to appropriately print it. The objective is to be able to direct specific payloads as jobs to a line printer in a camel flow.
This component only supports a camel producer endpoint.
The functionality allows for the payload to be printed on a default printer, named local, remote or wirelessly linked printer using the javax printing API under the covers.
URI format
Since the URI scheme for a printer has not been standardized (the nearest thing to a standard being the IETF print standard) and therefore not uniformly applied by vendors, we have chosen "lpr" as the scheme.
lpr://localhost/default[?options] lpr://remotehost:port/path/to/printer[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mediaSize | MediaSizeName.NA_LETTER | Sets the stationary as defined by enumeration settings in the javax.print.attribute.standard.MediaSizeName API. The default setting is to use North American Letter sized stationary |
| copies | 1 | Sets number of copies based on the javax.print.attribute.standard.Copies API |
| sides | Sides.ONE_SIDED | Sets one sided or two sided printing based on the javax.print.attribute.standard.Sides API |
| flavor | DocFlavor.BYTE_ARRAY | Sets DocFlavor based on the javax.print.DocFlavor API |
| mimeType | AUTOSENSE | Sets mimeTypes supported by the javax.print.DocFlavor API |
Sending Messages to a Printer
Printer Producer
Sending data to the printer is very straightforward and involves creating a producer endpoint that can be sent message exchanges on in route.
Usage Samples
Example 1: Printing text based payloads on a Default printer using letter stationary and one-sided mode
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from(file://inputdir/?delete=true) .to("lpr://localhost/default?copies=2" + "&flavor=DocFlavor.INPUT_STREAM&" + "&mimeType=AUTOSENSE" + "&mediaSize=na-letter" + "&sides=one-sided") }};
Example 2: Printing GIF based payloads on a Remote printer using A4 stationary and one-sided mode
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from(file://inputdir/?delete=true) .to("lpr://remotehost/sales/salesprinter" + "?copies=2&sides=one-sided" + "&mimeType=GIF&mediaSize=iso-a4" + "&flavor=DocFlavor.INPUT_STREAM") }};
Example 3: Printing JPEG based payloads on a Remote printer using Japanese Postcard stationary and one-sided mode
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from(file://inputdir/?delete=true) .to("lpr://remotehost/sales/salesprinter" + "?copies=2&sides=one-sided" + "&mimeType=JPEG" + "&mediaSize=japanese-postcard" + "&flavor=DocFlavor.INPUT_STREAM") }};
Ref Component
The ref: component is used for lookup of existing endpoints bound in the Registry.
URI format
ref:someName
Where someName is the name of an endpoint in the Registry (usually, but not always, the Spring registry). If you are using the Spring registry, someName would be the bean ID of an endpoint in the Spring registry.
Runtime lookup
This component can be used when you need dynamic discovery of endpoints in the Registry where you can compute the URI at runtime. Then you can look up the endpoint using the following code:
// lookup the endpoint String myEndpointRef = "bigspenderOrder"; Endpoint endpoint = context.getEndpoint("ref:" + myEndpointRef); Producer producer = endpoint.createProducer(); Exchange exchange = producer.createExchange(); exchange.getIn().setBody(payloadToSend); // send the exchange producer.process(exchange); ...
And you could have a list of endpoints defined in the Registry such as:
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <endpoint id="normalOrder" uri="activemq:order.slow"/> <endpoint id="bigspenderOrder" uri="activemq:order.high"/> ... </camelContext>
Sample
In the sample below we use the ref: in the URI to reference the endpoint with the spring ID, endpoint2:
<bean id="mybean" class="org.apache.camel.spring.example.DummyBean"> <property name="endpoint" ref="endpoint1"/> </bean> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <endpoint id="endpoint1" uri="direct:start"/> <endpoint id="endpoint2" uri="mock:end"/> <route> <from ref="endpoint1"/> <to uri="ref:endpoint2"/> </route> </camelContext>
You could, of course, have used the ref attribute instead:
<to ref="endpoint2"/>
Which is the more common way to write it.
See Also
Restlet Component
The Restlet component provides Restlet based endpoints for consuming and producing RESTful resources.
URI format
restlet:restletUrl[?options]
Format of restletUrl:
protocol://hostname[:port][/resourcePattern]
Restlet promotes decoupling of protocol and application concerns. The reference implementation of Restlet Engine supports a number of protocols. However, we have tested the HTTP protocol only. The default port is port 80. We do not automatically switch default port based on the protocol yet.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| headerFilterStrategy=#refName (2.x or later) | An instance of RestletHeaderFilterStrategy | Use the # notation (headerFilterStrategy=#refName) to reference a header filter strategy in the Camel Registry. The strategy will be plugged into the restlet binding if it is HeaderFilterStrategyAware. |
| restletBindingRef (1.x), restletBinding=#refName (2.x or later) | An instance of DefaultRestletBinding | The bean ID of a RestletBinding object in the Camel Registry. |
| restletMethod | GET | On a producer endpoint, specifies the request method to use. On a consumer endpoint, specifies that the endpoint consumes only restletMethod requests. The string value is converted to org.restlet.data.Method by the Method.valueOf(String) method. |
| restletMethods (2.x or later) | None | Consumer only Specify one or more methods separated by commas (e.g. restletMethods=post,put) to be serviced by a restlet consumer endpoint. If both restletMethod and restletMethods options are specified, the restletMethod setting is ignored. |
| restletRealmRef (1.x), restletRealm=#refName (2.x or later) | null | The bean ID of the Realm Map in the Camel Registry. |
| restletUriPatterns=#refName (2.x or later) | None | Consumer only Specify one ore more URI templates to be serviced by a restlet consumer endpoint, using the # notation to reference a List<String> in the Camel Registry. If a URI pattern has been defined in the endpoint URI, both the URI pattern defined in the endpoint and the restletUriPatterns option will be honored. |
Message Headers
Camel 1.x
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.restlet.auth.login | String | Login name for basic authentication. It is set on the IN message by the application and gets filtered before the restlet request header by Camel. |
| org.apache.camel.restlet.auth.password | String | Password name for basic authentication. It is set on the IN message by the application and gets filtered before the restlet request header by Camel. |
| org.apache.camel.restlet.mediaType | String | Specifies the content type, which can be set on the OUT message by the application/processor. The value is the content-type of the response message. If this header is not set, the content-type is set based on the object type of the OUT message body. |
| org.apache.camel.restlet.queryString | String | The query string of the request URI. It is set on the IN message by DefaultRestletBinding when the restlet component receives a request. |
| org.apache.camel.restlet.responseCode | String or Integer | The response code can be set on the OUT message by the application/processor. The value is the response code of the response message. If this header is not set, the response code is set by the restlet runtime engine. |
| org.restlet.* | Attributes of a restlet message that get propagated to Camel IN headers. |
Camel 2.0
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CamelContentType | String | Specifies the content type, which can be set on the OUT message by the application/processor. The value is the content-type of the response message. If this header is not set, the content-type is based on the object type of the OUT message body. |
| CamelHttpMethod | String | The HTTP request method. This is set in the IN message header. |
| CamelHttpQuery | String | The query string of the request URI. It is set on the IN message by DefaultRestletBinding when the restlet component receives a request. |
| CamelHttpRsponseCode | String or Integer | The response code can be set on the OUT message by the application/processor. The value is the response code of the response message. If this header is not set, the response code is set by the restlet runtime engine. |
| CamelHttpUri | String | The HTTP request URI. This is set in the IN message header. |
| CamelRestletLogin | String | Login name for basic authentication. It is set on the IN message by the application and gets filtered before the restlet request header by Camel. |
| CamelRestletPassword | String | Password name for basic authentication. It is set on the IN message by the application and gets filtered before the restlet request header by Camel. |
| org.restlet.* | Attributes of a Restlet message that get propagated to Camel IN headers. |
Message Body
Camel will store the restlet response from the external server on the OUT body. All headers from the IN message will be copied to the OUT message, so that headers are preserved during routing.
Samples
Restlet Endpoint with Authentication
The following route starts a restlet consumer endpoint that listens for POST requests on http://localhost:8080. The processor creates a response that echoes the request body and the value of the id header.
from("restlet:http://localhost:9080/securedOrders?restletMethod=post&restletRealm=#realm").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { exchange.getOut().setBody( "received [" + exchange.getIn().getBody() + "] as an order id = " + exchange.getIn().getHeader("id")); } });
The restletRealm setting (in 2.x, use the # notation, that is, restletRealm=#refName)in the URI query is used to look up a Realm Map in the registry. If this option is specified, the restlet consumer uses the information to authenticate user logins. Only authenticated requests can access the resources. In this sample, we create a Spring application context that serves as a registry. The bean ID of the Realm Map should match the restletRealmRef.
<util:map id="realm"> <entry key="admin" value="foo" /> <entry key="bar" value="foo" /> </util:map>
The following sample starts a direct endpoint that sends requests to the server on http://localhost:8080 (that is, our restlet consumer endpoint).
// Note: restletMethod and restletRealmRef are stripped // from the query before a request is sent as they are // only processed by Camel. from("direct:start-auth").to("restlet:http://localhost:9080/securedOrders?restletMethod=post");
That is all we need. We are ready to send a request and try out the restlet component:
final String id = "89531"; Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<String, Object>(); headers.put(RestletConstants.RESTLET_LOGIN, "admin"); headers.put(RestletConstants.RESTLET_PASSWORD, "foo"); headers.put("id", id); String response = (String) template.requestBodyAndHeaders("direct:start-auth", "<order foo='1'/>", headers);
The sample client sends a request to the direct:start-auth endpoint with the following headers:
- CamelRestletLogin (used internally by Camel)
- CamelRestletPassword (used internally by Camel)
- id (application header)
| Note org.apache.camel.restlet.auth.login and org.apache.camel.restlet.auth.password will not be propagated as Restlet header. |
The sample client gets a response like the following:
received [<order foo='1'/>] as an order id = 89531
Single restlet endpoint to service multiple methods and URI templates (2.0 or later)
It is possible to create a single route to service multiple HTTP methods using the restletMethods option. This snippet also shows how to retrieve the request method from the header:
from("restlet:http://localhost:9080/users/{username}?restletMethods=post,get") .process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { // echo the method exchange.getOut().setBody(exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_METHOD, String.class)); } });
In addition to servicing multiple methods, the next snippet shows how to create an endpoint that supports multiple URI templates using the restletUriPatterns option. The request URI is available in the header of the IN message as well. If a URI pattern has been defined in the endpoint URI (which is not the case in this sample), both the URI pattern defined in the endpoint and the restletUriPatterns option will be honored.
from("restlet:http://localhost:9080?restletMethods=post,get&restletUriPatterns=#uriTemplates") .process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { // echo the method String uri = exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_URI, String.class); String out = exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_METHOD, String.class); if ("http://localhost:9080/users/homer".equals(uri)) { exchange.getOut().setBody(out + " " + exchange.getIn().getHeader("username", String.class)); } else if ("http://localhost:9080/atom/collection/foo/component/bar".equals(uri)) { exchange.getOut().setBody(out + " " + exchange.getIn().getHeader("id", String.class) + " " + exchange.getIn().getHeader("cid", String.class)); } } });
The restletUriPatterns=#uriTemplates option references the List<String> bean defined in the Spring XML configuration.
<bean id="uriTemplates"> <list> <value>/users/{username}</value> <value>/atom/collection/{id}/component/{cid}</value> </list> </bean>
RMI Component
The rmi: component binds PojoExchanges to the RMI protocol (JRMP).
Since this binding is just using RMI, normal RMI rules still apply regarding what methods can be invoked. This component supports only PojoExchanges that carry a method invocation from an interface that extends the Remote interface. All parameters in the method should be either Serializable or Remote objects.
URI format
rmi://rmi-regisitry-host:rmi-registry-port/registry-path[?options]
For example:
rmi://localhost:1099/path/to/service
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| method | null | As of Camel 1.3, you can set the name of the method to invoke. |
Using
To call out to an existing RMI service registered in an RMI registry, create a route similar to the following:
from("pojo:foo").to("rmi://localhost:1099/foo");
To bind an existing camel processor or service in an RMI registry, define an RMI endpoint as follows:
RmiEndpoint endpoint= (RmiEndpoint) endpoint("rmi://localhost:1099/bar"); endpoint.setRemoteInterfaces(ISay.class); from(endpoint).to("pojo:bar");
Note that when binding an RMI consumer endpoint, you must specify the Remote interfaces exposed.
See Also
RSS Component
The rss: component is used for polling RSS feeds. Camel will default poll the feed every 60th seconds.
Note: The component currently only supports polling (consuming) feeds.
New in Camel 2.0
URI format
rss:rssUri
Where rssUri is the URI to the RSS feed to poll.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| splitEntries | true | If true, Camel splits a feed into its individual entries and returns each entry, poll by poll. For example, if a feed contains seven entries, Camel returns the first entry on the first poll, the second entry on the second poll, and so on. When no more entries are left in the feed, Camel contacts the remote RSS URI to obtain a new feed. If false, Camel obtains a fresh feed on every poll and returns all of the feed's entries. |
| filter | true | Use in combination with the splitEntries option in order to filter returned entries. By default, Camel applies the UpdateDateFilter filter, which returns only new entries from the feed, ensuring that the consumer endpoint never receives an entry more than once. The filter orders the entries chronologically, with the newest returned last. |
| lastUpdate | null | Use in combination with the filter option to block entries earlier than a specific date/time (uses the entry.updated timestamp). The format is: yyyy-MM-ddTHH:MM:ss. Example: 2007-12-24T17:45:59. |
| feedHeader | true | Specifies whether to add the ROME SyndFeed object as a header. |
| sortEntries | false | If splitEntries is true, this specifies whether to sort the entries by updated date. |
| consumer.delay | 60000 | Delay in milliseconds between each poll. |
| consumer.initialDelay | 1000 | Milliseconds before polling starts. |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | false | Set to true to use fixed delay between pools, otherwise fixed rate is used. See ScheduledExecutorService in JDK for details. |
Exchange data types
Camel initializes the In body on the Exchange with a ROME SyndFeed. Depending on the value of the splitEntries flag, Camel returns either a SyndFeed with one SyndEntry or a java.util.List of SyndEntrys.
| Option | Value | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| splitEntries | true | A single entry from the current feed is set in the exchange. |
| splitEntries | false | The entire list of entries from the current feed is set in the exchange. |
Message Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.component.rss.feed | Camel 1.x: The entire SyncFeed object. |
| CamelRssFeed | Camel 2.0: The entire SyncFeed object. |
RSS Dataformat
The RSS component ships with an RSS dataformat that can be used to convert between String (as XML) and ROME RSS model objects.
- marshal = from ROME SyndFeed to XML String
- unmarshal = from XML String to ROME SyndFeed
A route using this would look something like this:
from("rss:file:src/test/data/rss20.xml?splitEntries=false&consumer.delay=1000").marshal().rss().to("mock:marshal");
The purpose of this feature is to make it possible to use Camel's lovely built-in expressions for manipulating RSS messages. As shown below, an XPath expression can be used to filter the RSS message:
// only entries with Camel in the title will get through the filter from("rss:file:src/test/data/rss20.xml?splitEntries=true&consumer.delay=100") .marshal().rss().filter().xpath("//item/title[contains(.,'Camel')]").to("mock:result");
Merging multiple incoming feeds
To merge multiple incoming feeds into a single feed, you can apply the custom aggregator, AggregationCollection, provided with camel-rss. For example:
from("rss:file:src/test/data/rss20.xml?sortEntries=true&consumer.delay=50").to("seda:temp"); from("rss:file:target/rss20.xml?sortEntries=true&consumer.delay=50").to("seda:temp"); from("seda:temp").aggregate(new AggregateRssFeedCollection()).batchTimeout(5000L).to("mock:result");
Here we use a SEDA queue to gather up entries from two RSS feeds. The entries are then fed into the custom aggregator which combines these entries into a single ROME SyndFeed object.
Filtering entries
You can filter out entries quite easily using XPath, as shown in the data format section above. You can also exploit Camel's Bean Integration to implement your own conditions. For instance, a filter equivalent to the XPath example above would be:
// only entries with Camel in the title will get through the filter from("rss:file:src/test/data/rss20.xml?splitEntries=true&consumer.delay=100"). filter().method("myFilterBean", "titleContainsCamel").to("mock:result");
The custom bean for this would be:
public static class FilterBean { public boolean titleContainsCamel(@Body SyndFeed feed) { SyndEntry firstEntry = (SyndEntry) feed.getEntries().get(0); return firstEntry.getTitle().contains("Camel"); } }
See Also
SEDA Component
The seda: component provides asynchronous SEDA behavior, so that messages are exchanged on a BlockingQueue and consumers are invoked in a separate thread from the producer.
Note that queues are only visible within a single CamelContext. If you want to communicate across CamelContext instances (for example, communicating between Web applications), see the VM component.
This component does not implement any kind of persistence or recovery, if the VM terminates while messages are yet to be processed. If you need persistence, reliability or distributed SEDA, try using either JMS or ActiveMQ.
| Synchronous The Direct component provides synchronous invocation of any consumers when a producer sends a message exchange. |
URI format
seda:someName[?options]
Where someName can be any string that uniquely identifies the endpoint within the current CamelContext.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
| Same URI must be used for both producer and consumer An exactly identical SEDA endpoint URI must be used for both the producer endpoint and the consumer endpoint. Otherwise Camel will create a second SEDA endpoint, even thought the someName portion of the URI is identical. For example: from("direct:foo").to("seda:bar?concurrentConsumers=5"); from("seda:bar?concurrentConsumers=5").to("file://output"); Notice that we have to use the full URI including options in both the producer and consumer. |
Options
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| size | 1000 | The maximum size of the SEDA queue. |
| concurrentConsumers | 1 | Camel 1.6.1/2.0: Number of concurrent threads processing exchanges. |
| waitForTaskToComplete | IfReplyExpected | Camel 2.0: Option to specify whether the caller should wait for the async task to complete or not before continuing. The following three options are supported: Always, Never or IfReplyExpected. The first two values are self-explanatory. The last value, IfReplyExpected, will only wait if the message is Request Reply based. The default option is IfReplyExpected. See more information about Async messaging. |
| timeout | 30000 | Camel 2.0: Timeout in millis a seda producer will at most waiting for an async task to complete. See waitForTaskToComplete and Async for more details. |
Changes in Camel 2.0
In Camel 2.0 the SEDA component supports using Request Reply, where the caller will wait for the Async route to complete. For instance:
from("mina:tcp://0.0.0.0:9876?textline=true&sync=true").to("seda:input"); from("seda:input").to("bean:processInput").to("bean:createResponse");
In the route above, we have a TCP listener on port 9876 that accepts incoming requests. The request is routed to the seda:input queue. As it is a Request Reply message, we wait for the response. When the consumer on the seda:input queue is complete, it copies the response to the original message response.
Camel 1.x does not have this feature implemented, the SEDA queues in Camel 1.x will newer wait.
Concurrent consumers
By default, the SEDA endpoint uses a single consumer thread, but you can configure it to use concurrent consumer threads. So instead of thread pools you can use:
from("seda:stageName?concurrentConsumers=5").process(...)
Difference between thread pools and concurrent consumers
The thread pool is a pool that can increase/shrink dynamically at runtime depending on load, whereas the concurrent consumers are always fixed.
Thread pools
Be aware that adding a thread pool to a SEDA endpoint by doing something like:
from("seda:stageName").thread(5).process(...)
Can wind up with two BlockQueues: one from the SEDA endpoint, and one from the workqueue of the thread pool, which may not be what you want. Instead, you might want to consider configuring a Direct endpoint with a thread pool, which can process messages both synchronously and asynchronously. For example:
from("direct:stageName").thread(5).process(...)
You can also directly configure number of threads that process messages on a SEDA endpoint using the concurrentConsumers option.
Sample
In the route below we use the SEDA queue to send the request to this async queue to be able to send a fire-and-forget message for further processing in another thread, and return a constant reply in this thread to the original caller.
public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:start") // send it to the seda queue that is async .to("seda:next") // return a constant response .transform(constant("OK")); from("seda:next").to("mock:result"); }
Here we send a Hello World message and expects the reply to be OK.
Object out = template.requestBody("direct:start", "Hello World"); assertEquals("OK", out);
The "Hello World" message will be consumed from the SEDA queue from another thread for further processing. Since this is from a unit test, it will be sent to a mock endpoint where we can do assertions in the unit test.
See Also
Servlet Component
The servlet: component provides HTTP based endpoints for consuming HTTP requests that arrive at a HTTP endpoint and this endpoint is bound to a published Servlet.
Note: This component is new to Camel 2.0-M3.
Maven users will need to add the following dependency to their pom.xml for this component:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-servlet</artifactId>
<version>x.x.x</version>
<\!-\- use the same version as your Camel core version \-->
</dependency>
URI format
servlet://relative_path[?options]
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| httpBindingRef | null | Reference to an org.apache.camel.component.http.HttpBinding in the Registry. A HttpBinding implementation can be used to customize how to write a response. |
| matchOnUriPrefix | false | Whether or not the CamelServlet should try to find a target consumer by matching the URI prefix, if no exact match is found. |
| servletName | null | Specifies the servlet name that the servlet endpoint will bind to. If there is no servlet name specified, the servlet endpoint will be bind to first published Servlet |
Message Headers
Camel will apply the same Message Headers as the HTTP component.
Camel will also populate all request.parameter and request.headers. For example, if a client request has the URL, http://myserver/myserver?orderid=123, the exchange will contain a header named orderid with the value 123.
Usage
You can only consume from endpoints generated by the Servlet component. Therefore, it should only be used as input into your camel routes. To issue HTTP requests against other HTTP endpoints, use the HTTP Component
Sample
In this sample, we define a route that exposes a HTTP service at http://localhost:8080/camel/services/hello.
First, you need to publish the CamelHttpTransportServlet through the normal Web Container, or OSGi Service.
Use the Web.xml file to publish the CamelHttpTransportServlet as follows:
<web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>CamelServlet</servlet-name> <display-name>Camel Http Transport Servlet</display-name> <servlet-class> org.apache.camel.component.servlet.CamelHttpTransportServlet </servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>CamelServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/services/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Use an Activator to publish the CamelHttpTransportServlet on the OSGi platform
import java.util.Dictionary; import java.util.Hashtable; import javax.servlet.Servlet; import org.apache.camel.component.servlet.CamelHttpTransportServlet; import org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator; import org.osgi.framework.BundleContext; import org.osgi.framework.ServiceReference; import org.osgi.service.http.HttpContext; import org.osgi.service.http.HttpService; public final class ServletActivator implements BundleActivator { /** * HttpService reference. */ private ServiceReference httpServiceRef; /** * Called when the OSGi framework starts our bundle */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void start(BundleContext bc) throws Exception { httpServiceRef = bc.getServiceReference(HttpService.class.getName()); if (httpServiceRef != null) { final HttpService httpService = (HttpService)bc.getService(httpServiceRef); if (httpService != null) { // create a default context to share between registrations final HttpContext httpContext = httpService.createDefaultHttpContext(); // register the hello world servlet final Dictionary initParams = new Hashtable(); initParams.put("matchOnUriPrefix", "false"); initParams.put("servlet-name", "camelServlet"); httpService.registerServlet("/camel/services", // alias (Servlet)new CamelHttpTransportServlet(), // register servlet initParams, // init params httpContext // http context ); } } } /** * Called when the OSGi framework stops our bundle */ public void stop(BundleContext bc) throws Exception { if (httpServiceRef != null) { bc.ungetService(httpServiceRef); httpServiceRef = null; } } }
Then you can define your route as follows:
from("servlet:///hello?matchOnUriPrefix=true").process(new Processor() { public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception { String contentType = exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.CONTENT_TYPE, String.class); String path = exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_PATH, String.class); assertEquals("Get a wrong content type", CONTENT_TYPE, contentType); String charsetEncoding = exchange.getIn().getHeader(Exchange.HTTP_CHARACTER_ENCODING, String.class); assertEquals("Get a wrong charset name", "UTF-8", charsetEncoding); exchange.getOut().setHeader(Exchange.CONTENT_TYPE, contentType + "; charset=UTF-8"); exchange.getOut().setHeader("PATH", path); exchange.getOut().setBody("<b>Hello World</b>"); } });
| Specify the relative path for camel-servlet endpoint |
Since we are binding the Http transport with a published servlet, and we don't know the servlet's application context path, the camel-servlet endpoint uses the relative path to specify the endpoint's URL. A client can access the camel-servlet endpoint through the servlet publish address: ("http://localhost:8080/camel/services") + RELATIVE_PATH("/hello").
See Also
Smooks
The smooks component supports the Smooks Library for EDI parsing. The camel-smooks library is provided by the Camel Extra project which hosts all *GPL related components for Camel.
It is only the EDI parsing feature that is implemented in this component. The other features from Smooks are covered in existing camel components.
Parsing from any given data source to EDI is implemented using Camel Data Format.
EDI DataFormat
This component ships with a EDI dataformat that can be used to format from a java.io.InputStream to XML as a org.w3c.Document Object.
- marshal = currently not supported by Smooks
- unmarshal = from stream to XML (can be used when reading EDI files)
The EDIDataFormat must be configued with either a:
- setSmooksConfig(configfile) = a fully Smooks configuration file
- setMappingModel(modelfile) = just the mapping model xml file and Camel will use a default Smooks configuration
To use the data format simply instantiate an instance, set the configuration (above) and invoke the unmarshal operation in the route builder:
DataFormat edi = new EDIDataFormat(); edi.setMappingModel("my-order-mapping.xml"); ... from("file://edi/in"). unmarshal(edi). to("jms:queue:edi");
And you can also provide the full Smooks configuration file where you can configure Smooks as you want, in case the default configuration isn't useful:
DataFormat edi = new EDIDataFormat(); edi.setSmooksConfig("my-smooks-config.xml"); ... from("file://edi/in"). unmarshal(edi). to("jms:queue:edi");
Dependencies
To use EDI in your camel routes you need to add the a dependency on camel-smooks which implements this data format.
This component is hosted at the Camel Extra project since the Smooks library uses a licenses which cant be included directly in an Apache project.
SNMP Component
Available as of Camel 2.1
The snmp: component gives you the ability to poll SNMP capable devices or receiving traps.
URI format
snmp://hostname[:port][?Options]
The component supports polling OID values from an SNMP enabled device and receiving traps.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | none | The type of action you want to perform. Actually you can enter here poll or trap. The value poll will instruct the endpoint to poll a given host for the supplied OID keys. If you put in trap you will setup a listener for SNMP Trap Events. |
| address | none | This is the IP address and the port of the host to poll or where to setup the Trap Receiver. Example: 127.0.0.1:162 |
| protocol | none | Here you can select which protocol to use. By default it will be udp protocol but you may want to use tcp as well |
| retries | 2 | Defines how often a retry is made before canceling the request. |
| timeout | 1500 | Sets the timeout value for the request in millis. |
| snmpVersion | 0 (which means SNMPv1) | Sets the snmp version for the request. |
| snmpCommunity | public | Sets the community octet string for the snmp request. |
| delay | 60 seconds | Defines the delay in seconds between to poll cycles. |
| oids | none | Defines which values you are interested in. Please have a look at the Wikipedia to get a better understanding. You may provide a single OID or a coma separated list of OIDs. Example: oids="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0,1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.5.1,1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.5.1.1.1,1.3.6.1.2.1.43.5.1.1.11.1" |
The result of a poll
Given the situation, that I poll for the following OIDs:
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.5.1 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.5.1.1.1 1.3.6.1.2.1.43.5.1.1.11.1
The result will be the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <snmp> <entry> <oid>1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0</oid> <value>6 days, 21:14:28.00</value> </entry> <entry> <oid>1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.5.1</oid> <value>2</value> </entry> <entry> <oid>1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.5.1.1.1</oid> <value>3</value> </entry> <entry> <oid>1.3.6.1.2.1.43.5.1.1.11.1</oid> <value>6</value> </entry> <entry> <oid>1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0</oid> <value>My Very Special Printer Of Brand Unknown</value> </entry> </snmp>
As you maybe recognized there is one more result than requested....1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0.
This one is filled in by the device automatically in this special case. So it may absolutely happen, that you receive more than you requested...be prepared.
Examples
Polling a remote device:
snmp:192.168.178.23:161?protocol=udp&type=poll&oids=1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0
Setting up a trap receiver (Note that no OID info is needed here!):
snmp:127.0.0.1:162?protocol=udp&type=trap
Routing example in Java: (converts the SNMP PDU to XML String)
from("snmp:192.168.178.23:161?protocol=udp&type=poll&oids=1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0"). convertBodyTo(String.class). to("activemq:snmp.states");
See Also
Spring Integration Component
The spring-integration: component provides a bridge for Camel components to talk to spring integration endpoints.
URI format
spring-integration:defaultChannelName[?options]
Where defaultChannelName represents the default channel name which is used by the Spring Integration Spring context. It will equal to the inputChannel name for the Spring Integration consumer and the outputChannel name for the Spring Integration provider.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Description | Example | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| inputChannel | The Spring integration input channel name that this endpoint wants to consume from, where the specified channel name is defined in the Spring context. | inputChannel=requestChannel | No | |
| outputChannel | The Spring integration output channel name that is used to send messages to the Spring integration context. | outputChannel=replyChannel | No | |
| inOut | The exchange pattern that the Spring integration endpoint should use. | inOut=true | No | inOnly for the Spring integration consumer and outOnly for the Spring integration provider |
| consumer.delay | Delay in milliseconds between each poll. | consumer.delay=60000 | No | 500 |
| consumer.initialDelay | Milliseconds before polling starts. | consumer.initialDelay=10000 | No | 1000 |
| consumer.userFixedDelay | Specify true to use fixed delay between polls, otherwise fixed rate is used. See the JavaScheduledExecutorService class for details. | consumer.userFixedDelay=false | No | false |
Usage
The Spring integration component is a bridge that connects Camel endpoints with Spring integration endpoints through the Spring integration's input channels and output channels. Using this component, we can send Camel messages to Spring Integration endpoints or receive messages from Spring integration endpoints in a Camel routing context.
Examples
Using the Spring integration endpoint
You can set up a Spring integration endpoint using a URI, as follows:
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration/spring-integration-1.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <channel id="inputChannel"/> <channel id="outputChannel"/> <channel id="onewayChannel"/> <service-activator input-channel="inputChannel" ref="helloService" method="sayHello"/> <service-activator input-channel="onewayChannel" ref="helloService" method="greet"/> <beans:bean id="helloService" class="org.apache.camel.component.spring.integration.HelloWorldService"/> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:twowayMessage"/> <!-- Using the & as the separator of & --> <to uri="spring-integration:inputChannel?inOut=true&inputChannel=outputChannel"/> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:onewayMessage"/> <to uri="spring-integration:onewayChannel?inOut=false"/> </route> </camelContext>
<channel id="requestChannel"/> <channel id="responseChannel"/> <beans:bean id="myProcessor" class="org.apache.camel.component.spring.integration.MyProcessor"/> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <!-- Using the & as the separator of & --> <from uri="spring-integration://requestChannel?outputChannel=responseChannel&inOut=true"/> <process ref="myProcessor"/> </route> </camelContext>
Or directly using a Spring integration channel name:
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration/spring-integration-1.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <channel id="outputChannel"/> <camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <!-- camel will create a spring integration endpoint automatically --> <from uri="outputChannel"/> <to uri="mock:result"/> </route> </camelContext>
The Source and Target adapter
Spring integration also provides the Spring integration's source and target adapters, which can route messages from a Spring integration channel to a Camel endpoint or from a Camel endpoint to a Spring integration channel.
This example uses the following namespaces:
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:camel-si="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/integration" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration http://www.springframework.org/schema/integration/spring-integration-1.0.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/integration http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/integration/camel-spring-integration.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd ">
You can bind your source or target to a Camel endpoint as follows:
<!-- Create the camel context here --> <camelContext id="camelTargetContext" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:EndpointA" /> <to uri="mock:result" /> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:EndpointC"/> <process ref="myProcessor"/> </route> </camelContext> <!-- We can bind the camelTarget to the camel context's endpoint by specifying the camelEndpointUri attribute --> <camel-si:camelTarget id="camelTargetA" camelEndpointUri="direct:EndpointA" expectReply="false"> <camel-si:camelContextRef>camelTargetContext</camel-si:camelContextRef> </camel-si:camelTarget> <camel-si:camelTarget id="camelTargetB" camelEndpointUri="direct:EndpointC" replyChannel="channelC" expectReply="true"> <camel-si:camelContextRef>camelTargetContext</camel-si:camelContextRef> </camel-si:camelTarget> <camel-si:camelTarget id="camelTargetD" camelEndpointUri="direct:EndpointC" expectReply="true"> <camel-si:camelContextRef>camelTargetContext</camel-si:camelContextRef> </camel-si:camelTarget> <beans:bean id="myProcessor" class="org.apache.camel.component.spring.integration.MyProcessor"/>
<camelContext id="camelSourceContext" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:OneWay"/> <to uri="direct:EndpointB" /> </route> <route> <from uri="direct:TwoWay"/> <to uri="direct:EndpointC" /> </route> </camelContext> <!-- camelSource will redirect the message coming for direct:EndpointB to the spring requestChannel channelA --> <camel-si:camelSource id="camelSourceA" camelEndpointUri="direct:EndpointB" requestChannel="channelA" expectReply="false"> <camel-si:camelContextRef>camelSourceContext</camel-si:camelContextRef> </camel-si:camelSource> <!-- camelSource will redirect the message coming for direct:EndpointC to the spring requestChannel channelB then it will pull the response from channelC and put the response message back to direct:EndpointC --> <camel-si:camelSource id="camelSourceB" camelEndpointUri="direct:EndpointC" requestChannel="channelB" replyChannel="channelC" expectReply="true"> <camel-si:camelContextRef>camelSourceContext</camel-si:camelContextRef> </camel-si:camelSource>
See Also
Stream Component
The stream: component provides access to the System.in, System.out and System.err streams as well as allowing streaming of file and URL.
URI format
stream:in[?options] stream:out[?options] stream:err[?options] stream:header[?options]
In addition, the file and url endpoint URIs are supported in Camel 2.0:
stream:file?fileName=/foo/bar.txt stream:url[?options]
If the stream:header URI is specified, the stream header is used to find the stream to write to. This option is available only for stream producers (that is, it cannot appear in from()).
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| delay | 0 | Initial delay in milliseconds before consuming or producing the stream. |
| encoding | JVM Default | As of 1.4, you can configure the encoding (is a charset name) to use text-based streams (for example, message body is a String object). If not provided, Camel uses the JVM default Charset. |
| promptMessage | null | Camel 2.0: Message prompt to use when reading from stream:in; for example, you could set this to Enter a command: |
| promptMessageDelay | 0 | Camel 2.0: Optional delay in milliseconds before showing the message prompt. Can be used during system startup to avoid message prompts being written while other logging is done to the system out. |
| promptDelay | 0 | Camel 2.0: Optional delay in milliseconds before showing the message prompt. |
| promptInitialDelay | 2000 | Camel 2.0: Initial delay in milliseconds before showing the message prompt. This delay occurs only once. Can be used during system startup to avoid message prompts being written while other logging is done to the system out. |
| fileName | null | Camel 2.0: When using the stream:file URI format, this option specifies the filename to stream to/from. |
| scanStream | false | Camel 2.0: To be used for continuously reading a stream such as the unit tail command. |
| scanStreamDelay | 0 | Camel 2.0: Delay in milliseconds between read attempts when using scanStream. |
Message content
The stream: component supports either String or byte[] for writing to streams. Just add either String or byte[] content to the message.in.body.
The special stream:header URI is used for custom output streams. Just add a java.io.OutputStream object to message.in.header in the key header.
See samples for an example.
Samples
In the following sample we route messages from the direct:in endpoint to the System.out stream:
@Test public void testStringContent() throws Exception { template.sendBody("direct:in", "Hello Text World\n"); } @Test public void testBinaryContent() { template.sendBody("direct:in", "Hello Bytes World\n".getBytes()); } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:in").to("stream:out"); } }; }
The following sample demonstrates how the header type can be used to determine which stream to use. In the sample we use our own output stream, MyOutputStream.
private OutputStream mystream = new MyOutputStream(); private StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); @Test public void testStringContent() { template.sendBody("direct:in", "Hello"); // StreamProducer appends \n in text mode assertEquals("Hello\n", sb.toString()); } @Test public void testBinaryContent() { template.sendBody("direct:in", "Hello".getBytes()); // StreamProducer is in binary mode so no \n is appended assertEquals("Hello", sb.toString()); } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() { from("direct:in").setHeader("stream", constant(mystream)). to("stream:header"); } }; } private class MyOutputStream extends OutputStream { public void write(int b) throws IOException { sb.append((char)b); } }
The following sample demonstrates how to continuously read a file stream (analogous to the UNIX tail command):
from("stream:file?fileName=/server/logs/server.log?scanStream=true&scanStreamDelay=1000").to("bean:logService?method=parseLogLine");
See Also
String Template
The string-template: component allows you to process a message using a String Template. This can be ideal when using Templating to generate responses for requests.
URI format
string-template:templateName[?options]
Where templateName is the classpath-local URI of the template to invoke; or the complete URL of the remote template.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| contentCache | false | New option in Camel 1.4. Cache for the resource content when its loaded. |
Headers
Camel will store a reference to the resource in the message header with key, org.apache.camel.stringtemplate.resource. The Resource is an org.springframework.core.io.Resource object.
Hot reloading
The string template resource is by default hot-reloadable for both file and classpath resources (expanded jar). If you set contentCache=true, Camel loads the resource only once and hot-reloading is not possible. This scenario can be used in production when the resource never changes.
StringTemplate Attributes
Camel will provide exchange information as attributes (just a java.util.Map) to the string template. The Exchange is transfered as:
| key | value |
|---|---|
| exchange | The Exchange itself. |
| headers | The headers of the In message. |
| camelContext | The Camel Context. |
| request | The In message. |
| in | The In message. |
| body | The In message body. |
| out | The Out message (only for InOut message exchange pattern). |
| response | The Out message (only for InOut message exchange pattern). |
Samples
For example you could use a string template as follows in order to formulate a response to a message:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("string-template:com/acme/MyResponse.tm");
The Email Sample
In this sample we want to use a string template to send an order confirmation email. The email template is laid out in StringTemplate as:
Dear $headers.lastName$, $headers.firstName$
Thanks for the order of $headers.item$.
Regards Camel Riders Bookstore
$body$
And the java code is as follows:
private Exchange createLetter() { Exchange exchange = context.getEndpoint("direct:a").createExchange(); Message msg = exchange.getIn(); msg.setHeader("firstName", "Claus"); msg.setHeader("lastName", "Ibsen"); msg.setHeader("item", "Camel in Action"); msg.setBody("PS: Next beer is on me, James"); return exchange; } @Test public void testVelocityLetter() throws Exception { MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Dear Ibsen, Claus! Thanks for the order of Camel in Action. Regards Camel Riders Bookstore PS: Next beer is on me, James"); template.send("direct:a", createLetter()); mock.assertIsSatisfied(); } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:a").to("string-template:org/apache/camel/component/stringtemplate/letter.tm").to("mock:result"); } }; }
See Also
SQL Component
The sql: component allows you to work with databases using JDBC queries. The difference between this component and JDBC component is that in case of SQL the query is a property of the endpoint and it uses message payload as parameters passed to the query.
This component uses spring-jdbc behind the scenes for the actual SQL handling.
URI format
The SQL component can only be used to define producer endpoints. In other words, you cannot define an SQL endpoint in a from() statement. |
The SQL component uses the following endpoint URI notation:
sql:select * from table where id=# order by name[?options]
Notice that the standard ? symbol that denotes the parameters to an SQL query is substituted with the # symbol, because the ? symbol is used to specify options for the endpoint.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| dataSourceRef | String | null | Camel 1.5.1/2.0: Reference to a DataSource to look up in the registry. |
| template.<xxx> | null | Sets additional options on the Spring JdbcTemplate that is used behind the scenes to execute the queries. For instance, template.maxRows=10. For detailed documentation, see the JdbcTemplate javadoc documentation. |
Treatment of the message body
The SQL component tries to convert the message body to an object of java.util.Iterator type and then uses this iterator to fill the query parameters (where each query parameter is represented by a # symbol in the endpoint URI). If the message body is not an array or collection, the conversion results in an iterator that iterates over only one object, which is the body itself.
For example, if the message body is an instance of java.util.List, the first item in the list is substituted into the first occurrence of # in the SQL query, the second item in the list is substituted into the second occurrence of #, and so on.
Result of the query
For select operations, the result is an instance of List<Map<String, Object>> type, as returned by the JdbcTemplate.queryForList() method. For update operations, the result is the number of updated rows, returned as an Integer.
Header values
When performing update operations, the SQL Component stores the update count in the following message headers:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| SqlProducer.UPDATE_COUNT | Camel 1.x: The number of rows updated for update operations, returned as an Integer object. |
| CamelSqlUpdateCount | Camel 2.0: The number of rows updated for update operations, returned as an Integer object. |
| CamelSqlRowCount | Camel 2.0: The number of rows returned for select operations, returned as an Integer object. |
Configuration in Camel 1.5.0 or lower
The SQL component must be configured before it can be used. In Spring, you can configure it as follows:
<bean id="sql" class="org.apache.camel.component.sql.SqlComponent"> <property name="dataSource" ref="myDS"/> </bean> <bean id="myDS" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds" /> <property name="username" value="username" /> <property name="password" value="password" /> </bean>
Configuration in Camel 1.5.1 or higher
You can now set a reference to a DataSource in the URI directly:
sql:select * from table where id=# order by name?dataSourceRef=myDS
Sample
In the sample below we execute a query and retrieve the result as a List of rows, where each row is a Map<String, Object and the key is the column name.
First, we set up a table to use for our sample. As this is based on an unit test, we do it java code:
// this is the database we create with some initial data for our unit test jdbcTemplate.execute("create table projects (id integer primary key," + "project varchar(10), license varchar(5))"); jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into projects values (1, 'Camel', 'ASF')"); jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into projects values (2, 'AMQ', 'ASF')"); jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into projects values (3, 'Linux', 'XXX')");
Then we configure our route and our sql component. Notice that we use a direct endpoint in front of the sql endpoint. This allows us to send an exchange to the direct endpoint with the URI, direct:simple, which is much easier for the client to use than the long sql: URI. Note that the DataSource is looked up up in the registry, so we can use standard Spring XML to configure our DataSource.
from("direct:simple") .to("sql:select * from projects where license = # order by id?dataSourceRef=jdbc/myDataSource") .to("mock:result");
And then we fire the message into the direct endpoint that will route it to our sql component that queries the database.
MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); // send the query to direct that will route it to the sql where we will execute the query // and bind the parameters with the data from the body. The body only contains one value // in this case (XXX) but if we should use multi values then the body will be iterated // so we could supply a List<String> instead containing each binding value. template.sendBody("direct:simple", "XXX"); mock.assertIsSatisfied(); // the result is a List List received = assertIsInstanceOf(List.class, mock.getReceivedExchanges().get(0).getIn().getBody()); // and each row in the list is a Map Map row = assertIsInstanceOf(Map.class, received.get(0)); // and we should be able the get the project from the map that should be Linux assertEquals("Linux", row.get("PROJECT"));
We could configure the DataSource in Spring XML as follows:
<jee:jndi-lookup id="myDS" jndi-name="jdbc/myDataSource"/>
See Also
Test Component
Testing of distributed and asynchronous processing is notoriously difficult. The Mock, Test and DataSet endpoints work great with the Camel Testing Framework to simplify your unit and integration testing using Enterprise Integration Patterns and Camel's large range of Components together with the powerful Bean Integration.The test component extends the Mock component to support pulling messages from another endpoint on startup to set the expected message bodies on the underlying Mock endpoint. That is, you use the test endpoint in a route and messages arriving on it will be implicitly compared to some expected messages extracted from some other location.
So you can use, for example, an expected set of message bodies as files. This will then set up a properly configured Mock endpoint, which is only valid if the received messages match the number of expected messages and their message payloads are equal.
URI format
test:expectedMessagesEndpointUri
Where expectedMessagesEndpointUri refers to some other Component URI that the expected message bodies are pulled from before starting the test.
Example
For example, you could write a test case as follows:
from("seda:someEndpoint"). to("test:file://data/expectedOutput?noop=true");
If your test then invokes the MockEndpoint.assertIsSatisfied(camelContext) method, your test case will perform the necessary assertions.
Here is a real example test case using Mock and Spring along with its Spring XML.
To see how you can set other expectations on the test endpoint, see the Mock component.
See Also
Timer Component
The timer: component is used to generate message exchanges when a timer fires You can only consume events from this endpoint.
URI format
timer:name[?options]
Where name is the name of the Timer object, which is created and shared across endpoints. So if you use the same name for all your timer endpoints, only one Timer object and thread will be used.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Note: The IN body of the generated exchange is null. So exchange.getIn().getBody() returns null.
| Advanced Scheduler See also the Quartz component that supports much more advanced scheduling. |
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| time | null | A java.util.Date the first event should be generated. If using the URI, the pattern expected is: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss or yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss. |
| pattern | null | Camel 1.6.2/2.0: Allows you to specify a custom Date pattern to use for setting the time option using URI syntax. |
| period | 1000 | If greater than 0, generate periodic events every period milliseconds. |
| delay | 0 | The number of milliseconds to wait before the first event is generated. Should not be used in conjunction with the time option. |
| fixedRate | false | Events take place at approximately regular intervals, separated by the specified period. |
| daemon | true | Specifies whether or not the thread associated with the timer endpoint runs as a daemon. |
Exchange Properties
When the timer is fired, it adds the following information as properties to the Exchange:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.timer.name | String | The value of the name option. |
| org.apache.camel.timer.time | Date | The value of the time option. |
| org.apache.camel.timer.period | long | The value of the period option. |
| org.apache.camel.timer.firedTime | Date | Camel 1.5: The time when the consumer fired. |
Message Headers
When the timer is fired, it adds the following information as headers to the IN message
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| firedTime | java.util.Date | Camel 1.5: The time when the consumer fired |
Sample
To set up a route that generates an event every 60 seconds:
from("timer://foo?fixedRate=true&period=60000").to("bean:myBean?method=someMethodName");
The above route will generate an event and then invoke the someMethodName method on the bean called myBean in the Registry such as JNDI or Spring.
And the route in Spring DSL:
<route> <from uri="timer://foo?fixedRate=true&period=60000"/> <to uri="bean:myBean?method=someMethodName"/> </route>
See Also
Validation Component
The Validation component performs XML validation of the message body using the JAXP Validation API and based on any of the supported XML schema languages, which defaults to XML Schema
Note that the Jing component also supports the following useful schema languages:
The MSV component also supports RelaxNG XML Syntax.
URI format
validator:someLocalOrRemoteResource
Where someLocalOrRemoteResource is some URL to a local resource on the classpath or a full URL to a remote resource or resource on the file system which contains the XSD to validate against. For example:
- msv:org/foo/bar.xsd
- msv:file:../foo/bar.xsd
- msv:http://acme.com/cheese.xsd
- validator:com/mypackage/myschema.xsd
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| useDom | false | Camel 2.0: Whether DOMSource/DOMResult or SaxSource/SaxResult should be used by the validator. |
Example
The following example shows how to configure a route from endpoint direct:start which then goes to one of two endpoints, either mock:valid or mock:invalid based on whether or not the XML matches the given schema (which is supplied on the classpath).
<camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="direct:start"/> <doTry> <to uri="validator:org/apache/camel/component/validator/schema.xsd"/> <to uri="mock:valid"/> <doCatch> <exception>org.apache.camel.ValidationException</exception> <to uri="mock:invalid"/> </doCatch> <doFinally> <to uri="mock:finally"/> </doFinally> </doTry> </route> </camelContext>
See Also
Velocity
The velocity: component allows you to process a message using an Apache Velocity template. This can be ideal when using Templating to generate responses for requests.
URI format
velocity:templateName[?options]
Where templateName is the classpath-local URI of the template to invoke; or the complete URL of the remote template (eg: file://folder/myfile.vm).
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| loaderCache | true | Velocity based file loader cache. |
| contentCache | New option in Camel 1.4: Cache for the resource content when it is loaded. By default, it's false in Camel 1.x. By default, it's true in Camel 2.x. | |
| encoding | null | New option in Camel 1.6: Character encoding of the resource content. |
| propertiesFile | null | New option in Camel 2.1: The URI of the properties file which is used for VelocityEngine initialization. |
Message Headers
The velocity component sets a couple headers on the message (you can't set these yourself and from Camel 2.1 velocity component will not set these headers which will cause some side effect on the dynamic template support):
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
| org.apache.camel.velocity.resource | Camel 1.x: The resource as an org.springframework.core.io.Resource object. |
| org.apache.camel.velocity.resourceUri | Camel 1.x: The templateName as a String object. |
| CamelVelocityResource | Camel 2.0: The resource as an org.springframework.core.io.Resource object. |
| CamelVelocityResourceUri | Camel 2.0: The templateName as a String object. |
In Camel 1.4 headers set during the Velocity evaluation are returned to the message and added as headers. Then its kinda possible to return values from Velocity to the Message.
For example, to set the header value of fruit in the Velocity template .tm:
$in.setHeader('fruit', 'Apple')
The fruit header is now accessible from the message.out.headers.
Velocity Context
Camel will provide exchange information in the Velocity context (just a Map). The Exchange is transfered as:
| key | value |
|---|---|
| exchange | The Exchange itself. |
| headers | The headers of the In message. |
| camelContext | The Camel Context intance. |
| request | The In message. |
| in | The In message. |
| body | The In message body. |
| out | The Out message (only for InOut message exchange pattern). |
| response | The Out message (only for InOut message exchange pattern). |
Hot reloading
The Velocity template resource is, by default, hot reloadable for both file and classpath resources (expanded jar). If you set contentCache=true, Camel will only load the resource once, and thus hot reloading is not possible. This scenario can be used in production, when the resource never changes.
Dynamic templates
Available as of Camel 2.1
Camel provides two headers by which you can define a different resource location for a template or the template content itself. If any of these headers is set then Camel uses this over the endpoint configured resource. This allows you to provide a dynamic template at runtime.
| Header | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CamelVelocityResourceUri | String | Camel 2.1: A URI for the template resource to use instead of the endpoint configured. |
| CamelVelocityTemplate | String | Camel 2.1: The template to use instead of the endpoint configured. |
Samples
For example you could use something like
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm");
To use a Velocity template to formulate a response to a message for InOut message exchanges (where there is a JMSReplyTo header).
If you want to use InOnly and consume the message and send it to another destination, you could use the following route:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
And to use the content cache, e.g. for use in production, where the .vm template never changes:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:com/acme/MyResponse.vm?contentCache=true"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
And a file based resource:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("velocity:file://myfolder/MyResponse.vm?contentCache=true"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
In Camel 2.1 it's possible to specify what template the component should use dynamically via a header, so for example:
from("direct:in"). setHeader("CamelVelocityResourceUri").constant("path/to/my/template.vm"). to("velocity:dummy");
In Camel 2.1 it's possible to specify a template directly as a header the component should use dynamically via a header, so for example:
from("direct:in"). setHeader("CamelVelocityTemplate").constant("Hi this is a velocity template that can do templating ${body}"). to("velocity:dummy");
The Email Sample
In this sample we want to use Velocity templating for an order confirmation email. The email template is laid out in Velocity as:
Dear ${headers.lastName}, ${headers.firstName}
Thanks for the order of ${headers.item}.
Regards Camel Riders Bookstore
${body}
And the java code:
private Exchange createLetter() { Exchange exchange = context.getEndpoint("direct:a").createExchange(); Message msg = exchange.getIn(); msg.setHeader("firstName", "Claus"); msg.setHeader("lastName", "Ibsen"); msg.setHeader("item", "Camel in Action"); msg.setBody("PS: Next beer is on me, James"); return exchange; } @Test public void testVelocityLetter() throws Exception { MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:result"); mock.expectedMessageCount(1); mock.expectedBodiesReceived("Dear Ibsen, Claus\n\nThanks for the order of Camel in Action.\n\nRegards Camel Riders Bookstore\nPS: Next beer is on me, James"); template.send("direct:a", createLetter()); mock.assertIsSatisfied(); } protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception { return new RouteBuilder() { public void configure() throws Exception { from("direct:a").to("velocity:org/apache/camel/component/velocity/letter.vm").to("mock:result"); } }; }
See Also
VM Component
The vm: component provides asynchronous SEDA behavior so that messages are exchanged on a BlockingQueue and consumers are invoked in a separate thread pool to the producer.
This component differs from the SEDA component in that VM supports communication across CamelContext instances, so you can use this mechanism to communicate across web applications, provided that the camel-core.jar is on the system/boot classpath.
This component is an extension to the SEDA component.
URI format
vm:someName[?options]
Where someName can be any string to uniquely identify the endpoint within the JVM (or at least within the classloader which loaded the camel-core.jar)
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
See the SEDA component for options and other important usage as the same rules applies for this VM component.
Samples
In the route below we send the exchange to the VM queue that is working across CamelContext instances:
from("direct:in").bean(MyOrderBean.class).to("vm:order.email");
And then in another Camel context such as deployed as in another .war application:
from("vm:order.email").bean(MyOrderEmailSender.class);
See Also
XMPP Component
The xmpp: component implements an XMPP (Jabber) transport.
URI format
xmpp://[login@]hostname[:port][/participant][?Options]
The component supports both room based and private person-person conversations.
The component supports both producer and consumer (you can get messages from XMPP or send messages to XMPP). Consumer mode supports rooms starting from camel-1.5.0.
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| room | If this option is specified, the component will connect to MUC (Multi User Chat). Usually, the domain name for MUC is different from the login domain. For example, if you are superman@jabber.org and want to join the krypton room, then the room URL is krypton@conference.jabber.org. Note the conference part. Starting from camel-1.5.0, it is not a requirement to provide the full room JID. If the room parameter does not contain the @ symbol, the domain part will be discovered and added by Camel |
| user | User name (without server name). If not specified, anonymous login will be attempted. |
| password | Password. |
| resource | XMPP resource. The default is Camel. |
| createAccount | If true, an attempt to create an account will be made. Default is false. |
| participant | JID (Jabber ID) of person to receive messages. room parameter has precedence over participant. |
| nickname | Use nickname when joining room. If room is specified and nickname is not, user will be used for the nickname. |
| serviceName | Camel 1.6/2.0 The name of the service you are connecting to. For Google Talk, this would be gmail.com. |
Headers and setting Subject or Language
Camel sets the message IN headers as properties on the XMPP message. You can configure a HeaderFilterStategy if you need custom filtering of headers.
In Camel 1.6.2/2.0 the Subject and Language of the XMPP message are also set if they are provided as IN headers.
Examples
User superman to join room krypton at jabber server with password, secret:
xmpp://superman@jabber.org/?room=krypton@conference.jabber.org&password=secret
User superman to send messages to joker:
xmpp://superman@jabber.org/joker@jabber.org?password=secret
Routing example in Java:
from("timer://kickoff?period=10000"). setBody(constant("I will win!\n Your Superman.")). to("xmpp://superman@jabber.org/joker@jabber.org?password=secret");
Consumer configuration, which writes all messages from joker into the queue, evil.talk.
from("xmpp://superman@jabber.org/joker@jabber.org?password=secret"). to("activemq:evil.talk");
Consumer configuration, which listens to room messages (supported from camel-1.5.0):
from("xmpp://superman@jabber.org/?password=secret&room=krypton@conference.jabber.org"). to("activemq:krypton.talk");
Room in short notation (no domain part; for camel-1.5.0+):
from("xmpp://superman@jabber.org/?password=secret&room=krypton"). to("activemq:krypton.talk");
When connecting to the Google Chat service, you'll need to specify the serviceName as well as your credentials (as of Camel 1.6/2.0):
// send a message from fromuser@gmail.com to touser@gmail.com from("direct:start"). to("xmpp://talk.google.com:5222/touser@gmail.com?serviceName=gmail.com&user=fromuser&password=secret"). to("mock:result");
See Also
XQuery
The xquery: component allows you to process a message using an XQuery template. This can be ideal when using Templating to generate respopnses for requests.
URI format
xquery:templateName
Where templateName is the classpath-local URI of the template to invoke; or the complete URL of the remote template.
For example you could use something like this:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("xquery:com/acme/mytransform.xquery");
To use an XQuery template to formulate a response to a message for InOut message exchanges (where there is a JMSReplyTo header).
If you want to use InOnly, consume the message, and send it to another destination, you could use the following route:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("xquery:com/acme/mytransform.xquery"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|
See Also
XSLT
The xslt: component allows you to process a message using an XSLT template. This can be ideal when using Templating to generate respopnses for requests.
URI format
xslt:templateName[?options]
Where templateName is the classpath-local URI of the template to invoke; or the complete URL of the remote template. Refer to the Spring Documentation for more detail of the URI syntax
You can append query options to the URI in the following format, ?option=value&option=value&...
Here are some example URIs
| URI | Description |
|---|---|
xslt:com/acme/mytransform.xsl | refers to the file com/acme/mytransform.xsl on the classpath |
xslt:file:///foo/bar.xsl
| refers to the file /foo/bar.xsl |
xslt:http://acme.com/cheese/foo.xsl
| refers to the remote http resource |
Options
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| converter | null | Option to override default XmlConverter. Will lookup for the converter in the Registry. The provided converted must be of type org.apache.camel.converter.jaxp.XmlConverter. |
| transformerFactory | null | New added in Camel 1.6 Option to override default TransformerFactory. Will lookup for the transformerFactory in the Registry. The provided transformer factory must be of type javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory. |
| transformerFactoryClass | null | New added in Camel 1.6 Option to override default TransformerFactory. Will create a TransformerFactoryClass instance and set it to the converter. |
Using XSLT endpoints
For example you could use something like
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("xslt:com/acme/mytransform.xsl");
To use an XSLT template to forumulate a response for a message for InOut message exchanges (where there is a JMSReplyTo header).
If you want to use InOnly and consume the message and send it to another destination you could use the following route:
from("activemq:My.Queue"). to("xslt:com/acme/mytransform.xsl"). to("activemq:Another.Queue");
Getting Parameters into the XSLT to work with
By default, all headers are added as parameters which are available in the XSLT.
To do this you will need to declare the parameter so it is then useable.
<setHeader headerName="myParam"><constant>42</constant></setHeader> <to uri="xslt:MyTransform.xsl"/>
And the XSLT just needs to declare it at the top level for it to be available:
<xsl: ...... > <xsl:param name="myParam"/> <xsl:template ...>
Spring XML versions
To use the above examples in Spring XML you would use something like
<camelContext xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring"> <route> <from uri="activemq:My.Queue"/> <to uri="xslt:org/apache/camel/spring/processor/example.xsl"/> <to uri="activemq:Another.Queue"/> </route> </camelContext>
There is a test case along with its Spring XML if you want a concrete example.
Notes on using XSTL and Java Versions
Here are some observations from Sameer, a Camel user, which he kindly shared with us:
In case anybody faces issues with the XSLT endpoint please review these points.
I was trying to use an xslt endpoint for a simple transformation from one xml to another using a simple xsl. The output xml kept appearing (after the xslt processor in the route) with outermost xml tag with no content within.
No explanations show up in the DEBUG logs. On the TRACE logs however I did find some error/warning indicating that the XMLConverter bean could no be initialized.
After a few hours of cranking my mind, I had to do the following to get it to work (thanks to some posts on the users forum that gave some clue):
1. Use the transformerFactory option in the route ("xslt:my-transformer.xsl?transformerFactory=tFactory") with the tFactory bean having bean defined in the spring context for class="org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl".
2. Added the Xalan jar into my maven pom.My guess is that the default xml parsing mechanism supplied within the JDK (I am using 1.6.0_03) does not work right in this context and does not throw up any error either. When I switched to Xalan this way it works. This is not a Camel issue, but might need a mention on the xslt component page.
Another note, jdk 1.6.0_03 ships with JAXB 2.0 while Camel needs 2.1. One workaround is to add the 2.1 jar to the jre/lib/endorsed directory for the jvm or as specified by the container.
Hope this post saves newbie Camel riders some time.